Infrared spectroscopy

OVIRS instrument of the Osiris-REx probe is a visible and infrared spectrometer
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) involves the interaction of infrared radiation with matter. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. As with all spectroscopic techniques, it can be used to identify and study chemicals. Samples may be solid, liquid, or gas. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) to produce an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of frequency used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters (sometimes called wave numbers), with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to wave numbers in a reciprocal way. A common laboratory instrument that uses this technique is a Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer. Two-dimensional IR is also possible as discussed below.
The infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is usually divided into three regions; the near-, mid- and far- infrared, named for their relation to the visible spectrum. The higher-energy near-IR, approximately 14000–4000 cm−1 (0.7–2.5 μm wavelength) can excite overtone or harmonic vibrations. The mid-infrared, approximately 4000–400 cm−1 (2.5–25 μm) may be used to study the fundamental vibrations and associated rotational-vibrational structure. The far-infrared, approximately 400–10 cm−1 (25–1000 μm), lying adjacent to the microwave region, has low energy and may be used for rotational spectroscopy. The names and classifications of these subregions are conventions, and are only loosely based on the relative molecular or electromagnetic properties.
Contents
1 Theory
1.1 Number of vibrational modes
1.2 Special effects
2 Practical IR spectroscopy
2.1 Sample preparation
2.2 Comparing to a reference
2.3 FTIR
3 Absorption bands
3.1 Regions
3.2 Badger's rule
4 Uses and applications
5 Isotope effects
6 Two-dimensional IR
7 See also
8 References
9 External links
Theory

Sample of an IR spec. reading; this one is from bromomethane (CH3Br), showing peaks around 3000, 1300, and 1000 cm−1 (on the horizontal axis).
Infrared spectroscopy exploits the fact that molecules absorb frequencies that are characteristic of their structure. These absorptions occur at resonant frequencies, i.e. the frequency of the absorbed radiation matches the vibrational frequency. The energies are affected by the shape of the molecular potential energy surfaces, the masses of the atoms, and the associated vibronic coupling.

3D animation of the symmetric stretching of the C–H bonds of bromomethane
In particular, in the Born–Oppenheimer and harmonic approximations, i.e. when the molecular Hamiltonian corresponding to the electronic ground state can be approximated by a harmonic oscillator in the neighborhood of the equilibrium molecular geometry, the resonant frequencies are associated with the normal modes corresponding to the molecular electronic ground state potential energy surface. The resonant frequencies are also related to the strength of the bond and the mass of the atoms at either end of it. Thus, the frequency of the vibrations are associated with a particular normal mode of motion and a particular bond type.
Number of vibrational modes
In order for a vibrational mode in a sample to be "IR active", it must be associated with changes in the dipole moment. A permanent dipole is not necessary, as the rule requires only a change in dipole moment.[1]
A molecule can vibrate in many ways, and each way is called a vibrational mode. For molecules with N number of atoms, linear molecules have 3N – 5 degrees of vibrational modes, whereas nonlinear molecules have 3N – 6 degrees of vibrational modes (also called vibrational degrees of freedom). As an example H2O, a non-linear molecule, will have 3 × 3 – 6 = 3 degrees of vibrational freedom, or modes.
Simple diatomic molecules have only one bond and only one vibrational band. If the molecule is symmetrical, e.g. N2, the band is not observed in the IR spectrum, but only in the Raman spectrum. Asymmetrical diatomic molecules, e.g. CO, absorb in the IR spectrum. More complex molecules have many bonds, and their vibrational spectra are correspondingly more complex, i.e. big molecules have many peaks in their IR spectra.
The atoms in a CH2X2 group, commonly found in organic compounds and where X can represent any other atom, can vibrate in nine different ways. Six of these vibrations involve only the CH2 portion: symmetric and antisymmetric stretching, scissoring, rocking, wagging and twisting, as shown below. Structures that do not have the two additional X groups attached have fewer modes because some modes are defined by specific relationships to those other attached groups. For example, in water, the rocking, wagging, and twisting modes do not exist because these types of motions of the H represent simple rotation of the whole molecule rather than vibrations within it.
Symmetry Direction | Symmetric | Antisymmetric |
|---|---|---|
| Radial | 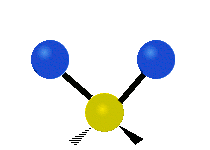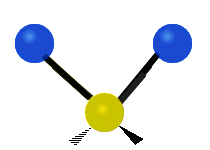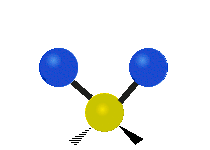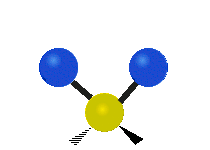 Symmetric stretching | 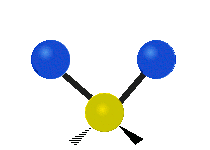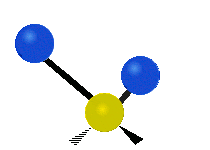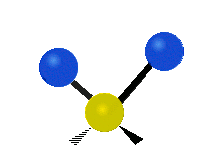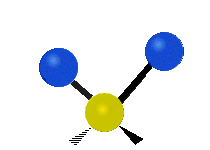 Antisymmetric stretching |
| Latitudinal |  Scissoring | 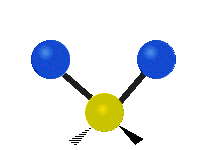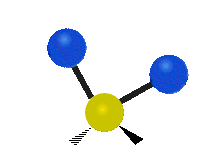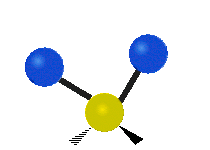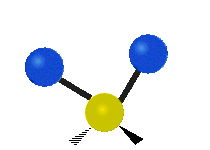 Rocking |
| Longitudal |  Wagging | 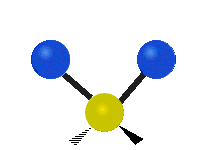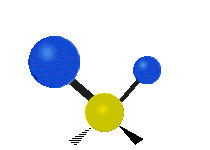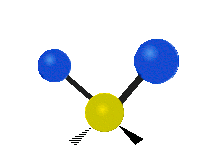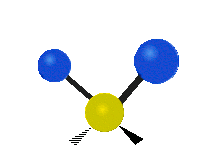 Twisting |
These figures do not represent the "recoil" of the C atoms, which, though necessarily present to balance the overall movements of the molecule, are much smaller than the movements of the lighter H atoms.
Special effects
The simplest and most important or fundamental IR bands arise from the excitations of normal modes, the simplest distortions of the molecule, from the ground state with vibrational quantum number v = 0 to the first excited state with vibrational quantum number v = 1. In some cases, overtone bands are observed. An overtone band arises from the absorption of a photon leading to a direct transition from the ground state to the second excited vibrational state (v = 2). Such a band appears at approximately twice the energy of the fundamental band for the same normal mode. Some excitations, so-called combination modes, involve simultaneous excitation of more than one normal mode. The phenomenon of Fermi resonance can arise when two modes are similar in energy; Fermi resonance results in an unexpected shift in energy and intensity of the bands etc.
Practical IR spectroscopy
The infrared spectrum of a sample is recorded by passing a beam of infrared light through the sample. When the frequency of the IR is the same as the vibrational frequency of a bond or collection of bonds, absorption occurs. Examination of the transmitted light reveals how much energy was absorbed at each frequency (or wavelength). This measurement can be achieved by scanning the wavelength range using a monochromator. Alternatively, the entire wavelength range is measured using a Fourier transform instrument and then a transmittance or absorbance spectrum is generated using a dedicated procedure.
This technique is commonly used for analyzing samples with covalent bonds. Simple spectra are obtained from samples with few IR active bonds and high levels of purity. More complex molecular structures lead to more absorption bands and more complex spectra.

Typical IR solution cell. The windows are CaF2.
Sample preparation
Gaseous samples require a sample cell with a long pathlength to compensate for the diluteness. The pathlength of the sample cell depends on the concentration of the compound of interest. A simple glass tube with length of 5 to 10 cm equipped with infrared-transparent windows at the both ends of the tube can be used for concentrations down to several hundred ppm. Sample gas concentrations well below ppm can be measured with a White's cell in which the infrared light is guided with mirrors to travel through the gas. White's cells are available with optical pathlength starting from 0.5 m up to hundred meters.
Liquid samples can be sandwiched between two plates of a salt (commonly sodium chloride, or common salt, although a number of other salts such as potassium bromide or calcium fluoride are also used).[2]
The plates are transparent to the infrared light and do not introduce any lines onto the spectra.
Solid samples can be prepared in a variety of ways. One common method is to crush the sample with an oily mulling agent (usually mineral oil Nujol). A thin film of the mull is applied onto salt plates and measured. The second method is to grind a quantity of the sample with a specially purified salt (usually potassium bromide) finely (to remove scattering effects from large crystals). This powder mixture is then pressed in a mechanical press to form a translucent pellet through which the beam of the spectrometer can pass.[2] A third technique is the "cast film" technique, which is used mainly for polymeric materials. The sample is first dissolved in a suitable, non hygroscopic solvent. A drop of this solution is deposited on surface of KBr or NaCl cell. The solution is then evaporated to dryness and the film formed on the cell is analysed directly. Care is important to ensure that the film is not too thick otherwise light cannot pass through. This technique is suitable for qualitative analysis. The final method is to use microtomy to cut a thin (20–100 µm) film from a solid sample. This is one of the most important ways of analysing failed plastic products for example because the integrity of the solid is preserved.
In photoacoustic spectroscopy the need for sample treatment is minimal. The sample, liquid or solid, is placed into the sample cup which is inserted into the photoacoustic cell which is then sealed for the measurement. The sample may be one solid piece, powder or basically in any form for the measurement. For example, a piece of rock can be inserted into the sample cup and the spectrum measured from it.
Comparing to a reference

Schematics of a two-beam absorption spectrometer. A beam of infrared light is produced, passed through an interferometer (not shown), and then split into two separate beams. One is passed through the sample, the other passed through a reference. The beams are both reflected back towards a detector, however first they pass through a splitter, which quickly alternates which of the two beams enters the detector. The two signals are then compared and a printout is obtained. This "two-beam" setup gives accurate spectra even if the intensity of the light source drifts over time.
It is typical to record spectrum of both the sample and a "reference". This step controls for a number of variables, e.g. infrared detector, which may affect the spectrum. The reference measurement makes it possible to eliminate the instrument influence.
The appropriate "reference" depends on the measurement and its goal. The simplest reference measurement is to simply remove the sample (replacing it by air). However, sometimes a different reference is more useful. For example, if the sample is a dilute solute dissolved in water in a beaker, then a good reference measurement might be to measure pure water in the same beaker. Then the reference measurement would cancel out not only all the instrumental properties (like what light source is used), but also the light-absorbing and light-reflecting properties of the water and beaker, and the final result would just show the properties of the solute (at least approximately).
A common way to compare to a reference is sequentially: first measure the reference, then replace the reference by the sample and measure the sample. This technique is not perfectly reliable; if the infrared lamp is a bit brighter during the reference measurement, then a bit dimmer during the sample measurement, the measurement will be distorted. More elaborate methods, such as a "two-beam" setup (see figure), can correct for these types of effects to give very accurate results. The Standard addition method can be used to statistically cancel these errors.
Nevertheless, among different absorption based techniques which are used for gaseous species detection, Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) can be used as a calibration free method. The fact that CRDS is based on the measurements of photon life-times (and not the laser intensity) makes it needless for any calibration and comparison with a reference [3]
FTIR
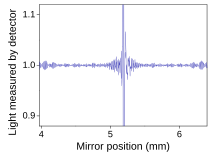
An interferogram from an FTIR measurement. The horizontal axis is the position of the mirror, and the vertical axis is the amount of light detected. This is the "raw data" which can be Fourier transformed to get the actual spectrum.
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is a measurement technique that allows one to record infrared spectra. Infrared light is guided through an interferometer and then through the sample (or vice versa). A moving mirror inside the apparatus alters the distribution of infrared light that passes through the interferometer. The signal directly recorded, called an "interferogram", represents light output as a function of mirror position. A data-processing technique called Fourier transform turns this raw data into the desired result (the sample's spectrum): Light output as a function of infrared wavelength (or equivalently, wavenumber). As described above, the sample's spectrum is always compared to a reference.
An alternate method for acquiring spectra is the "dispersive" or "scanning monochromator" method. In this approach, the sample is irradiated sequentially with various single wavelengths. The dispersive method is more common in UV-Vis spectroscopy, but is less practical in the infrared than the FTIR method. One reason that FTIR is favored is called "Fellgett's advantage" or the "multiplex advantage": The information at all frequencies is collected simultaneously, improving both speed and signal-to-noise ratio. Another is called "Jacquinot's Throughput Advantage": A dispersive measurement requires detecting much lower light levels than an FTIR measurement.[4] There are other advantages, as well as some disadvantages,[4] but virtually all modern infrared spectrometers are FTIR instruments.
Absorption bands
IR spectroscopy is often used to identify structures because functional groups give rise to characteristic bands both in terms of intensity and position (frequency). The positions of these bands are summarized in correlation tables as shown below.

List of main IR spectroscopy bands. For example, the carboxyl group will contain a C = O band at 1700 cm−1 and an OH band at 3500 cm−1 (total group -COOH). Wavenumbers listed in cm−1.
Regions
A spectrograph is often interpreted as having two regions.[5]
functional group region ≥1500cm−1{displaystyle geq 1500cm^{-1}}
In the functional region there are one to a few troughs per functional group.[5]
fingerprint region <1500cm−1{displaystyle <1500cm^{-1}}
In the fingerprint region there are many troughs which form an intricate pattern which can be used like a fingerprint to determine the compound.[5]
Badger's rule
For many kinds of samples, the assignments are known, i.e. which bond deformation(s) are associated with which frequency. In such cases further information can be gleaned about the strength on a bond, relying on the empirical guideline called Badger's Rule. Originally published by Richard Badger in 1934,[6] this rule states that the strength of a bond correlates with the frequency of its vibrational mode. That is, increase in bond strength leads to corresponding frequency increase and vice versa.
Uses and applications

US Food and Drug Administration scientist uses portable near infrared spectroscopy device to detect potentially illegal substances
Infrared spectroscopy is a simple and reliable technique widely used in both organic and inorganic chemistry, in research and industry. It is used in quality control, dynamic measurement, and monitoring applications such as the long-term unattended measurement of CO2 concentrations in greenhouses and growth chambers by infrared gas analyzers.
It is also used in forensic analysis in both criminal and civil cases, for example in identifying polymer degradation. It can be used in determining the blood alcohol content of a suspected drunk driver.
IR-spectroscopy has been successfully used in analysis and identification of pigments in paintings[7] and other art objects[8] such as illuminated manuscripts.[9]
A useful way of analyzing solid samples without the need for cutting samples uses ATR or attenuated total reflectance spectroscopy. Using this approach, samples are pressed against the face of a single crystal. The infrared radiation passes through the crystal and only interacts with the sample at the interface between the two materials.
With increasing technology in computer filtering and manipulation of the results, samples in solution can now be measured accurately (water produces a broad absorbance across the range of interest, and thus renders the spectra unreadable without this computer treatment).
Some instruments also automatically identify the substance being measured from a store of thousands of reference spectra held in storage.
Infrared spectroscopy is also useful in measuring the degree of polymerization in polymer manufacture. Changes in the character or quantity of a particular bond are assessed by measuring at a specific frequency over time. Modern research instruments can take infrared measurements across the range of interest as frequently as 32 times a second. This can be done whilst simultaneous measurements are made using other techniques. This makes the observations of chemical reactions and processes quicker and more accurate.
Infrared spectroscopy has also been successfully utilized in the field of semiconductor microelectronics:[10] for example, infrared spectroscopy can be applied to semiconductors like silicon, gallium arsenide, gallium nitride, zinc selenide, amorphous silicon, silicon nitride, etc.
Another important application of Infrared Spectroscopy is in the food industry to measure the concentration of various compounds in different food products[11][12]
The instruments are now small, and can be transported, even for use in field trials.
Infrared Spectroscopy is also used in gas leak detection devices such as the DP-IR and EyeCGAs.[13] These devices detect hydrocarbon gas leaks in the transportation of natural gas and crude oil.
In February 2014, NASA announced a greatly upgraded database, based on IR spectroscopy, for tracking polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the universe. According to scientists, more than 20% of the carbon in the universe may be associated with PAHs, possible starting materials for the formation of life. PAHs seem to have been formed shortly after the Big Bang, are widespread throughout the universe, and are associated with new stars and exoplanets.[14]
Recent developments include a miniature IR-spectrometer that's linked to a cloud based database and suitable for personal everyday use,[15] and NIR-spectroscopic chips[16] that can be embedded in smartphones and various gadgets.
Isotope effects
The different isotopes in a particular species may exhibit different fine details in infrared spectroscopy. For example, the O–O stretching frequency (in reciprocal centimeters) of oxyhemocyanin is experimentally determined to be 832 and 788 cm−1 for ν(16O–16O) and ν(18O–18O), respectively.
By considering the O–O bond as a spring, the wavenumber of absorbance, ν can be calculated:
- ν=12πckμ{displaystyle nu ={frac {1}{2pi c}}{sqrt {frac {k}{mu }}}}
where k is the spring constant for the bond, c is the speed of light, and μ is the reduced mass of the A–B system:
- μ=mAmBmA+mB{displaystyle mu ={frac {m_{A}m_{B}}{m_{A}+m_{B}}}}
(mi{displaystyle m_{i}}

The reduced masses for 16O–16O and 18O–18O can be approximated as 8 and 9 respectively. Thus
- ν(16O)ν(18O)=98≈832788.{displaystyle {frac {nu (^{16}O)}{nu (^{18}O)}}={sqrt {frac {9}{8}}}approx {frac {832}{788}}.}
Where ν{displaystyle nu }
The effect of isotopes, both on the vibration and the decay dynamics, has been found to be stronger than previously thought. In some systems, such as silicon and germanium, the decay of the anti-symmetric stretch mode of interstitial oxygen involves the symmetric stretch mode with a strong isotope dependence. For example, it was shown that for a natural silicon sample, the lifetime of the anti-symmetric vibration is 11.4 ps. When the isotope of one of the silicon atoms is increased to 29Si, the lifetime increases to 19 ps. In similar manner, when the silicon atom is changed to 30Si, the lifetime becomes 27 ps.[17]
Two-dimensional IR
Two-dimensional infrared correlation spectroscopy analysis combines multiple samples of infrared spectra to reveal more complex properties. By extending the spectral information of a perturbed sample, spectral analysis is simplified and resolution is enhanced. The 2D synchronous and 2D asynchronous spectra represent a graphical overview of the spectral changes due to a perturbation (such as a changing concentration or changing temperature) as well as the relationship between the spectral changes at two different wavenumbers.

Pulse Sequence used to obtain a two-dimensional Fourier transform infrared spectrum. The time period τ1{displaystyle tau _{1}}
 is usually referred to as the coherence time and the second time period τ2{displaystyle tau _{2}}
is usually referred to as the coherence time and the second time period τ2{displaystyle tau _{2}} is known as the waiting time. The excitation frequency is obtained by Fourier transforming along the τ1{displaystyle tau _{1}}
is known as the waiting time. The excitation frequency is obtained by Fourier transforming along the τ1{displaystyle tau _{1}} axis.
axis.Nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy[18][19] is the infrared version of correlation spectroscopy. Nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy is a technique that has become available with the development of femtosecond infrared laser pulses. In this experiment, first a set of pump pulses is applied to the sample. This is followed by a waiting time during which the system is allowed to relax. The typical waiting time lasts from zero to several picoseconds, and the duration can be controlled with a resolution of tens of femtoseconds. A probe pulse is then applied, resulting in the emission of a signal from the sample. The nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectrum is a two-dimensional correlation plot of the frequency ω1 that was excited by the initial pump pulses and the frequency ω3 excited by the probe pulse after the waiting time. This allows the observation of coupling between different vibrational modes; because of its extremely fine time resolution, it can be used to monitor molecular dynamics on a picosecond timescale. It is still a largely unexplored technique and is becoming increasingly popular for fundamental research.
As with two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (2DNMR) spectroscopy, this technique spreads the spectrum in two dimensions and allows for the observation of cross peaks that contain information on the coupling between different modes. In contrast to 2DNMR, nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy also involves the excitation to overtones. These excitations result in excited state absorption peaks located below the diagonal and cross peaks. In 2DNMR, two distinct techniques, COSY and NOESY, are frequently used. The cross peaks in the first are related to the scalar coupling, while in the latter they are related to the spin transfer between different nuclei. In nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy, analogs have been drawn to these 2DNMR techniques. Nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy with zero waiting time corresponds to COSY, and nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy with finite waiting time allowing vibrational population transfer corresponds to NOESY. The COSY variant of nonlinear two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy has been used for determination of the secondary structure content of proteins.[20]
See also
|
|
|
References
^ Paula, Peter Atkins, Julio de (2009). Elements of physical chemistry (5th ed.). Oxford: Oxford U.P. p. 459. ISBN 978-0-19-922672-6..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab Laurence M. Harwood; Christopher J. Moody (1989). Experimental organic chemistry: Principles and Practice (Illustrated ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. p. 292. ISBN 978-0-632-02017-1.
^ Soran Shadman; Charles Rose; Azer P. Yalin (2016). "Open-path cavity ring-down spectroscopy sensor for atmospheric ammonia". Applied Physics B. 122 (7): 194. Bibcode:2016ApPhB.122..194S. doi:10.1007/s00340-016-6461-5.
^ ab Chromatography/Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and its applications, by Robert White, p7
^ abc Smith, Janice Gorzynski (2011). "Chapter 13 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy" (Book). Organic chemistry (3rd ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. pp. 463–488. ISBN 978-0-07-337562-5.
^ Badger, Richard (1934). "A Relation Between Internuclear Distances and Bond Force Constants" (PDF). J Chem Phys. 2 (3): 128. Bibcode:1934JChPh...2..128B. doi:10.1063/1.1749433.
^ Infrared spectroscopy at ColourLex. Retrieved December 11, 2015
^ Derrick, M.R., Stulik, D. and Landry J.M., Infrared Spectroscopy in Conservation Science, Scientific Tools for Conservation, Getty Publications, 2000. Retrieved December 11, 2015
^ Paola Ricciardi, Unlocking the secrets of illuminated manuscripts. Retrieved December 11, 2015
^ Lau, W.S. (1999). Infrared characterization for microelectronics. World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-02-2352-6.
^ Osborne, Brian G. (2006). "Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Food Analysis". Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470027318.a1018. ISBN 9780470027318.
^ Villar, A.; Gorritxategi, E.; Aranzabe, E.; Fernandez, S.; Otaduy, D.; Fernandez, L.A. (2012). "Low-cost visible–near infrared sensor for on-line monitoring of fat and fatty acids content during the manufacturing process of the milk". Food Chemistry. 135 (4): 2756–2760. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.07.074. PMID 22980869.
^ www.TRMThemes.com, TRM Theme by. "Infrared (IR) / Optical Based Archives - Heath Consultants". Heath Consultants. Retrieved 2016-04-12.
^ Hoover, Rachel (February 21, 2014). "Need to Track Organic Nano-Particles Across the Universe? NASA's Got an App for That". NASA. Retrieved February 22, 2014.
^ "What Happened When We Took the SCiO Food Analyzer Grocery Shopping". IEEE Spectrum: Technology, Engineering, and Science News. 2017-03-14. Retrieved 2017-03-23.
^ "A Review of New Small-Scale Technologies for Near Infrared Measurements". www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com. Retrieved 2017-03-23.
^ Kohli, K.; Davies, Gordon; Vinh, N.; West, D.; Estreicher, S.; Gregorkiewicz, T.; Izeddin, I.; Itoh, K. (2006). "Isotope Dependence of the Lifetime of the 1136-cm-1 Vibration of Oxygen in Silicon". Physical Review Letters. 96 (22): 225503. Bibcode:2006PhRvL..96v5503K. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.225503. PMID 16803320.
^ P. Hamm; M. H. Lim; R. M. Hochstrasser (1998). "Structure of the amide I band of peptides measured by femtosecond nonlinear-infrared spectroscopy". J. Phys. Chem. B. 102 (31): 6123. doi:10.1021/jp9813286.
^ S. Mukamel (2000). "Multidimensional Fentosecond Correlation Spectroscopies of Electronic and Vibrational Excitations". Annual Review of Physical Chemistry. 51 (1): 691–729. Bibcode:2000ARPC...51..691M. doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.51.1.691. PMID 11031297.
^ N. Demirdöven; C. M. Cheatum; H. S. Chung; M. Khalil; J. Knoester; A. Tokmakoff (2004). "Two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy of antiparallel beta-sheet secondary structure" (PDF). Journal of the American Chemical Society. 126 (25): 7981–90. doi:10.1021/ja049811j. PMID 15212548.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Infrared spectroscopy. |
- A useful gif animation of different vibrational modes: SHU.ac.uk
- Illustrated guide to basic IR spectra interpretation
- Infrared spectroscopy for organic chemists
- Organic compounds spectrum database
- Gas phase infrared spectra, organic and inorganic compounds




