Republic of Crimea
Republic of Crimea Республика Крым (Russian) Республіка Крим (Ukrainian) Къырым Джумхуриети (Crimean Tatar) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — Republic — | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Anthem: "Нивы и горы твои волшебны, Родина" (Russian) Nivy i gory tvoi volshebny, Rodina (transliteration) Your fields and mountains are magical, Motherland | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Coordinates: 45°24′N 35°18′E / 45.400°N 35.300°E / 45.400; 35.300Coordinates: 45°24′N 35°18′E / 45.400°N 35.300°E / 45.400; 35.300 | |||||||||
| Political status | |||||||||
| Country | Russia | ||||||||
| Federal district | Southern[1][2] | ||||||||
| Economic region | North Caucasus[3] | ||||||||
| Established | 18 March 2014[4] | ||||||||
| Capital | Simferopol | ||||||||
| Government (as of October 2014) | |||||||||
| • Head | Sergey Aksyonov[5] | ||||||||
| • Legislature | State Council | ||||||||
| Statistics | |||||||||
Area [6] | |||||||||
| • Total | 26,100 km2 (10,100 sq mi) | ||||||||
Population (2014 est.) | |||||||||
| • Total | 1,891,465[7] | ||||||||
Time zone(s) | MSK (UTC+03:00)[8] | ||||||||
| License plates | 82[9][10] | ||||||||
| Official languages | Russian;[12] Ukrainian;[11]Crimean Tatar[11] | ||||||||
| Official website | |||||||||
The Republic of Crimea (/kraɪˈmiːə, krɪ-/; Russian: Республика Крым, Respublika Krym [rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə krɨm]; Ukrainian: Республіка Крим, Respublika Krym; Crimean Tatar: Къырым Джумхуриети, Qırım Cumhuriyeti) is a federal subject of Russia that is located on the Crimean Peninsula. The capital city and largest city within the republic is Simferopol which is also the second largest city of Crimea, behind the federal city of Sevastopol. At the last census the republic had a population of 1,891,465 (2014 Census).[13]
In March 2014, following the takeover of Crimea by pro-Russian separatists and the Russian Armed Forces, an unconstitutional [14][15][16]referendum was held on the issue of reunification with Russia, which official results and opinion polls indicated was supported by a large majority of Crimeans.[17] The official result was that Crimeans overwhelmingly wished to join with Russia.[18] Russia then annexed the Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol as federal subjects of Russia.[19]
While Russia and 26 other UN member states recognize Crimea as part of the Russian Federation, Ukraine continues to claim Crimea as an integral part of its territory as the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, supported by most foreign governments, United Nations General Assembly Resolution 68/262 and United Nations General Assembly Resolution A/C.3/72/L.42.[20][21]
Contents
1 History
1.1 Background
1.2 Declaration of Independence from Ukraine
1.3 Annexation and integration to Russian Federation
1.4 Post-annexation
2 Government and politics
2.1 Administrative divisions
3 Geography
3.1 Political geography
4 Demographics
4.1 Ethnic groups
4.2 Languages
4.3 Religion
5 Economy
5.1 Industry
5.2 Energy
5.3 Overview
5.4 Tourism
6 Human rights
6.1 Crimean Tatars
7 International status
8 See also
9 Notes
10 References
11 External links
History
Background

Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet "About the transfer of the Crimean Oblast", 1954
In 1792, under the Russian Empress Catherine the Great, Crimea was ceded to Russia by the Ottoman Empire under the Treaty of Jassy, which formally ended the Russo-Turkish war of 1787-1792. From 1802, it constituted a southern part of the Taurida Governorate of the Russian Empire until the collapse thereof in 1917. During the Russian Civil War (1917–1921) Crimea changed hands multiple times, being inter alia the last territory held by the White Russian government in the European part of Russia in 1920, and finally became an autonomous republic within Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) in 1921.
During World War II, in 1944, the central Soviet authorities deported the Crimean Tatars for alleged collaboration with the Nazi occupation regime; in 1945, the region was stripped of its autonomy status.
In 1954, the Presidium of the USSR Supreme Soviet transferred the region from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic to the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, another constituent republic of the USSR, then a highly centralised state, wherein borders between constituent republics was a technical issue of administration, despite the fact that Ukraine was a separate member of the UN. The Crimean Tatars were allowed to return to Crimea in the mid-1980s under perestroika.[22]
With the collapse of the Soviet Union, Crimea became part of the newly independent Ukraine, which led to tensions between Russia and Ukraine.[nb 1] With the Black Sea Fleet based on the peninsula, worries of armed skirmishes were occasionally raised. Crimean Tatars began returning from exile and resettling in Crimea. Ukraine restored Crimea's autonomous status in 1991. Crimea's autonomous status was re-affirmed in 1996 with the ratification of Ukraine's current constitution, which designated Crimea as the "Autonomous Republic of Crimea", but also an "inseparable constituent part of Ukraine".[24]
Declaration of Independence from Ukraine
On 11 March 2014, the Crimean parliament and the Sevastopol City Council jointly issued a letter of intent to unilaterally declare independence from Ukraine in the event of a 'Yes' vote in the referendum to join the region to Russia, that was to be held on 16 March.[25] The document specifically mentioned Kosovo as a precedent in the lead part.[25]
The referendum on the status of Crimea allowed citizens to vote on whether Crimea should apply to join Russia as a federal subject of the Russian Federation, or restore the 1992 Crimean constitution and Crimea's status as a part of Ukraine. The available choices did not include keeping the status quo of Crimea and Sevastopol as they were at the time the referendum was held.[26]
On 16 March 2014, according to statements of organizers of Crimean status referendum, a large majority (reported as 96.77% of the 81.36% of the population of Crimea who voted) voted in favour of independence of Crimea from Ukraine and joining Russia as a federal subject.[27][28] The referendum was not recognized by most of the international community and the reported results were disputed by numerous independent observers. The BBC reported that most of the Crimean Tatars that they interviewed were boycotting the vote.[27] Reports from the UN criticised the circumstances surrounding the referendum, especially the presence of paramilitaries, self-defence groups and unidentifiable soldiers.[29] The European Union, Canada, Japan and the United States condemned the vote as illegal.[27][30]
After the referendum, Crimean lawmakers formally voted both to secede from Ukraine and applied for their admission into Russia. The Sevastopol City Council, however, requested the port's separate admission as a federal city.[31]
Annexation and integration to Russian Federation

Diagram showing the merge, short-lived independence, and separation of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and Sevastopol that led to the Republic of Crimea becoming a federal subject of Russia.
On 18 March 2014, the self-proclaimed independent Republic of Crimea signed a treaty of accession to the Russian Federation. The accession was granted but separately for each the former regions that composed it: one accession for the Autonomous Republic of Crimea as the Republic of Crimea— the same name as the short-lived self-proclaimed independent republic - and another accession for Sevastopol as a federal city. The accession was only recognised internationally by a few states with most regarding the action as illegal. Though Ukraine refused to accept the annexation, the Ukrainian military began to withdraw from Crimea on 19 March.[32] A transition period, during which both parties to the accession treaty were to resolve the issues of integration of the new subjects "in the economic, financial, credit and legal system of the Russian Federation", was set to last until 1 January 2015'[33]
The integration process started within days: on 24 March the Russian ruble went into official circulation with parallel circulation of the Ukrainian hryvnia permitted until 1 January 2016, though Taxes and fees were to be paid in rubles only, and wages to the workers of budget-receiving organisations were also made in rubles.[34] On 29 March, the clocks in Crimea were moved forward to Moscow time[35] and on 31 March the Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev announced a series of programmes aimed at swiftly incorporating the territory into Russia's economy and infrastructure and also announced the creation of a new ministry for Crimean affairs.[36] Also on 31 March, the Russian Foreign Ministry stated that foreign citizens visiting Crimea needed to apply for a visa to the Russian Federation in one of the Russian diplomatic missions of Russian consulates.[37]
On 3 April 2014, Moscow sent a diplomatic note to Ukraine on terminating the actions of agreements concerning the deployment of the Russian Federation's Black Sea Fleet on the territory of Ukraine. As part of the agreements, Russia paid the Ukrainian government $530 million annually for the base, and wrote off nearly $100 million of Kiev's debt for the right to use Ukrainian waters. Ukraine also received a discount of $100 on each 1,000 cubic meters of natural gas imported from Russia, which was provided for by cutting export duties on the gas, money that would have gone into the Russian state budget. The Kremlin stated that as the base is no longer located in Ukraine, there were no legal grounds for the discount to be continued.[38]

Sevastopol, Crimea, 9 May 2014, the celebration of the Victory Day
On 3 April 2014, Crimea and the city of Sevastopol became part of Russia's Southern Military District.[39]
On 11 April 2014, the parliament of Crimea approved a new constitution, with 88 out of 100 lawmakers voting in favor of its adoption.[40] The constitution ensures the Republic of Crimea as a democratic state within the Russian Federation and says that its territory is united and inseparable. The Crimean parliament will become smaller and have 75 members instead of current 100.[41] According to the Kommersant newspaper, the authorities, including the State Council chair Vladimir Konstantinov unofficially promised that certain quotas would be reserved for Crimean Tatars in various government bodies.[42] On the same day a new revision of the Russian Constitution was officially released with the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol included in the list of federal subjects of the Russian Federation.[43]
On 12 April 2014, the Constitution of the Republic of Crimea, adopted at the session of the State Council on 11 April entered into legal force. The Constitution was published by the Krymskiye Izvestiya newspaper, and it has entered into legal force today, the State Council of Crimea said. The Constitution of Crimea consists of 10 chapters and 95 articles; its main regulations are analogous to the articles of the Constitution of the Russian Federation. The text states that the Republic of Crimea is a democratic, legal state within the Russian Federation and an equal subject of the Russian Federation. The source of power in the Crimean Republic is its people, which is part of the multinational people of the Russian Federation. It is noted that the supreme direct manifestation of the power of the people is referendum and free elections, seizure of power and appropriation of power authorization is unacceptable.[44]
On 15 April 2014, the Ukrainian parliament declared Crimea and the city of Sevastopol "occupied territories".[45]
On 1 June 2014, Crimea officially switched over to the Russian ruble as its only form of legal tender.[46]
On 7 May 2015, Crimea switched its phone codes (Ukrainian number system) to the Russian number system.[47]
In July 2015, Russian Prime Minister, Dmitry Medvedev, declared that Crimea had been fully integrated into Russia.[48]
Post-annexation
After annexation, Crimean authorities started nationalization of what they called strategically important enterprises, which included not only transportation and energy production enterprises, but also, for example, a wine factory in Massandra. The enterprises which belonged to Russian citizens were nationalized against financial reimbursement, which was, however, much lower than the actual value; those which belonged to Ukrainian citizens, for example, PrivatBank owned by Ihor Kolomoyskyi or Ukrtelecom owned by Rinat Akhmetov, were expropriated without any reimbursement. The future of the nationalized enterprises is decided by the government.[49]
In July 2016 Crimea ceased to be a separate federal district of Russian Federation and was included into the Southern federal district instead.[50][51]
Government and politics

Dmitry Medvedev and Crimean PM Aksyonov meeting Crimean school children in Simferopol, 31 March 2014
The State Council of Crimea is a legislative body with a 75-seat parliament.[52] Elections held on 14 September 2014 resulted in United Russia securing 70 of the 75 members elected.[53]
The executive power is represented by the Council of Ministers, headed by the Prime Minister (officially called Head of the Republic). The authority and operation of the State Council and the Council of Ministers of Crimea are determined by the Constitution of the Republic of Crimea and other Crimean laws, as well as by regular decisions carried out by the Council.[54]
Justice is administered by courts, as part of the judiciary of Russia. Under Russian law, all decisions delivered by the Crimean branches of the judiciary of Ukraine up to its annexation remain valid.[55] This includes sentences (for "encroaching on Ukraine's territorial integrity and inviolability") for pre-2014 calls for an incorporation of Crimea into Russia.[55]
Crimeans who refused to get Russian citizenship are barred from holding government and municipal jobs.[56]
By July 2015, 20,000 Crimeans had renounced their Ukrainian citizenship.[57] From the time of Russia's annexation until October 2016, more than 8,800 Crimean residents received Ukrainian passports.[58]
Administrative divisions
The Republic of Crimea continues to use the administrative divisions previously used by the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and is thus subdivided into 25 regions: 14 districts (raions) and 11 city municipalities (gorodskoj sovet or gorsovet), officially known as territories governed by city councils.[59][not in citation given]
Raions
| City municipalities
| 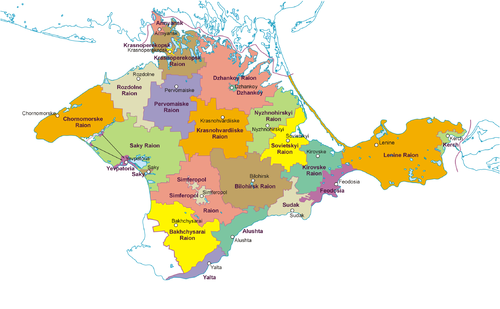 |
Geography
Political geography
Crimea is one of two parts of European Russia that have no land connection to the rest of the country, the other being Kaliningrad Oblast on the Baltic Sea. In May 2015, work began on a multibillion-dollar road–rail bridge across the Kerch Strait. It is projected to be fully completed and operational by 2019.[60]
If Crimea is considered separate from Ukraine, which continues to claim sovereignty over the peninsula, then Ukraine is the only country with which it shares a land border, with a number of road and rail connections. These crossings have been under the control of Russian troops since at least mid-March 2014.
Demographics
Ethnic groups

Interior of the Church of the Resurrection of Christ in Yalta.
According to the 2014 Crimean Federal District census, the ethnic makeup of the population of the whole Crimean Federal District at the time comprised the following self-reported groups:
Russians:1,188,978 (65.2%),
Ukrainians: 291,603 (16.0%),
Crimean Tatars: 229,526 (12.6%),
Tatars: 42,254 (2.3%),
Belarusians: 17,919 (1.0%),
Armenians: 9,634 (0.5%),
According to the 2014 census, 84% of Crimean inhabitants named Russian as their native language; 7.9% named Crimean Tatar; 3.7% Tatar and 3.3% Ukrainian.
It was the first official Russian census in Crimea since the Ukrainian one that was held in 2001.[61]
Languages
According to the Constitution of the Republic of Crimea:[62]
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
Article 10
- 1. Official languages of the Republic of Crimea are Russian, Ukrainian and Crimean Tatar.
According to the Republic of Crimea Ministry of Education, Science, and Youth,[63] most primary and secondary school pupils have decided to study in Russian in 2015.
- In Russian - 96,74%
- In Crimean Tatar - 2.76%. 5083 pupils (+188 to 2014 year) study in Crimean Tatar language in 53 schools in 17 districts. There have been opened 37 the 1st grade classes of primary school.
- In Ukrainian - 0.5%. 949 pupils study in Ukrainian language in 22 schools in 13 districts. There have been opened 2 the 1st grade classes of primary school (in 2014 - 0).
Its Education Minister Natalia Goncharova announced mid-August 2014 that (since no parents of first-graders wrote an application for learning Ukrainian) Crimea had decided not to form Ukrainian language classes in its primary schools.[64] Goncharova said that since more than a quarter of parents at the Ukrainian gymnasium in Simferopol had written an application to teach children in Ukrainian; this school might have Ukrainian language classes.[64] Goncharova also added that the parents of first-graders had written application for learning the Russian language, and (in areas inhabited by Crimean Tatars) for learning Crimean Tatar.[64] Goncharova stated on 10 October 2014 that at that time Crimea had 20 schools where all subjects were conducted in Ukrainian.[65]
A report (realised in the summer of 2015) of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) claimed that the Republic of Crimea had the aim to "end the teaching of Ukrainian" by "pressure on school administrations, teachers, parents, and children".[66]
Religion
Religion in Crimea (2013)[67]
Orthodox (58%)
Muslim (15%)
Belief without religion (10%)
Atheist (2%)
Other religion (2%)
Not stated (13%)
In 2013, Orthodox Christians made up 58% of the Crimean population, followed by Muslims (15%, mainly Tatars) and believers without religion (10%).[67]
Economy
Peninsula economy is based on tourism, agriculture (wines, fruits, wheat, rice and further crops), fishing, pearls, mining and natural resources (mainly iron, titanium, aluminium, manganese, calcite, sandstone, quartz and silicates, amethyst, other), metallurgical and steel industry, shipbuilding and repair, oil gas and petrochemical, chemical industry, electronics and devices machinery, instruments making, glass, electronics and electric parts devices, materials and building .
- (Mineralurgical data, Aluminum Arsenic Gold Boron Barium Bromine Carbon Cadmium Calcium Chlorine Copper Fluorine Iron Hydrogen Mercury Iodine Potassium Lithium Magnesium Manganese Nitrogen Sodium Nickel Oxygen Phosphorus Lead Sulfur Antimony Silicon Strontium Titanium Vanadium Zinc)
Industry
- Fiolent, Simferopol (two plants)
Zaliv Shipyard , Kerch south- FOMZ Opto Mechanical Plant FKOZ, (Ordzhonikidze) Gidropribor FeOMMZ and ship yard, Sudokompozit, More PO (Primorsk), Feodosia
- Sevastopol Aircraft Plant, SMZ Sevastopol Shipyards (main at Naval Bay) & Inkerman Shipyards, Balaklava Bay Shipyard
- Eupatoria Aircraft Plant and Repair EupAZ EARZ , Kerch Aircraft Repair Plant KeARZ
- Impuls 2 SMZ , AO FNGUP Granit Almaz Antej (Sevastopol)
- Titan Krym, Armjansk north
- Soda Plant, Bromine Plant, Krasnoperekopsk north east
- NPO Iodobrom, SChP Chemical Plant Saki Fedorivka, southeastern Eupatoria
Chornomornaftogaz § Chernomorneftegaz (Chjornomor), oil gas extraction, petrochemical, jack rigs and oil plantforms, LNG and oil tankers.- Simferopol (PEK PromElektroKontakt & PSchitK, SEM SElktroMash SELMZ, PO Foton TV LCD, ChPO Sfera IzmertelnPribor, SELTZ ElectroTechnical Plant, TsSI Tavrida SKMKZ, Slava Truda SCMNG, Monolit SMZKon, Santekhprom SSTP, Chornomornaftogaz, Chemical Plant, Simferopol Motor Plants, Pnevmatika Plastotekhnika and more rubbers plastic and tires plants)
- Feodosia FMZ Engineering/Machine-building Plant
- Feodosia FPZ (Priborostroeni Priladobudivni) Instrument-making Plant
- AO Vympel NPO Eupatoria (MicroElectronics Electronics and Electrical parts, connectors, television and other devices and machinery, metallurgical engineering technology); Eupatoria Chemical Plant
- Sevastopol (Parus SPriborMZ, Mayak, NPO Elektron, NPP Kvant, Tavrida Elektronik, Musson, other plants, industry)
- Sevastopol economic zone (south), Feodosia economic zone (west-SW)
- Persej SMZ ship remont and floating dock yard plant (South Bay, Sevastopol)
- Feodosia ship remont yard (mostly, service the Black Sea Fleet); Chemical plant
- Feodosia Economic Industrial Zone FPZ (west area)
- Sevastopol Economic Industrial Zone SevPZ (south SE area)
- Digital Valley (Tsifrovaya Dolina), MicroElectronics Silicon Computers IT and other related areas (Simferopol, near the airport)
- Sevastopol ship remont and floating docks yards (various)
- Kerch ship remont and floating docks yards (various, main = KSRZ uvas-trans and KMZ KMTP SV Fregat yards); Kerch Chemical Plant
- Kvartz Quartz Glass Factory Plant, Iris TehnoMash, PSZ Albatros (Kerch)
- KMZ KMK Metallurgical Plant, Kerch east; (Kerch SW) Kamysh Burun Iron Metallurgy Plant
- Various Mining and Metallurgy, Chemical Plants, and other industry across the peninsula
- Agricolture, crops, rice wheat wines thea fruits, tobacco (lesser), other products . Fishing and farming .
- Mining, iron titanium manganese aluminium, calcite silicates soda bromine iodium, amethyst, pearls, other .
- Kerch bridge, Taurida highway, Simferopol Airport, Sevastopol and Simferopol GTES plus peninsula solar FV plants, Frunze project port .
Energy
- Electricity
- Hydroelectric
- Thermal , gas and liquid fuels , coal
- CHP Sevastopol Simferopol (gas GTD110M or GTE160 180 - steam combined cycle) , Saki (added GTE25P unit) , Simferopol TPC Agrarne , Kerch Feodosia Eupatoria , Sevastopol (Ganz elektrik and AEG units) , other plants around the peninsula
- mobile GT units FT8P GTU GTA TPE (Sevastopol Simferopol mainly , Eup Feo Ker ? nd)
- Solar Photovoltaic , five to eight PV parks , mainly southern half from west to east
- Energetical
Oil and Gas fields all around sea (w sw s se east) and inland , Shelkino wells , Kerch peninsula , other ; coal deposits
- oil platforms and rigs , some refineries , petrochemical , oil gas storage , Strelkove pressure flow valve
Overview
In March 2014 Crimean GDP was estimated at $4.3 billion[68] or 0.2% of Russia based on current prices and 0.5% based on purchasing power parity.
After annexation of the peninsula, Russia doubled payments to about 560,000 pensioners and 200,000 public workers (in Crimea).[69] Those raises were cut back in April 2015.[70]
In June 2015 The Economist estimated that the average salary in Crimea was about two-third of the average salary in Russia.[70] According to Russian statistics by March 2015 the inflation in Crimea was 80%.[71] According to the Crimean authorities local food prices have grown 2.5 times since Russia's annexation.[72] Since then the peninsula now has to import most of its food from Russia.
Starting in the summer of 2014 Crimea's government nationalized various large Crimean companies and assets; reasons given for this were (among others) "the company helped to finance military operations against Donetsk People's Republic and Lugansk People's Republic" and "the resort complex illegally blocked public access to nearby park lands".[73] The government can nationalise assets considered to have "particular social, cultural, or historical value".[73] In the case of the Zalyv Shipbuilding yard, Crimean "self-defense" forces stormed the company's headquarters to demand nationalization.[73]Head of the Republic Sergey Aksyonov claimed that in at least one case "Employees established control of the enterprise on their own, we just helped them a little".[73] The Crimean assets of Ihor Kolomoyskyi have also been nationalized; according to Aksyonov this was "totally justified due to the fact that he is one of the initiators and financiers of the special anti-terrorist operation in the Eastern Ukraine where Russian citizens are being killed".[74][75]
By late October 2014 90% of the heads of Crimean government-owned corporation were fired as part of a supposed anti-corruption campaign, although no charges have been filed against anyone. Human rights activists in the region have described the seizures as lacking a legal basis and dismissed the "anti-corruption" rationale.[76] In June 2015 the Federal Security Service (FSB) started several anti-corruption criminal cases against high ranking Crimean officials.[77] According to Aksyonov the FSB had opened these criminal cases because it was "interested in destabilizing the situation in Crimea".[77]
On 6 May 2014 the National Bank of Ukraine ordered Ukrainian banks to cease operations in Crimea; the following weeks the Central Bank of Russia closed all Ukrainian banks on the peninsula because "they had failed to meet their obligations to creditors".[78] Eight months after the 21 March 2014 formal annexation of Crimea by Russia it had become impossible for clients of Ukrainian banks to access their deposit and most of them did not by their interest (on loans).[79][clarification needed] A "Fund for the Protection of Depositors in Crimea", as part of Russia's Deposit Insurance Agency, was set up by Russia to compensate Crimeans.[79] By 6 November 2014 it had paid out more than $500 million to 196,400 depositors; the fund has a limit of about $15,000 per bank account.[79] In July 2015 25 banks operated in Crimea, prior to Russia's annexation of the peninsula there were 180 banks in Crimea.[80]
Many international businesses have left Crimea but because of fear of sanctions few Russian companies invest in Crimea.[69]
Because of international sanctions Crimea's once bustling IT-sector has been reduced to a few IT companies.[72]
Tourism

Tourists in Crimea in June 2015
In 2014 about two million tourists holidayed in Crimea, including 300,000 Ukrainians.[81] In 2013 3.5 million Ukrainian and 1.5 million Russian tourists visited Crimea.[81] Tourism is the mainstay of the Crimean economy.[81] In August 2014 Head of the Republic Aksyonov was confident that in 2015 Crimea will welcome "at least five million visitors - I have no doubts about that".[81] Early August 2015 the press service of his government stated that in 2015 2.02 million tourist had visited Crimea (16.5% more than in 2014).[82] They stated in January 2016 (that in 2015) more than 4 million tourists had vacationed in the peninsula.[83]
Human rights
United Nations monitors (that had been in Crimea from 2 April to 6 May 2014) expressed concern on the treatment of journalists, sexual, religious and ethnic minorities and AIDS patients.[84] The monitors had found that journalists and activists who had opposed the 2014 Crimean referendum had been harassed and abducted.[85] They also claimed that Crimeans who had not applied for Russian citizenship faced harassment and intimidation.[84] Russia criticized their report as politically motivated and as an attempt to whitewash "the self-proclaimed Kiev authorities".[84] Russia added that it did not support the deployment of human rights monitors in Crimea.[85] The (new) Crimean authorities vowed to investigate the reports of human rights violations.[85]
According to Human Rights Watch "Russia has violated multiple obligations it has as an occupying power under international humanitarian law – in particular in relation to the protection of civilians' rights."[86][87]
In its November 2014 report on Crimea Human Rights Watch stated that "The de facto authorities in Crimea have limited free expression, restricted peaceful assembly, and intimidated and harassed those who have opposed Russia's actions in Crimea".[88] According to the report 15 people had gone missing since March 2014, according to Ukrainian authorities this number was 21 people.[56]Head of the Republic Sergey Aksyonov pledged to find the missing men and the culprits behind the kidnappings.[56] Aksyonov regularly meets with a group of parents, whose children have gone missing, and human rights activists.[56] These parents and human rights activists have complained that rotation of the team of investigators into these missing persons has harmed these investigations.[56]
Crimean Tatars

Vladimir Putin meeting with representatives of the Crimean Tatars, 16 May 2014
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People has come under the scrutiny of the Russian Federal Security Service, which reportedly took control of the building where the Mejlis meets and searched it on 16 September 2014. Crimean Tatar media said FSB officers also searched the office of the Avdet newspaper, which is based inside the Mejlis building. Several members of the Mejlis were also reportedly subjected to FSB searches at their homes. Several Crimean Tatar opposition figures were banned from entering Crimea for five years.[89] Since Russia annexed Crimea several Crimean Tatars have disappeared or have been found dead after being reported missing.[90][91][92] Crimean authorities state these deaths and disappearances are connected to "smoking an unspecified substance" and volunteers for the Syrian civil war; human rights activists claim the disappearances are part of a repression campaign against the Crimean Tatar.[87][90][91]
International status

Results of the United Nations General Assembly vote about the territorial integrity of Ukraine on March 2014.
In favour Against Abstentions Absent
The status of the republic is disputed as Russia and some other states recognised the independence declared by the Autonomous Republic and Sevastopol and their subsequent incorporation into the Russian Federation. Most other nations do not recognise these actions due to the Russian military intervention that occurred as these events unfolded. Russia argues that the results of a referendum held in Crimea and Sevastopol justify the accession. In the West, Russia's actions have been widely condemned as a violation of sovereignty of Ukraine and as an act of aggression. Ukraine still considers both the Autonomous Republic and Sevastopol as subdivisions of Ukraine under Ukrainian territory and subject to Ukrainian law. According to some unverified media reports, The Ukrainian government did however discontinue supplying the region with water through the North Crimean Canal.
The official line of the US, EU and Australia is that they don't grant visas for Crimeans with Russian passports.[70][93] Nevertheless, Russian media claims Crimeans get visas from some EU countries.[94][95]
On 21 March 2014, Armenia recognised the Crimean referendum, which led to Ukraine recalling its ambassador to that country.[96] The unrecognized Nagorno-Karabakh Republic also recognised the referendum earlier that week on 17 March.[97] On 22 March 2014, President Hamid Karzai of Afghanistan told a U.S. delegation that he recognised and supported the Crimean referendum and "respects the free will of the people of Crimea and Sevastopol to decide their own future".[98] On 23 March 2014, Belarus recognised Crimea as de facto part of Russia.[99] On 27 March 2014, Nicaragua unconditionally recognised the incorporation of Crimea into Russia.[100]
On 27 March 2014, the UN General Assembly voted on a non-binding resolution claiming that the referendum was invalid and reaffirming Ukraine's territorial integrity, by a vote of 100 to 11, with 58 abstentions and 24 absent.[101][102]Australia, Canada, Chile, France, Germany, Italy, Indonesia, Japan, Mexico, United Kingdom, United States and other 89 countries voted for; Armenia, Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, North Korea, Nicaragua, Sudan, Syria, Venezuela and Zimbabwe, as well as Russia, voted against.[103] Among the abstaining countries were China, India, and Brazil; Israel was among the countries listed as absent. RT reported that Western countries resorted to "political blackmail and economic threats" to coerce diplomats to vote for the resolution,[104] whereas Reuters reported per anonymous UN diplomats, the Russian delegation threatened punitive action against certain Eastern European and Central Asian countries if they supported the resolution.[105]
See also
- Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
- Crimean Peninsula
- Legislative Assembly of Sevastopol
- 2014 Crimean Crisis
Notes
^ In a summer 2013 poll by VTSIOM where respondents in Russia were asked what they consider Russian territory 56% claimed that Crimea was part of Russia.[23]
References
^ "Crimea becomes part of vast Southern federal district of Russia". Ukraine Today. 28 July 2016. Archived from the original on 29 July 2016. Retrieved 28 July 2016..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
^ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
^ "Putin reveals secrets of Russia's Crimea takeover plot". BBC. 9 March 2015. Retrieved 3 August 2016.Crimea was formally absorbed into Russia on 18 March, to international condemnation, after unidentified gunmen took over the peninsula.
^ "Crimea Deputies Back Acting Leader Sergei Aksyonov to Head Republic - News". The Moscow Times.
^ "Autonomous Republic of Crimea". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Ukraine. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
^ "2014 Crimean Federal District census".
^ "Crimea sets clocks to Moscow time". Bangkok Post. 30 March 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
^ "Order of Interior Ministry of Russia №316". Interior Ministry of Russia. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
^ Для крымских автомобилистов приготовили новые номера. Segodnya (in Russian). 2 April 2014. Archived from the original on 6 July 2015. Retrieved 6 July 2015.
^ ab "Putin addresses Russia's parliament in Crimea". al Jazeera.
^ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
^ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2014). "Таблица 1.3. Численность населения Крымского федерального округа, городских округов, муниципальных районов, городских и сельских поселений" [Table 1.3. Population of Crimean Federal District, Its Urban Okrugs, Municipal Districts, Urban and Rural Settlements]. Федеральное статистическое наблюдение «Перепись населения в Крымском федеральном округе». ("Population Census in Crimean Federal District" Federal Statistical Examination) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 4, 2016.
^ КС признал неконституционным постановление крымского парламента о вхождении АРК в состав РФ и проведении референдума о статусе автономии [Constitutional Court of Ukraine deemed Crimean parliament resolution on accession of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea to the Russian Federation and holding of the Crimean status referendum unconstitutional] (in Russian). Interfax-Ukraine. 14 March 2014.
^ Tokarev, Alexey (2014). Электоральная история постсоветского Крыма: от УССР до России [The electoral history of the post-Soviet Crimea: from Ukrainian SSR to Russia] (PDF). MGIMO Review of International Relations (in Russian). 5 (44): 32–41.Спустя 22 года и 364 дня после первого в СССР референдума в автономной республике Украины Крым состоялся последний референдум. Проводился он вопреки украинскому законодательству, не предусматривающему понятия региональный референдум и предписывающему решать территориальные вопросы только на всеукраинском референдуме
^ Marxen, Christian (2014). "The Crimea Crisis – An International Law Perspective" (PDF). Zeitschrift für ausländisches öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht (Heidelberg Journal of International Law). 74.Organizing and holding the referendum on Crimea's accession to Russia was illegal under the Ukrainian constitution. Article 2 of the constitution establishes that "Ukraine shall be a unitary state" and that the "territory of Ukraine within its present border is indivisible and inviolable". This is confirmed in regard to Crimea by Chapter X of the constitution, which provides for the autonomous status of Crimea. Article 134 sets forth that Crimea is an "inseparable constituent part of Ukraine". The autonomous status provides Crimea with a certain set of authorities and allows, inter alia, to hold referendums. These rights are, however, limited to local matters. The constitution makes clear that alterations to the territory of Ukraine require an all-Ukrainian referendum.
^ "Crimea 'votes to rejoin Russia' after controversial poll". ITV. 16 March 2014. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
^ "Crimea applies to be part of Russian Federation after vote to leave Ukraine". The Guardian. 17 March 2014.
^ Распоряжение Президента Российской Федерации от 17 March 2014 № 63-рп "О подписании Договора между Российской Федерацией и Республикой Крым о принятии в Российскую Федерацию Республики Крым и образовании в составе Российской Федерации новых субъектов" [Order of the President of the Russian Federation of 17 March 2014 number № 63 "On signing the Treaty between the Russian Federation and the Republic of Crimea on the acceptance of the Republic of Crimea into the Russian Federation and the formation of new subjects in the Russian Federation"] (in Russian). The Russian Federation's official internet-portal of legal information. 18 March 2014. Archived from the original on 18 March 2014.
^ "Kremlin: Crimea and Sevastopol are now part of Russia, not Ukraine". CNN. 18 March 2014.
^ http://euromaidanpress.com/2016/12/20/un-officially-recognized-russia-as-an-occupying-power-in-crimea/
^ "The Crimean Tatars began repatriating on a massive scale beginning in the late 1980s and continuing into the early 1990s. The population of Crimean Tatars in Crimea rapidly reached 250,000 and leveled off at 270,000 where it remains as of this writing [2001]. There are believed to be between 30,000 and 100,000 remaining in places of former exile in Central Asia."
Greta Lynn Uehling, The Crimean Tatars (Encyclopedia of the Minorities, Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn) iccrimea.org
^ (in Ukrainian) Майже 60% росіян вважають, що Крим - це Росія Almost 60% of Russians believe, that Crimea - is Russian, Ukrayinska Pravda (10 September 2013)
^
"Constitution of Ukraine, 1996". Retrieved 12 March 2014.
^ ab "Парламент Крыма принял Декларацию о независимости АРК и г. Севастополя". Государственный Совет Республики Крым. 11 March 2014. Archived from the original on 11 March 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2014.
^ "При воссоединении с Россией крымчане дискомфорта не почувствуют! - Krym Info". Krym Info. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
^ abc "Crimea referendum: Voters 'back Russia union'". BBC News.
^ "Crimeans vote over 90 percent to quit Ukraine for Russia". Reuters. 16 March 2014.
^ "UN report on Euronews - 15 April 2014". Euronews. 11 March 2014. Retrieved 16 April 2014.
^ "Japan does not recognise Crimea vote - govt spokesman". Reuters. 17 March 2014.
^ Herszenhorn, David M.; Cowell, Alan (17 March 2014). "Lawmakers in Crimea Move Swiftly to Split From Ukraine". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
^ Carol Morello and Kathy Lally (19 March 2014). "Ukraine says it is preparing to leave Crimea". The Washington Post.
^ "Treaty to accept Crimea, Sevastopol to Russian Federation signed". Russia Today. 18 March 2014.
^ "TASS: Russia - Russian ruble goes into official circulation in Crimea as of Monday". TASS.
^ "Ukraine crisis: Crimea celebrates switch to Moscow time". BBC News. 29 March 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
^ Lukas I. Alpert, Alexander Kolyandr. "Medvedev visits Crimea, vows development aid". Market Watch.
^ "Now foreigners need Russian visas to visit Crimea - Russian Foreign Ministry". voiceofrussia.com.
^ Sputnik (3 April 2014). "Moscow Sent Diplomatic Note to Ukraine on Terminating Black Sea Fleet Agreements". ria.ru.
^ Republic of Crimea, Sevastopol become part of Southern Military District - News - Russia - The Voice of Russia: News, Breaking news, Politics, Economics, Business, Russia, Int...
^ Sputnik (11 April 2014). "Crimean Parliament Approves New Constitution". ria.ru.
^ "Crimea approves new Constitution". PravdaReport.
^ "Crimea's new constitution put up for discussion". RT English.
^ Sputnik (11 April 2014). "Russia Amends Constitution to Include Crimea, Sevastopol". ria.ru.
^ Crimean Constitution comes into legal force - News - Russia - The Voice of Russia: News, Breaking news, Politics, Economics, Business, Russia, International current events, Ex...
^ Sputnik (15 April 2014). "Ukraine's Parliament Declares Crimea, Sevastopol 'Occupied Territory'". ria.ru.
^ Verbyany, Volodymyr (1 June 2014). "Crimea Adopts Ruble as Ukraine Continues Battling Rebels". Bloomberg.
^ Crimea switches to Russian telephone codes, Interfax-Ukraine (7 May 2015)
^ Jess McHugh (15 July 2015). "Putin Eliminates Ministry Of Crimea, Region Fully Integrated Into Russia, Russian Leaders Say". International Business Times. Retrieved 10 January 2016.
^ Sambros, Andrey (27 February 2015). "Изображая Чавеса: чем закончился год национализаций в Крыму". carnegie.ru. Retrieved 3 January 2016.
^ "Crimea becomes part of vast Southern federal district of Russia". Retrieved 29 July 2016.
^ "Крым, который лопнул. Как Путин снова обманул полуостров". 29 July 2016. Retrieved 29 July 2016.
^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 18 March 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2014.CS1 maint: Archived copy as title (link)
^ "Election Victories Strengthen Putin's Grip Around Russia and Crimea". nytimes.com. 14 September 2014. Retrieved 16 April 2016.
^ "Autonomous Republic of Crimea – Information card". Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine. Retrieved 22 February 2007.
^ ab Pro-Russian Activist Falls On Hard Times In Annexed Crimea, Radio Free Europe (16 January 2016)
^ abcde Ukraine human rights 'deteriorating rapidly', Al Jazeera English (3 Dec 2014)
Disappearing Crimea's anti-Russia activists , Al Jazeera English ()
^ Thomas de Waal. "The New Siege of Crimea". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
^ (in Ukrainian) Nearly 9 thousand Crimean residents received Ukrainian passports after annexation, Ukrayinska Pravda (16 October 2016)
^ "Infobox card – Avtonomna Respublika Krym". Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine (in Ukrainian). Archived from the original on 1 October 2007. Retrieved 23 February 2007.
^ "Putin orders military exercise as protesters clash in Crimea". reuters. 18 April 2016. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
^ "Census of the population is transferred to 2016". Dzerkalo Tzhnia (in Ukrainian). 20 September 2013. Retrieved 7 March 2014.
^ http://crimeaconstitution.ru/glava1/
^ "На крымско-татарском и украинском языках в Крыму обучаются чуть более 3% детей — Министерство образования, науки и молодежи Республики Крым - Правительство Республики Крым". rk.gov.ru.
^ abc (in Ukrainian) Crimea has no longer Ukrainian classes, Ukrayinska Pravda (14 August 2014)
^ (in Russian) In Crimea, Ukrainian schools left - "Minister of Education", UNIAN (10 October 2014)
^ Two Years After Annexation, Crimeans Wait On Russia's Unfulfilled Promises, Radio Free Europe (18 March 2016)
^ ab "Public Opinion Survey Residents of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea" (PDF)., The sample consisted of 1,200 permanent Crimea residents older than the age of 18 and eligible to vote and is representative of the general population by age, gender, education and religion.
^ "Crimea's economy in numbers and pictures". RT English.
^ ab "In Crimea, cash is king". gulfnews.com.
^ abc "Bad_Memory". The Economist. 11 June 2015.
^ Dreams in Isolation: Crimea 2 Years After Annexation, The Moscow Times (18 March 2016)
^ ab Alexey Eremenko. "Crimea One Year After Russia Referendum Is Isolated From World". NBC News.
^ abcd Russia Delivers a New Shock to Crimean Business: Forced Nationalization, Bloomberg News (18 November 2014 )
^ Kolomoyskyi’s assets to be nationalized in Crimea – Sergey Aksyonov, CEE INSIGHT (5 September 2014)
^ Ukrainian tycoon’s estate in Crimea sold for $18 mln, Russian News Agency TASS (3 February 2016)
^ Crimea’s rapid Russification means pride for some but perplexity for others, Guardian Weekly (11 November 2014)
^ ab "The Moscow Times — News, Business, Culture & Events". Themoscowtimes.com. 2016-07-07. Retrieved 2017-04-12.
^ Six More Ukrainian Banks Expelled from Crimea, Moscow Times (13 May 2014)
^ abc Months After Russian Annexation, Crimeans Ask: 'Where Is Our Money?', Moscow Times (20 November 2014)
^ (in Ukrainian) Grey financial zone: why with annexed the Crimea are Russian banks, Deutsche Welle (2 August 2015)
^ abcd Tourism takes a nosedive in Crimea, BBC News (7 August 2014)
Russia's takeover of Crimea is killing tourism industry, Kyiv Post (14 August 2014)
^ (in Russian) In Crimea, we saw an increase in tourist traffic as compared to the year 2014, Radio Free Europe (2 August 2015)
^ (in Ukrainian) Crimea - Aksenov predicts "huge flow of tourists" and operators - appreciation, Ukrayinska Pravda (19 January 2016)
^ abc "U.N. monitors warn on human rights in east Ukraine, Crimea". Reuters. Archived from the original on 18 May 2014.
^ abc U.N. Cites Abuses in Crimea Before Russia Annexation Vote
^ "Crimean Tatars: Human Rights Watch Publishes Report Detailing Serious Human Rights Abuses". Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization. Retrieved 27 November 2014.
^ ab "Rights in Retreat: Abuses in Crimea". Human Rights Watch. 17 November 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
^ Russia Abusing Rights in Annexed Crimea, Human Rights Watch Says, Bloomberg News (17 November 2014)
Human Rights Watch releases damning report on Crimea, Kyiv Post (18 November 2014)
^ "Russian FSB surrounds Crimean Tatar parliament-UPDATED". World Bulletin. 16 September 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
^ ab "Missing Crimean Tatar Reportedly Found Dead". RadioFreeEurope/RadioLiberty.
^ ab "Crimea: Enforced Disappearances". Human Rights Watch. 7 October 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2015.
^ Кримського татарина, який зник після анексії, знайдено мертвим [The Crimean Tartar, who disappeared after the annexation, was found dead]. Ukrayinska Pravda (in Ukrainian). 28 October 2017. Retrieved 28 October 2017.
^ "Crimean residents may not be able to visit Western countries using Russian passports". uatoday.tv.
^ "TASS: Russia - Crimean citizens get Schengen visas in Moscow despite EU ban". TASS.
^ "Греция выдаст крымчанам шенгенские визы". Горящие туры в Египет, туры в Турцию, Грецию. Скидки. Поиск туров - Турскидки.ру.
^ "Ukraine Recalls Ambassador to Armenia over Crimea Recognition". Asbarez Armenian News. 21 March 2014.
^ "Karabakh Foreign Ministry Issues Statement on Crimea". Asbarez Armenian News. 17 March 2014.
^ "Afghanistan respects Crimea's right to self-determination – Karzai". Russia Today. 22 March 2014.
^ "Belarusian president: Crimea is de facto part of Russia". Russia Today. 23 March 2014.
^ "Nicaragua unconditionally recognises incorporation of Crimea into Russia". The Voice of Russia. 27 March 2014.
^ "United Nations News Centre". UN News Service Section. 27 March 2014.
^ "U.N. General Assembly declares Crimea secession vote invalid". Reuters. 27 March 2014.
^ "UN Gen Assembly adopts resolution backing Ukraine's territorial integrity". RT English.
^ "UN vote shows Russia far from isolated – Churkin". RT English.
^ Charbonneau, Louis (28 March 2014). "Russia Threatened Countries Ahead Of UN Vote On Ukraine, Diplomats Say". The Huffington Post. Retrieved 28 March 2014.
External links
- Agreement on the accession of the Republic of Crimea to the Russian Federation signed
- Constitution of the Republic of Crimea




