Otitis media
| Otitis media | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Otitis media with effusion: serous otitis media, secretory otitis media |
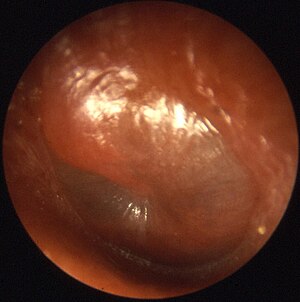 | |
| A bulging tympanic membrane which is typical in a case of acute otitis media | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| Symptoms | Ear pain, fever, hearing loss[1][2] |
| Types | Acute otitis media, otitis media with effusion, chronic suppurative otitis media[3][4] |
| Causes | Viral, bacterial[4] |
| Risk factors | Smoke exposure, daycare[4] |
| Prevention | Vaccination, breastfeeding[1] |
| Medication | Paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops[1] |
| Frequency | 471 million (2015)[5] |
| Deaths | 3,200 (2015)[6] |
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear.[2] The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME).[3] AOM is an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain.[1] In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep.[1] Decreased eating and a fever may also be present.[1] OME is typically not associated with symptoms.[1] Occasionally a feeling of fullness is described.[4] It is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear for more than three months.[4]Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation of greater than two weeks that results in episodes of discharge from the ear.[4] It may be a complication of acute otitis media.[4] Pain is rarely present.[4] All three may be associated with hearing loss.[2][3] The hearing loss in OME, due to its chronic nature, may affect a child's ability to learn.[4]
The cause of AOM is related to childhood anatomy and immune function.[4] Either bacteria or viruses may be involved.[4] Risk factors include exposure to smoke, use of pacifiers, and attending daycare.[4] It occurs more commonly among Indigenous peoples and those who have Down syndrome.[4][7] OME frequently occurs following AOM and may be related to viral upper respiratory infections, irritants such as smoke, or allergies.[3][4] Looking at the eardrum is important for making the correct diagnosis.[8] Signs of AOM include bulging or a lack of movement of the tympanic membrane from a puff of air.[1][9] New discharge not related to otitis externa also indicates the diagnosis.[1]
A number of measures decrease the risk of otitis media including pneumococcal and influenza vaccination, breastfeeding, and avoiding tobacco smoke.[1] The use of pain medications for AOM is important.[1] This may include paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops, or opioids.[1] In AOM, antibiotics may speed recovery but may result in side effects.[10] Antibiotics are often recommended in those with severe disease or under two years old.[9] In those with less severe disease they may only be recommended in those who do not improve after two or three days.[9] The initial antibiotic of choice is typically amoxicillin.[1] In those with frequent infections tympanostomy tubes may decrease recurrence.[1] In children with otitis media with effusion antibiotics may increase resolution of symptoms, but may cause diarrhoea, vomiting and skin rash.[11]
Worldwide AOM affects about 11% of people a year (about 325 to 710 million cases).[12][13] Half the cases involve children less than five years of age and it is more common among males.[4][12] Of those affected about 4.8% or 31 million develop chronic suppurative otitis media.[12] Before the age of ten OME affects about 80% of children at some point.[4] Otitis media resulted in 3,200 deaths in 2015 – down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.[6][14]
Contents
1 Signs and symptoms
2 Causes
3 Diagnosis
3.1 Acute otitis media
3.2 Otitis media with effusion
3.3 Chronic suppurative otitis media
3.4 Adhesive otitis media
4 Prevention
5 Management
5.1 Antibiotics
5.2 Tympanostomy tube
5.3 Otitis media with effusion
5.4 Alternative medicine
6 Outcomes
6.1 Membrane rupture
6.2 Hearing loss
7 Epidemiology
8 Etymology
9 References
10 External links
Signs and symptoms
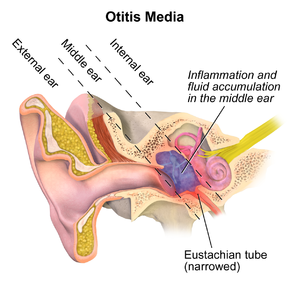
Otitis media.
An integral symptom of acute otitis media is ear pain; other possible symptoms include fever, and irritability (in infants). Since an episode of otitis media is usually precipitated by an upper respiratory tract infection (URTI), there are often accompanying symptoms like a cough and nasal discharge.[15]
Discharge from the ear can be caused by acute otitis media with perforation of the ear drum, chronic suppurative otitis media, tympanostomy tube otorrhea, or acute otitis externa. Trauma, such as a basilar skull fracture, can also lead to discharge from the ear due to cerebral spinal drainage from the brain and its covering (meninges).
Causes
The common cause of all forms of otitis media is dysfunction of the Eustachian tube.[16] This is usually due to inflammation of the mucous membranes in the nasopharynx, which can be caused by a viral URTI, strep throat, or possibly by allergies.[17] Because of the dysfunction of the Eustachian tube, the gas volume in the middle ear is trapped and parts of it are slowly absorbed by the surrounding tissues, leading to negative pressure in the middle ear. Eventually, the negative middle-ear pressure can reach a point where fluid from the surrounding tissues is sucked into the middle ear's cavity (tympanic cavity), causing a middle-ear effusion. This is seen as a progression from a Type A tympanogram to a Type C to a Type B tympanogram.
By reflux or aspiration of unwanted secretions from the nasopharynx into the normally sterile middle-ear space, the fluid may then become infected — usually with bacteria. The virus that caused the initial URI (upper respiratory infection) can itself be identified as the pathogen causing the infection.[17]
Diagnosis

Perforation of the right tympanic membrane resulting from a previous severe acute otitis media
As its typical symptoms overlap with other conditions, such as acute external otitis, clinical history alone is not sufficient to predict whether acute otitis media is present; it has to be complemented by visualization of the tympanic membrane.[18][19] Examiners use a pneumatic otoscope with a rubber bulb attached to assess the mobility of the tympanic membrane.
In more severe cases, such as those with associated hearing loss or high fever, audiometry, tympanogram, temporal bone CT and MRI can be used to assess for associated complications, such as mastoid effusion, subperiosteal abscess formation, bony destruction, venous thrombosis or meningitis.[20]
Acute otitis media in children with moderate to severe bulging of the tympanic membrane or new onset of otorrhea (drainage) is not due to external otitis. Also, the diagnosis may be made in children who have mild bulging of the ear drum and recent onset of ear pain (less than 48 hours) or intense erythema (redness) of the ear drum.
To confirm the diagnosis, middle-ear effusion and inflammation of the eardrum have to be identified; signs of these are fullness, bulging, cloudiness and redness of the eardrum.[15] It is important to attempt to differentiate between acute otitis media and otitis media with effusion (OME), as antibiotics are not recommended for OME.[15] It has been suggested that bulging of the tympanic membrane is the best sign to differentiate AOM from OME, with a bulging of the membrane suggesting AOM rather than OME.[21]
Viral otitis may result in blisters on the external side of the tympanic membrane, which is called bullous myringitis (myringa being Latin for "eardrum").[22]
However, sometimes even examination of the eardrum may not be able to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the canal is small. If wax in the ear canal obscures a clear view of the eardrum it should be removed using a blunt cerumen curette or a wire loop. Also, an upset young child's crying can cause the eardrum to look inflamed due to distension of the small blood vessels on it, mimicking the redness associated with otitis media.
Acute otitis media
The most common bacteria isolated from the middle ear in AOM are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis,[15] and Staphylococcus aureus.[23]
Otitis media with effusion
Otitis media with effusion (OME), also known as serous otitis media (SOM) or secretory otitis media (SOM), and colloquially referred to as 'glue ear,'[24] is fluid accumulation that can occur in the middle ear and mastoid air cells due to negative pressure produced by dysfunction of the Eustachian tube. This can be associated with a viral URI or bacterial infection such as otitis media.[25] An effusion can cause conductive hearing loss if it interferes with the transmission of vibrations of middle ear bones to the vestibulocochlear nerve complex that are created by sound waves.[26]
Early-onset OME is associated with feeding of infants while lying down, early entry into group child care, parental smoking, lack, or too short a period of breastfeeding and greater amounts of time spent in group child care, particularly those with a large number of children. These risk factors increase the incidence and duration of OME during the first two years of life.[27]
Chronic suppurative otitis media
Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is a chronic inflammation of the middle ear and mastoid cavity that is characterised by discharge from the middle ear through a perforated tympanic membrane for at least 6 weeks. CSOM occurs following an upper respiratory tract infection that has led to acute otitis media. This progresses to a prolonged inflammatory response causing mucosal (middle ear) oedema, ulceration and perforation. The middle ear attempts to resolve this ulceration by production of granulation tissue and polyp formation. This can lead to increased discharge and failure to arrest the inflammation, and to development of CSOM, which is also often associated with cholesteatoma. There may be enough pus that it drains to the outside of the ear (otorrhea), or the pus may be minimal enough to be seen only on examination with an otoscope or binocular microscope. Hearing impairment often accompanies this disease.
People are at increased risk of developing CSOM when they have poor eustachian tube function, a history of multiple episodes of acute otitis media, live in crowded conditions, and attend paediatric day care facilities. Those with craniofacial malformations such as cleft lip and palate, Down syndrome, and microcephaly are at higher risk.
Worldwide approximately 11% of the human population is affected by AOM every year, or 709 million cases.[12][28] About 4.4% of the population develop CSOM.[28]
According to the World Health Organization, CSOM is a primary cause of hearing loss in children.[29] Adults with recurrent episodes of CSOM have a higher risk of developing permanent conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
In Britain, 0.9% of children and 0.5% of adults have CSOM, with no difference between the sexes.[29]
The incidence of CSOM across the world varies dramatically where high income countries have a relatively low prevalence while in low income countries the prevalence may be up to three times as great.[12]
Each year 21,000 people worldwide die due to complications of CSOM.[29]
Adhesive otitis media
Adhesive otitis media occurs when a thin retracted ear drum becomes sucked into the middle-ear space and stuck (i.e., adherent) to the ossicles and other bones of the middle ear.

Acute otitis media
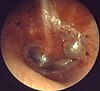
Acute otitis media, myringitis bullosa

Myringitis bullosa in influenza

Chronic otitis media (otitis media chronica mesotympanalis)

Otitis media chronica mesotympanalis

Otitis media chronica mesotympanalis

Otitis media chronica mesotympanalis
Prevention
AOM is far less common in breastfed infants than in formula-fed infants,[30] and the greatest protection is associated with exclusive breastfeeding (no formula use) for the first six months of life.[1] A longer duration of breastfeeding is correlated with a longer protective effect.[30]
Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCV) in early infancy decrease the risk of acute otitis media in healthy infants.[31] PCV is recommended for all children, and, if implemented broadly, PCV would have a significant public health benefit.[15]Influenza vaccine is recommended annually for all children.[15] PCV does not appear to decrease the risk of otitis media when given to high-risk infants or for older children who have previously experienced otitis media.[31]
Risk factors such as season, allergy predisposition and presence of older siblings are known to be determinants of recurrent otitis media and persistent middle-ear effusions (MEE).[32] History of recurrence, environmental exposure to tobacco smoke, use of daycare, and lack of breastfeeding have all been associated with increased risk of development, recurrence, and persistent MEE.[33][34] Pacifier use has been associated with more frequent episodes of AOM.[35]
Long-term antibiotics, while they decrease rates of infection during treatment, have an unknown effect on long-term outcomes such as hearing loss.[36] This method of prevention has been associated with emergence of antibiotic-resistant otitic bacteria. They are thus not recommended.[15]
There is moderate evidence that the sugar substitute xylitol may reduce infection rates in those who go to daycare.[37]
Evidence does not support zinc supplementation as an effort to reduce otitis rates except maybe in those with severe malnutrition such as marasmus.[38]
Management
Oral and topical pain killers are effective to treat the pain caused by otitis media. Oral agents include ibuprofen, paracetamol (acetaminophen), and opiates. Topical agents shown to be effective include antipyrine and benzocaine ear drops.[39]Decongestants and antihistamines, either nasal or oral, are not recommended due to the lack of benefit and concerns regarding side effects.[40] Half of cases of ear pain in children resolve without treatment in three days and 90% resolve in seven or eight days.[41] The use of steroids is not supported by the evidence for acute otitis media.[42]
Antibiotics
It is important to weigh the benefits and harms before using antibiotics for acute otitis media. As over 82% of acute episodes settle without treatment, about 20 children must be treated to prevent one case of ear pain, 33 children to prevent one perforation, and 11 children to prevent one opposite-side ear infection. For every 14 children treated with antibiotics, one child has an episode of either vomiting, diarrhea or a rash.[10] If pain is present, pain medications may be used.
For bilateral acute otitis media in infants younger than 24 months of age, there is evidence that the benefits of antibiotics outweigh the harms.[10] A 2015 Cochrane review concluded that watchful waiting is the preferred approach for children over six months with non severe acute otitis media.[43]
| Summary[43] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Findings in words | Findings in numbers | Quality of evidence |
| Pain | |||
| Pain at 24 hours | Antibiotics causes little or no reduction to the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on high quality evidence. | RR 0.89 (0.78 to 1.01) | High |
| Pain at 2 to 3 days | Antibiotics slightly reduces the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on high quality evidence. | RR 0.70 (0.57 to 0.86) | High |
| Pain at 4 to 7 days | Antibiotics slightly reduces the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on high quality evidence. | RR 0.76 (0.63 to 0.91) | High |
| Pain at 10 to 12 days | Antibiotics probably reduces the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on moderate quality evidence. | RR 0.33 (0.17 to 0.66) | Moderate |
| Abnormal tympanometry | |||
| 2 to 4 weeks | Antibiotics slightly reduces the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on high quality evidence. | RR 0.82 (0.74 to 0.90) | High |
| 3 months | Antibiotics causes little or no reduction to the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on high quality evidence. | RR 0.97 (0.76 to 1.24) | High |
| Vomiting | |||
| Diarrhoea or rash | Antibiotics slightly increases the chance of experiencing the outcome when compared with placebo for acute otitis media in children. Data are based on high quality evidence. | RR 1.38 (1.19 to 1.59) | High |
The evidence indicates that most children older than 6 months of age who have acute otitis media do not benefit from treatment with antibiotics. If antibiotics are used, amoxicillin is generally recommended.[15] If there is resistance or use of amoxicillin in the last 30 days then amoxicillin-clavulanate or another penicillin derivative plus beta lactamase inhibitor is recommended.[15] Taking amoxicillin once a day may be as effective as twice[44] or three times a day. While less than 7 days of antibiotics have fewer side effects, more than seven days appear to be more effective.[45] If there is no improvement after 2–3 days of treatment a change in therapy may be considered.[15]
A treatment option for chronic suppurative otitis media with discharge is topical antibiotics. A Cochrane review found that topical quinolone antibiotics can improve discharge better than oral antibiotics.[46] Safety is not really clear.[46]
Tympanostomy tube
Tympanostomy tubes (also called "grommets") are recommended with three or more episodes of acute otitis media in 6 months or four or more in a year, with at least one episode or more attacks in the preceding 6 months.[15] There is tentative evidence of reduced recurrence rates in the 6 months after placement.[47][48] Evidence does not support an effect on long-term hearing or language development.[49][48] A common complication of having a tympanostomy tube is otorrhea, which is a discharge from the ear.[50]
Oral antibiotics should not be used to treat uncomplicated acute tympanostomy tube otorrhea.[50] Oral antibiotics are not a sufficient response to bacteria that cause this condition and have significant side effects including increased risk of opportunistic infection.[50] In contrast, topical antibiotic eardrops can treat this condition.[50]
Otitis media with effusion
The decision to treat is usually made after a combination of physical exam and laboratory diagnosis, with additional testing including audiometry, tympanogram, temporal bone CT and MRI.[51][52][53] Decongestants,[54] glucocorticoids,[55] and topical antibiotics are generally not effective as treatment for non-infectious, or serous, causes of mastoid effusion.[51] Moreover, it is recommended against using antihistamines and decongestants in children with OME.[56] In less severe cases or those without significant hearing impairment, the effusion can resolve spontaneously or with more conservative measures such as autoinflation.[57] In more severe cases, tympanostomy tubes can be inserted, possibly with adjuvant adenoidectomy[51] as it shows a significant benefit as far as the resolution of middle ear effusion in children with OME is concerned.[58]
Alternative medicine
Complementary and alternative medicine is not recommended for otitis media with effusion because there is no evidence of benefit.[25]Homeopathic treatments have not been proven to be effective for acute otitis media in a study with children.[59] An osteopathic manipulation technique called the Galbreath technique[60] was evaluated in one randomized controlled clinical trial; one reviewer concluded that it was promising, but a 2010 evidence report found the evidence inconclusive.[61]
Outcomes

Disability-adjusted life year for otitis media per 100,000 inhabitants in 2004.
| no data < 10 10-14 14-18 18-22 22-26 26-30 | 30-34 34-38 38-42 42-46 46-50 > 50 |

Deaths from otitis media per million persons in 2012 .mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
0-0
1-1
2-4
Complications of acute otitis media consists of perforation of the ear drum, infection of the mastoid space behind the ear (mastoiditis), and more rarely intracranial complications can occur, such as bacterial meningitis, brain abscess, or dural sinus thrombosis.[62] It is estimated that each year 21,000 people die due to complications of otitis media.[12]
Membrane rupture
In severe or untreated cases, the tympanic membrane may perforate, allowing the pus in the middle-ear space to drain into the ear canal. If there is enough, this drainage may be obvious. Even though the perforation of the tympanic membrane suggests a highly painful and traumatic process, it is almost always associated with a dramatic relief of pressure and pain. In a simple case of acute otitis media in an otherwise healthy person, the body's defenses are likely to resolve the infection and the ear drum nearly always heals.
An option for severe acute otitis media in which analgesics are not controlling ear pain is to perform a tympanocentesis, i.e., needle aspiration through the tympanic membrane to relieve the ear pain and to identify the causative organism(s).
Hearing loss
Children with recurrent episodes of acute otitis media and those with otitis media with effusion or chronic suppurative otitis media have higher risks of developing conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Globally approximately 141 million people have mild hearing loss due to otitis media (2.1% of the population).[63] This is more common in males (2.3%) than females (1.8%).[63]
This hearing loss is mainly due to fluid in the middle ear or rupture of the tympanic membrane. Prolonged duration of otitis media is associated with ossicular complications and, together with persistent tympanic membrane perforation, contributes to the severity of the disease and hearing loss. When a cholesteatoma or granulation tissue is present in the middle ear, the degree of hearing loss and ossicular destruction is even greater.[64]
Periods of conductive hearing loss from otitis media may have a detrimental effect on speech development in children.[65] Some studies have linked otitis media to learning problems, attention disorders, and problems with social adaptation.[66] Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that patients with otitis media have more depression/anxiety-related disorders compared to individuals with normal hearing.[67] Once the infections resolve and hearing thresholds return to normal, childhood otitis media may still cause minor and irreversible damage to the middle ear and cochlea.[68]
Epidemiology
Acute otitis media is very common in childhood. It is the most common condition for which medical care is provided in children under five years of age in the US.[17] Acute otitis media affects 11% of people each year (709 million cases) with half occurring in those below five years.[12] Chronic suppurative otitis media affects about 5% or 31 million of these cases with 22.6% of cases occurring annually under the age of five years.[12] Otitis media resulted in 2,400 deaths in 2013—down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.[14]
Etymology
The term otitis media is composed of otitis, Ancient Greek for "inflammation of the ear", and media, Latin for "middle".
References
^ abcdefghijklmno Lieberthal, AS; Carroll, AE; Chonmaitree, T; Ganiats, TG; Hoberman, A; Jackson, MA; Joffe, MD; Miller, DT; Rosenfeld, RM; Sevilla, XD; Schwartz, RH; Thomas, PA; Tunkel, DE (March 2013). "The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media". Pediatrics. 131 (3): e964–99. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3488. PMID 23439909..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abc Qureishi, A; Lee, Y; Belfield, K; Birchall, JP; Daniel, M (10 January 2014). "Update on otitis media - prevention and treatment". Infection and Drug Resistance. 7: 15–24. doi:10.2147/IDR.S39637. PMC 3894142. PMID 24453496.
^ abcd "Ear Infections". cdc.gov. September 30, 2013. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
^ abcdefghijklmnop Minovi, A; Dazert, S (2014). "Diseases of the middle ear in childhood". GMS Current Topics in Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 13: Doc11. doi:10.3205/cto000114. PMC 4273172. PMID 25587371.
^ GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
^ ab GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
^ "Ear disease in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children" (PDF). AIHW. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 February 2017. Retrieved 12 May 2017.
^ Coker, TR; Chan, LS; Newberry, SJ; Limbos, MA; Suttorp, MJ; Shekelle, PG; Takata, GS (17 November 2010). "Diagnosis, microbial epidemiology, and antibiotic treatment of acute otitis media in children: a systematic review". JAMA. 304 (19): 2161–9. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1651. PMID 21081729.
^ abc "Otitis Media: Physician Information Sheet (Pediatrics)". cdc.gov. November 4, 2013. Archived from the original on 10 September 2015. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
^ abc Venekamp, RP; Sanders, SL; Glasziou, PP; Del Mar, CB; Rovers, MM (23 June 2015). "Antibiotics for acute otitis media in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD000219. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000219.pub4. PMID 26099233.
^ Venekamp, RP; Burton, MJ; van Dongen, TM; van der Heijden, GJ; van Zon, A; Schilder, AG (12 June 2016). "Antibiotics for otitis media with effusion in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD009163. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009163.pub3. PMID 27290722.
^ abcdefgh Monasta, L; Ronfani, L; Marchetti, F; Montico, M; Vecchi Brumatti, L; Bavcar, A; Grasso, D; Barbiero, C; Tamburlini, G (2012). "Burden of disease caused by otitis media: systematic review and global estimates". PLOS ONE. 7 (4): e36226. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036226. PMC 3340347. PMID 22558393.
^ Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators (22 August 2015). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60692-4. PMC 4561509. PMID 26063472.
^ ab GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (17 December 2014). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
^ abcdefghijk Lieberthal, AS; Carroll, AE; Chonmaitree, T; Ganiats, TG; Hoberman, A; Jackson, MA; Joffe, MD; Miller, DT; Rosenfeld, RM; Sevilla, XD; Schwartz, RH; Thomas, PA; Tunkel, DE (Feb 25, 2013). "The Diagnosis and Management of Acute Otitis Media". Pediatrics. 131 (3): e964–99. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3488. PMID 23439909.
^ Bluestone, CD (2005). Eustachian tube: structure, function, role in otitis media. Hamilton, London: BC Decker. pp. 1–219. ISBN 9781550090666.
^ abc John D Donaldson. "Acute Otitis Media". Medscape. Archived from the original on 28 March 2013. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
^ Laine MK, Tähtinen PA, Ruuskanen O, Huovinen P, Ruohola A (May 2010). "Symptoms or symptom-based scores cannot predict acute otitis media at otitis-prone age". Pediatrics. 125 (5): e1154–61. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-2689. PMID 20368317.
^ Shaikh, Nader (2010). "Videos in clinical medicine. Diagnosing otitis media--otoscopy and cerumen removal". NEJM. 362 (20): e62. doi:10.1056/NEJMvcm0904397. PMID 20484393.
^ Patel, MM; Eisenberg, L; Witsell, D; Schulz, KA (October 2008). "Assessment of acute otitis externa and otitis media with effusion performance measures in otolaryngology practices". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 139 (4): 490–494. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2008.07.030. PMID 18922333.
^ Shaikh, N; et al. (March 28, 2012). "Development of an algorithm for the diagnosis of otitis media" (PDF). Academic Pediatrics (Submitted manuscript). 12 (3): 214–218. doi:10.1016/j.acap.2012.01.007. PMID 22459064.
^ Roberts DB (April 1980). "The etiology of bullous myringitis and the role of mycoplasmas in ear disease: a review". Pediatrics. 65 (4): 761–6. PMID 7367083.
^ Benninger, Michael S. (2008-03-01). "Acute bacterial rhinosinusitis and otitis media: changes in pathogenicity following widespread use of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 138 (3): 274–278. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2007.11.011. ISSN 0194-5998. PMID 18312870.
^ "Glue Ear". NHS Choices. Department of Health. Archived from the original on 13 November 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2012.
^ ab Rosenfeld RM, Culpepper L, Yawn B, Mahoney MC (June 2004). "Otitis media with effusion clinical practice guideline". Am Fam Physician. 69 (12): 2776, 2778–9. PMID 15222643.
^ "Otitis media with effusion: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 17 February 2017. Retrieved 17 February 2017.
^ Owen MJ, Baldwin CD, Swank PR, Pannu AK, Johnson DL, Howie VM (1993). "Relation of infant feeding practices, cigarette smoke exposure, and group child care to the onset and duration of otitis media with effusion in the first two years of life". J. Pediatr. 123 (5): 702–11. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(05)80843-1. PMID 8229477.
^ ab Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators (22 August 2015). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. PMC 4561509. PMID 26063472.
^ abc Acuin, Jose; WHO Dept. of Child and Adolescent Health and Development; WHO Programme for the Prevention of Blindness and Deafness (2004). Chronic suppurative otitis media : burden of illness and management options. Geneve: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-159158-4. Archived from the original on 2017-02-28.
^ ab Lawrence, Ruth (2016). Breastfeeding : a guide for the medical profession, 8th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. pp. 216–217. ISBN 978-0-323-35776-0.
^ ab Fortanier, Alexandre C.; Venekamp, Roderick P.; Boonacker, Chantal W. B.; Hak, Eelko; Schilder, Anne G. M.; Sanders, Elisabeth A. M.; Damoiseaux, Roger A. M. J. (2014-04-02). "Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines for preventing otitis media". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (4): CD001480. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001480.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 24696098.
^ Rovers MM, Schilder AG, Zielhuis GA, Rosenfeld RM (2004). "Otitis media". Lancet. 363 (9407): 564–573. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15495-0. PMID 14962529.
^ Pukander J, Luotonem J, Timonen M, Karma P (1985). "Risk factors affecting the occurrence of acute otitis media among 2-3 year old urban children". Acta Otolaryngol. 100 (3–4): 260–265. doi:10.3109/00016488509104788. PMID 4061076.
^ Etzel RA (1987). "Smoke and ear effusions". Pediatrics. 79 (2): 309–311. PMID 3808812.
^ Rovers MM, Numans ME, Langenbach E, Grobbee DE, Verheij TJ, Schilder AG (August 2008). "Is pacifier use a risk factor for acute otitis media? A dynamic cohort study". Fam Pract. 25 (4): 233–6. doi:10.1093/fampra/cmn030. PMID 18562333.
^ Leach AJ, Morris PS (2006). Leach AJ, ed. "Antibiotics for the prevention of acute and chronic suppurative otitis media in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD004401. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004401.pub2. PMID 17054203.
^ Azarpazhooh, A; Lawrence, HP; Shah, PS (3 August 2016). "Xylitol for preventing acute otitis media in children up to 12 years of age". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (8): CD007095. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007095.pub3. PMID 27486835.

^ Gulani, A; Sachdev, HS (Jun 29, 2014). "Zinc supplements for preventing otitis media". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD006639. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006639.pub4. PMID 24974096.
^ Sattout, A.; Jenner, R. (February 2008). "Best evidence topic reports. Bet 1. The role of topical analgesia in acute otitis media". Emerg Med J. 25 (2): 103–4. doi:10.1136/emj.2007.056648. PMID 18212148.
^ Coleman C, Moore M (2008). Coleman C, ed. "Decongestants and antihistamines for acute otitis media in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD001727. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001727.pub4. PMID 18646076.
^ Thompson, M; Vodicka, TA; Blair, PS; Buckley, DI; Heneghan, C; Hay, AD; TARGET Programme, Team (Dec 11, 2013). "Duration of symptoms of respiratory tract infections in children: systematic review". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 347: f7027. doi:10.1136/bmj.f7027. PMC 3898587. PMID 24335668.
^ Principi, N; Bianchini, S; Baggi, E; Esposito, S (February 2013). "No evidence for the effectiveness of systemic corticosteroids in acute pharyngitis, community-acquired pneumonia and acute otitis media". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 32 (2): 151–60. doi:10.1007/s10096-012-1747-y. PMID 22993127.
^ ab Venekamp, R; Sanders, S; Glasziou, P (2015). "Antibiotics for acute otitis media in children". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 6 (6): CD000219.pub4. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000219.pub4. PMID 26099233.
^ Thanaviratananich, S; Laopaiboon, M; Vatanasapt, P (13 December 2013). "Once or twice daily versus three times daily amoxicillin with or without clavulanate for the treatment of acute otitis media". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 12 (12): CD004975. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004975.pub3. PMID 24338106.
^ Kozyrskyj, A; Klassen, TP; Moffatt, M; Harvey, K (8 September 2010). "Short-course antibiotics for acute otitis media". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (9): CD001095. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001095.pub2. PMID 20824827.
^ ab Macfadyen, CA; Acuin, JM; Gamble, C (Jan 25, 2006). "Systemic antibiotics versus topical treatments for chronically discharging ears with underlying eardrum perforations". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD005608. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005608. PMID 16437533.
^ McDonald S, Langton Hewer CD, Nunez DA (2008). McDonald S, ed. "Grommets (ventilation tubes) for recurrent acute otitis media in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD004741. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004741.pub2. PMID 18843668.
^ ab Steele, DW; Adam, GP; Di, M; Halladay, CH; Balk, EM; Trikalinos, TA (June 2017). "Effectiveness of Tympanostomy Tubes for Otitis Media: A Meta-analysis". Pediatrics. 139 (6): e20170125. doi:10.1542/peds.2017-0125. PMID 28562283.
^ Browning GG, Rovers MM, Williamson I, Lous J, Burton MJ (2010). Browning GG, ed. "Grommets (ventilation tubes) for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (10): CD001801. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001801.pub3. PMID 20927726.
^ abcd American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF), Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery, archived (PDF) from the original on May 13, 2015, retrieved August 1, 2013, which cites
Rosenfeld, R. M.; Schwartz, S. R.; Pynnonen, M. A.; Tunkel, D. E.; Hussey, H. M.; Fichera, J. S.; Grimes, A. M.; Hackell, J. M.; Harrison, M. F.; Haskell, H.; Haynes, D. S.; Kim, T. W.; Lafreniere, D. C.; LeBlanc, K.; Mackey, W. L.; Netterville, J. L.; Pipan, M. E.; Raol, N. P.; Schellhase, K. G. (2013). "Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy Tubes in Children". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 149 (1 Suppl): S1–S35. doi:10.1177/0194599813487302. ISSN 0194-5998. PMID 23818543.
^ abc Rosenfeld, RM; Shin, JJ; Schwartz, SR; Coggins, R; Gagnon, L; Hackell, JM; Hoelting, D; Hunter, LL; Kummer, AW; Payne, SC; Poe, DS; Veling, M; Vila, PM; Walsh, SA; Corrigan, MD (February 2016). "Clinical Practice Guideline: Otitis Media with Effusion (Update)". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 154 (1 Suppl): S1–S41. doi:10.1177/0194599815623467. PMID 26832942.
^ Wallace, IF; Berkman, ND; Lohr, KN; Harrison, MF; Kimple, AJ; Steiner, MJ (February 2014). "Surgical treatments for otitis media with effusion: a systematic review". Pediatrics. 133 (2): 296–311. doi:10.1542/peds.2013-3228. PMID 24394689.
^ Rosenfeld, RM; Schwartz, SR; Pynnonen, MA; Tunkel, DE; Hussey, HM; Fichera, JS; Grimes, AM; Hackell, JM; Harrison, MF; Haskell, H; Haynes, DS; Kim, TW; Lafreniere, DC; LeBlanc, K; Mackey, WL; Netterville, JL; Pipan, ME; Raol, NP; Schellhase, KG (July 2013). "Clinical practice guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 149 (1 Suppl): S1–35. doi:10.1177/0194599813487302. PMID 23818543.
^ Griffin, G; Flynn, CA (7 September 2011). "Antihistamines and/or decongestants for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (9): CD003423. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003423.pub3. PMID 21901683.
^ Simpson, SA; Lewis, R; van der Voort, J; Butler, CC (11 May 2011). "Oral or topical nasal steroids for hearing loss associated with otitis media with effusion in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (5): CD001935. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001935.pub3. PMID 21563132.
^ Griffin, G; Flynn, CA (7 September 2011). "Antihistamines and/or decongestants for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (9): CD003423. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003423.pub3. PMID 21901683.
^ Blanshard, JD; Maw, AR; Bawden, R (June 1993). "Conservative treatment of otitis media with effusion by autoinflation of the middle ear". Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences. 18 (3): 188–92. PMID 8365006.
^ van den Aardweg, MT; Schilder, AG; Herkert, E; Boonacker, CW; Rovers, MM (20 January 2010). "Adenoidectomy for otitis media in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD007810. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007810.pub2. PMID 20091650.
^ Jacobs, J; Springer, DA; Crothers, D (February 2001). "Homeopathic treatment of acute otitis media in children: a preliminary randomized placebo-controlled trial". The Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 20 (2): 177–83. doi:10.1097/00006454-200102000-00012. PMID 11224838.
^ Pratt-Harrington D (October 2000). "Galbreath technique: a manipulative treatment for otitis media revisited". J Am Osteopath Assoc. 100 (10): 635–9. PMID 11105452.
^ Bronfort G, Haas M, Evans R, Leininger B, Triano J (2010). "Effectiveness of manual therapies: the UK evidence report". Chiropr Osteopat. 18 (1): 3. doi:10.1186/1746-1340-18-3. PMC 2841070. PMID 20184717.
^ Jung, TT; Alper, CM; Hellstorm, SO; Hunter, LL; Casselbrant, ML; Groth, A; Kemaloglu, YK; Kim, SG; Lim, D; Nittrourer, S; Park, KH; Sabo, D; Sprately, J (April 2013). "Panel 8: Complications and sequelae". Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 148 (4 Suppl): E122–43. doi:10.1177/0194599812467425. PMID 23536529.
^ ab Vos, T; Flaxman, A. D.; Naghavi, M; Lozano, R; Michaud, C; Ezzati, M; Shibuya, K; Salomon, J. A.; Abdalla, S; Aboyans, V; Abraham, J; Ackerman, I; Aggarwal, R; Ahn, S. Y.; Ali, M. K.; Alvarado, M; Anderson, H. R.; Anderson, L. M.; Andrews, K. G.; Atkinson, C; Baddour, L. M.; Bahalim, A. N.; Barker-Collo, S; Barrero, L. H.; Bartels, D. H.; Basáñez, M. G.; Baxter, A; Bell, M. L.; Benjamin, E. J.; et al. (Dec 15, 2012). "Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMID 23245607.
^ Da Costa SS; Rosito, Letícia Petersen Schmidt; Dornelles, Cristina (February 2009). "Sensorineural hearing loss in patients with chronic otitis media". Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 266 (2): 221–4. doi:10.1007/s00405-008-0739-0. hdl:10183/125807. PMID 18629531.
^ Roberts K (June 1997). "A preliminary account of the effect of otitis media on 15-month-olds' categorization and some implications for early language learning". J Speech Lang Hear Res. 40 (3): 508–18. doi:10.1044/jslhr.4003.508. PMID 9210110. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04.
^ Bidadi S, Nejadkazem M, Naderpour M (November 2008). "The relationship between chronic otitis media-induced hearing loss and the acquisition of social skills". Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 139 (5): 665–70. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.004. PMID 18984261.
^ Gouma P, Mallis A, Daniilidis V, Gouveris H, Armenakis N, Naxakis S (January 2011). "Behavioral trends in young children with conductive hearing loss: a case-control study". Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 268 (1): 63–6. doi:10.1007/s00405-010-1346-4. PMID 20665042.
^ Yilmaz S, Karasalihoglu AR, Tas A, Yagiz R, Tas M (February 2006). "Otoacoustic emissions in young adults with a history of otitis media". J Laryngol Otol. 120 (2): 103–7. doi:10.1017/S0022215105004871. PMID 16359151.
External links
| Classification | D
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Otitis media. |
Neff MJ (June 2004). "AAP, AAFP, AAO-HNS release guideline on diagnosis and management of otitis media with effusion". Am Fam Physician. 69 (12): 2929–31. PMID 15222658.
Secretory otitis media (Ear disorder) at Encyclopædia Britannica
Otitis media (Pathology) at Encyclopædia Britannica






