Pallava dynasty
Pallava Empire | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 275 CE–897 CE | |||||||||||||
 Pallava territories during Narasimhavarman I c. 645. This includes the Chalukya territories occupied by the Pallavas. | |||||||||||||
| Status | Dynasty | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Kanchipuram | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Prakrit, Sanskrit, Tamil, Telugu | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Hinduism | ||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
• 275–300 | Simhavarman I | ||||||||||||
• 882–897 | Aparajitavarman | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical India | ||||||||||||
• Established | 275 CE | ||||||||||||
• Disestablished | 897 CE | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||
Pallava Kings (200s–800s) | |
| Vishnugopa II | |
Simhavarma III | |
Simhavishnu | |
Mahendravarma I | (600-630) |
Narasimhavarma I | (630–668) |
Mahendravarma II | (668–670) |
Parameswara varma I | (670–695) |
Narasimha varma II | (700-728) |
Paramesvara varma II | (728–731) |
Nandi varma II | (731–795) |
Danti varma | (795–846) |
Nandi varma III | (846-869) |
Aparajita varma | (880-897) |
The Pallava dynasty was a South Indian dynasty that existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a portion of southern India. They gained prominence after the eclipse of the Satavahana dynasty, whom the Pallavas served as feudatories.[2][3]
Pallavas became a major power during the reign of Mahendravarma I (571 – 630 CE) and Narasimhavarma I (630 – 668 CE) and dominated the Telugu and northern parts of the Tamil region for about 600 years until the end of the 9th century. Throughout their reign they were in constant conflict with both Chalukyas of Badami in the north and the Tamil kingdoms of Chola and Pandyas in the south and were finally defeated by the Chola kings in the 9th century CE.[citation needed]
Pallavas are most noted for their patronage of architecture, the finest example being the Shore Temple, a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Mahabalipuram. The Pallavas, who left behind magnificent sculptures and temples, established the foundations of medieval South Indian architecture. They developed the Pallava script from which Grantha ultimately descended. The Pallava script gave rise to several other southeast Asian scripts. Chinese traveller Xuanzang visited Kanchipuram during Pallava rule and extolled their benign rule.
Contents
1 Origins
2 Rivalries
2.1 With Cholas
2.2 With Kadambas
2.3 With Kalabhras
3 Birudas
4 Languages used
4.1 Writing system
5 Religion
6 Pallava architecture
7 Pallava society
8 Chronology
8.1 Sastri chronology
8.1.1 Early Pallavas
8.1.2 Later Pallavas
8.1.2.1 Later Pallavas of the Kadava Line
8.2 Aiyangar chronology
8.2.1 Early Pallavas
8.2.2 Middle Pallavas
8.2.3 Later Pallavas
8.2.3.1 Later Pallavas of the Kadava Line
9 Genealogy
10 Other relationships
11 See also
12 Notes
13 References
14 External links
Origins
| Outline of South Asian history | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Palaeolithic .mw-parser-output .nobold{font-weight:normal} (2,500,000–250,000 BC)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Neolithic (10,800–3300 BC)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chalcolithic (3500–1500 BC)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bronze Age (3300–1300 BC)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Iron Age (1500–200 BC)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Middle Kingdoms (230 BC – AD 1206)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Late medieval period (1206–1526)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Early modern period (1526–1858)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Colonial states (1510–1961)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Periods of Sri Lanka
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
National histories
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Regional histories
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Specialised histories
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Kailasanathar Temple, Kanchipuram, Tamil Nadu, 685-705
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}



Kailasanathar Temple, Kanchipuram
A Sangam Period classic, Manimekalai, attributes the origin of the first Pallava King from a liaison between the daughter of a Naga king of Manipallava named Pilli Valai (Pilivalai) with a Chola king, Killivalavan, out of which union was born a prince, who was lost in ship wreck and found with a twig (pallava) of Cephalandra Indica (Tondai) around his ankle and hence named Tondai-man. Another version states that "Pallava" was born from the union of the Brahmin Ashvatthama with a Naga Princess also supposedly supported in the sixth verse of the Bahur plates which states "From Ashvatthama was born the king named Pallava".[4] The Pallavas themselves claimed to descend from Brahma and Ashvatthama.[5]
Though Manimekalai posits Ilam Tiriyan as a Chola, not a Pallava, the Velurpalaiyam plates dated to 852, do not mention the Cholas. Instead, they credit the Naga liaison episode, and creation of the Pallava line, to a different Pallava king named Virakurcha, while preserving its legitimising significance:[6]
...from him (Aśvatthāman) in order (came) Pallava, the lord of the whole earth, whose fame was bewildering. Thence, came into existence the race of Pallavas... [including the son of Chūtapallava] Vīrakūrcha, of celebrated name, who simultaneously with (the hand of) the daughter of the chief of serpents grasped also the complete insignia of royalty and became famous.
Historically, early relations between Nagas and Pallavas became well-established before the myth of Pallava's birth to Ashvatthama took root.[7] A prashasti (literally "praise"), composed in 753 on the dynastic eulogy in the Kasakadi (Kasakudi) plates, by the Pallava Trivikrama, traces the Pallava lineage from creation through a series of mythic progenitors, and then praises the dynasty in terms of two similes hinged together by triple use of the word avatara ("descent"), as below:[6]
From [them] descended the powerful, spotless Pallava dynasty [vaṁśāvatāra], which resembled a partial incarnation [aṃśāvatāra] of Visnu, as it displayed unbroken courage in conquering the circle of the world...and which resembled the descent of the Ganges [gaṅgāvatāra] as it purified the whole world.
The Proceedings of the First Annual Conference of South Indian History Congress also notes: The word Tondai means a creeper and the term Pallava conveys a similar meaning.[8] Since the Pallavas ruled in the territory extending from Bellary to Bezwada, it led to the theory that they were a northern dynasty who contracted marriages with princesses of the Andhra Dynasty and so inherited a portion of southern Andhra Pradesh.[4]
Historian K. R. Subramanian says the Pallavas were originally a Telugu power rather than a Tamil one. Telugu sources know of a Trilochana Pallava as the earliest Telugu king and they are confirmed by later inscriptions.[9] The first Chalukya king is said to have been met, repulsed and killed by the same Trilochana near Mudivemu (Cuddappah district). A Buddhist story describes Kala the Nagaraja, resembling the Pallava Kalabhartar as a king of the region near Krishna district. The Pallava Bogga may be identified with the kingdom of Kala in Andhra which had close and early maritime and cultural relations with Ceylon.[7]
K. A. Nilakanta Sastri postulated that Pallavas were descendants of a North Indian dynasty who moved southwards, adopted local traditions to their own use, and named themselves as Tondaiyar after the land called Tondai.[8][10] K. P. Jayaswal also proposed a North Indian origin, putting forward the theory that the Pallavas were a branch of the Vakatakas.[8][11]
The earliest inscriptions of the Pallavas were found in the districts of Bellary, Guntur and Nellore and all the inscriptions of the dynasty till the rise of Simhavishnu were found in the latter two of those.[7]
Rivalries
With Cholas
The Pallavas captured Kanchi from the Cholas as recorded in the Velurpalaiyam Plates, around the reign of the fifth king of the Pallava line Kumaravishnu I. Thereafter Kanchi figures in inscriptions as the capital of the Pallavas. The Cholas drove the Pallavas away from Kanchi in the mid-4th century, in the reign of Vishugopa, the tenth king of the Pallava line. The Pallavas re-captured Kanchi in the mid-6th century, possibly in the reign of Simhavishnu, the fourteenth king of the Pallava line, whom the Kasakudi plates state as "the lion of the earth". Thereafter the Pallavas held on to Kanchi until the 9th century, until the reign of their last king, Vijaya-Nripatungavarman.[12]
With Kadambas
The Pallavas were in conflict with major kingdoms at various periods of time. A contest for political supremacy existed between the early Pallavas and the Kadambas. Numerous Kadamba inscriptions provide details of Pallava-Kadamba hostilities.[13]
Kadamba dynasty's founder Mayurasharma first succeeded in establishing himself in the forests of Shriparvata (possibly modern Srisailam in Andhra Pradesh) by defeating the Antharapalas (guards) of the Pallavas and subduing the Banas of Kolar in 345 CE. The Pallavas under Skandavarman were unable to contain Mayurasharma and recognised him as a sovereign in the regions from the Amara Ocean (Western Ocean) to Prehara (Malaprabha River). Some historians feel that Mayurasharma was initially appointed as a commander (Dandanayaka) in the army of the Pallavas, as the inscription uses such terms as Senani and calls Mayurasharma Shadanana (six-faced god of war). After a period of time, due to the confusion caused by the defeat of Pallava Vishnugopa by Samudragupta (Allahabad inscriptions), Mayurasharma formed his kingdom with Banavasi (near Talagunda) as his capital.[14]
With Kalabhras
During the reign of Vishnugopavarman II (approx. 500-525), political convulsion engulfed the Pallavas due to the Kalabhra invasion of the Tamil country. Towards the close of the 6th century, the Pallava Simhavishnu stuck a blow against the Kalabhras. The Pandyas followed suit. Thereafter the Tamil country was divided between the Pallavas in the north with Kanchipuram as their capital, and Pandyas in the south with Madurai as their capital.[15]
Birudas
The royal custom of using a series of descriptive honorific titles, Birudas, was particularly prevalent among the Pallavas. The birudas of Mahendravarman I are in Sanskrit, Tamil and Telugu. The Telugu birudas show Mahendravarman's involvement with the Andhra region continued to be strong at the time he was creating his cave-temples in the Tamil region. The suffix "Malla" was used by the Pallava rulers.[16] Mahendravarman I used the biruda, Satrumalla, "a warrior who overthrows his enemies", and his grandson Paramesvara I was called Ekamalla "the sole warrior or wrestler". Pallava kings, presumably exalted ones, were known by the title Mahamalla ("great wrestler").[6]
Languages used

Coin of the Pallavas of Coromandel, king Narasimhavarman I. (630-668 AD).Obv Lion left Rev Name of Narasimhavarman with solar and lunar symbols around.
All early Pallava royal inscriptions were either in Sanskrit or Prakrit, considered the official languages of the dynasty while the official scripts were Pallava and later Grantha. Similarly, inscriptions found in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka State are in Sanskrit and Prakrit.[17] The phenomenon of using Prakrit as official languages in which rulers left their inscriptions and epigraphies continued till the 6th century. It would have been in the interest of the ruling elite to protect their privileges by perpetuating their hegemony of Prakrit in order to exclude the common people from sharing power (Mahadevan 1995a: 173–188). The Pallavas in their Tamil country used Tamil and Sanskrit in their inscriptions.[18][19]
Tamil came to be the main language used by the Pallavas in their inscriptions, though a few records continued to be in Sanskrit.[19] This language was first adopted by Mahendravarman I himself in a few records of his; but from the time of Paramesvaravarman I, the practice came into vogue of inscribing a part of the record in Sanskrit and the rest in Tamil. Almost all the copper plate records, viz., Kasakudi, Tandantottam, Pattattalmangalm, Udayendiram and Velurpalaiyam are composed both in Sanskrit and Tamil.[19]
Writing system
Under the Pallava dynasty, a unique form of Grantha script, a descendant of Pallava script which is a type of Brahmic script, was used. Around the 6th century, it was exported eastwards and influenced the genesis of almost all Southeast Asian scripts.
Religion
Pallavas were followers of Hinduism and made gifts of land to gods and Brahmins. In line with the prevalent customs, some of the rulers performed the Aswamedha and other Vedic sacrifices.[20] They were, however, tolerant of other faiths. The Chinese monk Xuanzang who visited Kanchipuram during the reign of Narasimhavarman I reported that there were 100 Buddhist monasteries, and 80 temples in Kanchipuram.[21]
Pallava architecture

The Shore Temple at Mahabalipuram built by Narasimhavarman II
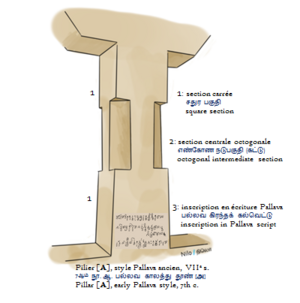
The Pallavas were instrumental in the transition from rock-cut architecture to stone temples. The earliest examples of Pallava constructions are rock-cut temples dating from 610–690 and structural temples between 690–900. A number of rock-cut cave temples bear the inscription of the Pallava king, Mahendravarman I and his successors.[22]
Among the accomplishments of the Pallava architecture are the rock-cut temples at Mahabalipuram. There are excavated pillared halls and monolithic shrines known as Rathas in Mahabalipuram. Early temples were mostly dedicated to Shiva. The Kailasanatha temple in Kanchipuram and the Shore Temple built by Narasimhavarman II, rock cut temple in Mahendravadi by Mahendravarman are fine examples of the Pallava style temples.[23] The temple of Nalanda Gedige in Kandy, Sri Lanka is another. The famous Tondeswaram temple of Tenavarai and the ancient Koneswaram temple of Trincomalee were patronized and structurally developed by the Pallavas in the 7th century.[citation needed]
Pallava society
The Pallava period beginning with Simhavishnu (575 AD – 900 AD) was a transitional stage in southern Indian society with monument building, foundation of devotional (bhakti) sects of Alvars and Nayanars, the flowering of rural brahmanical institutions of Sanskrit learning, and the establishment of chakravartin model of kingship over a territory of diverse people; which ended the pre-Pallavan era of territorially segmented people, each with their culture, under a tribal chieftain.[24] While a system of ranked relationship among groups existed in the classical period, the Pallava period extolled ranked relationships based on ritual purity as enjoined by the shastras.[25] Burton distinguishes between the chakravatin model and the kshatriya model, and likens kshatriyas to locally based warriors with ritual status sufficiently high enough to share with Brahmins; and states that in south India the kshatriya model did not emerge.[25] As per Burton, south India was aware of the Indo-Aryan varna organized society in which decisive secular authority was vested in the kshatriyas; but apart from the Pallava, Chola and Vijayanagar line of warriors which claimed chakravartin status, only few locality warrior families achieved the prestigious kin-linked organization of northern warrior groups.[25]
Chronology
Sastri chronology
The earliest documentation on the Pallavas is the three copper-plate grants, now referred to as the Mayidavolu, Hirehadagali and the British Museum plates (Durga Prasad, 1988) belonging to Skandavarman I and written in Prakrit.[26] Skandavarman appears to have been the first great ruler of the early Pallavas, though there are references to other early Pallavas who were probably predecessors of Skandavarman.[27] Skandavarman extended his dominions from the Krishna in the north to the Pennar in the south and to the Bellary district in the West. He performed the Aswamedha and other Vedic sacrifices and bore the title of "Supreme King of Kings devoted to dharma".[26]
The Hirahadagali copper plate (Bellary District) record in Prakrit is dated in the 8th year of Sivaskanda Varman to 283 CE and confirms the gift made by his father who is described merely as "Bappa-deva" (revered father) or Boppa. It will thus be clear that this dynasty of the Prakrit charters beginning with "Bappa-deva" were the historical founders of the Pallava dominion in South India.[28][29]

Early Pallavas-Prakrit records
The Hirahadagalli Plates were found in Hirehadagali, Bellary district in the Satavahanihara (Satavahana district, probably their homeland) and is one of the earliest copper plates in Karnataka and belongs to the reign of early Pallava ruler Shivaskanda Varma. Pallava King Sivaskandavarman of Kanchi of the early Pallavas ruled from 275 to 300 CE, and issued the charter in 283 CE.
Vijaya Skandavarman (Sivaskandavarman) was king of the Pallava kingdom at Bellary region in Andhra, and viceroy of Samudragupta at Kanchipuram. The writer of the grant was privy councillor Bhatti Sharman and was supposed to be valid for 100,000 years.
As per the Hirahadagalli Plates of 283 CE, Pallava King Sivaskandavarman granted an immunity viz the garden of Chillarekakodumka, which was formerly given by Lord Bappa to the Brahmins, freeholders of Chillarekakodumka and inhabitants of Apitti. Chillarekakodumka has been identified by some as ancient village Chillarige in Bellary, Karnataka.[28]

Final genealogy of early Pallavas by combining the earlier Prakrit and the later Sanskrit records
In the reign of Simhavarman IV, who ascended the throne in 436, the territories lost to the Vishnukundins in the north up to the mouth of the Krishna were recovered.[citation needed] The early Pallava history from this period onwards is furnished by a dozen or so copper-plate grants in Sanskrit. They are all dated in the regnal years of the kings.[20]
The following chronology was composed from these charters by Nilakanta Sastri in his A History of South India:[20]
Early Pallavas
Simhavarman I (275–300)
Skandavarman (unknown)
Visnugopa (350–355)
Kumaravishnu I (350–370)
Skandavarman II (370–385)
Viravarman (385–400)
Skandavarman III (400–436)
Simhavarman II (436–460)
Skandavarman IV (460–480)
Nandivarman I (480–510)
Kumaravishnu II (510–530)
Buddhavarman (530–540)
Kumaravishnu III (540–550)
Simhavarman III (550–560)
Later Pallavas

The rock-cut temples at Mamallapuram constructed during the reign of Narasimhavarman I

Elephant carved out of a single-stone
The incursion of the Kalabhras and the confusion in the Tamil country was broken by the Pandya Kadungon and the Pallava Simhavishnu.[30]Mahendravarman I extended the Pallava Kingdom and was one of the greatest sovereigns. Some of the most ornate monuments and temples in southern India, carved out of solid rock, were introduced under his rule. He also wrote the play Mattavilasa Prahasana.[31]
The Pallava kingdom began to gain both in territory and influence and were a regional power by the end of the 6th century, defeating kings of Ceylon and mainland Tamilakkam.[32]Narasimhavarman I and Paramesvaravarman I stand out for their achievements in both military and architectural spheres. Narasimhavarman II built the Shore Temple.
Simhavishnu (575–600)[31]
Mahendravarman I (600–630)[31]
Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla) (630–668)[31]
Mahendravarman II (668–672)
Paramesvaravarman I (670–695)[31]
Narasimhavarman II (Raja Simha) (695–722)[31]
Paramesvaravarman II (705–710)
Later Pallavas of the Kadava Line
The kings that came after Paramesvaravarman II belonged to the collateral line of Pallavas and were descendants of Bhimavarman, the brother of Simhavishnu. They called themselves as Kadavas, Kadavesa and Kaduvetti. Hiranyavarman, the father of Nandivarman Pallavamalla is said to have belonged to the Kadavakula in epigraphs.[33] Nandivarman II himself is described as "one who was born to raise the prestige of the Kadava family".[34]
Nandivarman II (Pallavamalla) (732–796) son of Hiranyavarman of Kadavakula[33][31]
Dantivarman (795–846)[31]
Nandivarman III (846–869)[31]
Aparajitavarman (879–897)[31]
Aiyangar chronology
According to the available inscriptions of the Pallavas, historian S. Krishnaswami Aiyangar proposes the Pallavas could be divided into four separate families or dynasties; some of whose connections are known and some unknown.[35] Aiyangar states
We have a certain number of charters in Prakrit of which three are important ones. Then follows a dynasty which issued their charters in Sanskrit; following this came the family of the great Pallavas beginning with Simha Vishnu; this was followed by a dynasty of the usurper Nandi Varman, another great Pallava. We are overlooking for the present the dynasty of the Ganga-Pallavas postulated by the Epigraphists. The earliest of these Pallava charters is the one known as the Mayidavolu 1 (Guntur district) copper-plates.
Based on a combination of dynastic plates and grants from the period, Aiyangar proposed their rule thus:
Early Pallavas
- Bappadevan (250-275) – married a Naga of Mavilanga (Kanchi) - The Great Founder of a Pallava lineage
- Shivaskandavarman I (275–300)
- Simhavarman (300-320)
- Bhuddavarman (320-335)
- Bhuddyankuran (335-340)
Middle Pallavas
- Visnugopa (340–355) (Yuvamaharaja Vishnugopa)
- Kumaravisnu I (355–370)
- Skanda Varman II (370–385)
- Vira Varman (385–400)
- Skanda Varman III (400–435)
- Simha Varman II (435–460)
- Skanda Varman IV (460–480)
- Nandi Varman I (480–500)
- Kumaravisnu II (c. 500–510)
- Buddha Varman (c. 510–520)
- Kumaravisnu III (c. 520–530)
- Simha Varman III (c. 530–537)
Later Pallavas
Simhavishnu (537-570)
Mahendravarman I (571–630)
Narasimhavarman I (Mamalla) (630–668)
Mahendravarman II (668–672)
Paramesvaravarman I (672–700)
Narasimhavarman II (Raja Simha) (700–727)
Paramesvaravarman II (705–710)
Later Pallavas of the Kadava Line
Nandivarman II (Pallavamalla) (732–796) son of Hiranyavarman of Kadavakula[33]
Dantivarman (775–825)
Nandivarman III (825–869)- Nirupathungan (869–882)
Aparajitavarman (882–896)
Genealogy
The genealogy of Pallavas mentioned in the Māmallapuram Praśasti is as follows:[6]
- Vishnu
- Brahma
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Bharadvaja
- Drona
- Ashvatthaman
- Pallava
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Simhavarman I (c. 275)
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Simhavarman IV (436 — c. 460)
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Skandashishya
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Simhavisnu (c. 550-585)
- Mahendravarman I (c. 571-630)
- Maha-malla Narasimhavarman I (630-668)
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Paramesvaravarman I (669-690)
- Rajasimha Narasimhavaram II (690-728)
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Pallavamalla Nandivarman II (731-796)
- Unknown / undecipherable
- Nandivarman III (846-69)
Other relationships
Pallava royal lineages were influential in the old kingdom of Kedah of the Malay Peninsula under Rudravarman I, Champa under Bhadravarman I and the Kingdom of the Funan in Cambodia.[36]
See also
- List of Tamil monarchs
- Kadava dynasty
Notes
^ Ancient Jaffna: Being a Research Into the History of Jaffna from Very Early Times to the Portuguese Period, C. Rasanayagam, p.241, Asian Educational Services 1926
^ The journal of the Numismatic Society of India, Volume 51, p.109
^ Alī Jāvīd and Tabassum Javeed. (2008). World heritage monuments and related edifices in India, p.107 [1]
^ ab Ordhendra Coomar Gangoly. The art of the Pallavas, Volume 2 of Indian Sculpture Series. G. Wittenborn, 1957. p. 2..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Jaiswal, Suvira (2000). Caste: origin, function, and dimensions of change. Manohar Publishers. p. 115. ISBN 9788173043345.
^ abcd Rabe, Michael D (1997). "The Māmallapuram Praśasti: A Panegyric in Figures". Artibus Asiae. 57 (3/4): 189–241. JSTOR 3249929. (Subscription required (help)).
^ abc KR Subramanian. (1989). Buddhist remains in Āndhra and the history of Āndhra between 224 & 610 A.D, p.71
^ abc South Indian History Congress. (February 15–17, 1980). Proceedings of the First Annual Conference. 1. The Congress and The Madurai Kamaraj University Co-op Printing Press.
^ KR Subramanian. (1989). Buddhist remains in Āndhra and the history of Āndhra between 224 & 610 A.D, p.71: The Pallavas were first a Telugu and not a Tamil power. Telugu traditions know a certain Trilochana Pallava as the earliest Telugu King and they are confirmed by later inscriptions. [2]
^ A.Krishnaswami. Topics in South Indian history: from early times upto 1565 A.D. Krishnaswami, 1975. pp. 89–90.
^ Tyagi, Anil Kumar (2016). "Political History of Southern India (500-750AD)". In Roma Chatterjee. Ancient India. New Delhi: Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, Government of India. pp. 118–124. ISBN 978-81-230-1896-6.
^ Rev. H Heras, SJ (1931) Pallava Genealogy: An attempt to unify the Pallava Pedigrees of the Inscriptions, Indian Historical Research Institute
^ KR Subramanian. (1989). Buddhist remains in Āndhra and the history of Āndhra between 224 & 610 A.D, p.106-109
^ Suryanath Kamat (1980). A Concise History of Karnataka: From Pre-historic Times to the Present. Archana Prakashana. pp. 31–33.
^ Sen, Sailendra Nath (1999). Ancient Indian History And Civilization. New Age International. p. 445. ISBN 9788122411980.
^ Marilyn Hirsh (1987) Mahendravarman I Pallava: Artist and Patron of Māmallapuram, Artibus Asiae, Vol. 48, Number 1/2 (1987), pp. 109-130
^ Rajan K. (Jan-Feb 2008). Situating the Beginning of Early Historic Times in Tamil Nadu: Some Issues and Reflections, Social Scientist, Vol. 36, Number 1/2, pp. 40-78
^ Heras, p 38
^ abc Venkayya, V (April 1911). "Velurpalaiyam Plates of Nandivarman III". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland: 521–524. JSTOR 25189883.
^ abc Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, p.92
^ Kulke and Rothermund, pp121–122
^ Nilakanta Sastri, pp412–413
^ Nilakanta Sastri, p139
^ Burton Stein (1980). Peasant state and society in medieval South India. Oxford University Press. pp. 63–64.
^ abc Burton Stein (1980). Peasant state and society in medieval South India. Oxford University Press. p. 70.
^ ab Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, p.91
^ Nilakanta Sastri, A History of South India, p.91–92
^ ab Aiyangar, S. Krishnaswami (2003). "Early History Of The Pallavas". Some Contributions Of South India To Indian Culture. Cosmo Publications (July 15, 2003). ISBN 978-8170200062.
^ Moraes, George M. (1995). The Kadamba Kula: A History of Ancient and Mediaeval Karnataka. Asian Educational Services. p. 6. ISBN 9788120605954.
^ Kulke and Rothermund, p.120
^ abcdefghij Sen, Sailendra (2013). A Textbook of Medieval Indian History. Primus Books. pp. 41–42. ISBN 978-9-38060-734-4.
^ Kulke and Rothermund, p111
^ abc V. Ramamurthy. History of Kongu, Volume 1. International Society for the Investigation of Ancient Civilization, 1986. p. 172.
^ Eugen Hultzsch. South Indian Inscriptions, Volume 12. Manager of Publications, 1986. p. viii.
^ S.Krishnaswami Aiyangar. Some Contributions Of South India To Indian Culture. Early History of the Pallavas
^ Cœdès, George (1968-01-01). The Indianized States of South-East Asia. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 9780824803681.
References
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
Avari, Burjor (2007). India: The Ancient Past. New York: Routledge.
Hermann, Kulke; Rothermund D (2001) [2000]. A History of India. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-32920-5.
Minakshi, Cadambi (1938). Administration and Social Life Under the Pallavas. Madras: University of Madras.
Prasad, Durga (1988). History of the Andhras up to 1565 A.D. Guntur, India: P.G. Publishers.
Raghava Iyengar, R (1949). Perumbanarruppatai, a commentary. Chidambaram, India: Annamalai University Press.
External links
 Media related to Pallava at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pallava at Wikimedia Commons
Middle kingdoms of India | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline and cultural period | Northwestern India (Punjab-Sapta Sindhu) | Indo-Gangetic Plain | Central India | Southern India | ||
| Upper Gangetic Plain (Kuru-Panchala) | Middle Gangetic Plain | Lower Gangetic Plain | ||||
IRON AGE | ||||||
Culture | Late Vedic Period | Late Vedic Period (Brahmin ideology)[a] Painted Grey Ware culture | Late Vedic Period (Kshatriya/Shramanic culture)[b] Northern Black Polished Ware | Pre-history | ||
6th century BC | Gandhara | Kuru-Panchala | Magadha | Adivasi (tribes) | ||
Culture | Persian-Greek influences | "Second Urbanisation" Rise of Shramana movements Jainism - Buddhism - Ājīvika - Yoga | Pre-history | |||
5th century BC | (Persian rule) | Shishunaga dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | |||
4th century BC | (Greek conquests) | Nanda empire | ||||
HISTORICAL AGE | ||||||
Culture | Spread of Buddhism | Pre-history | Sangam period (300 BC – 200 AD) | |||
3rd century BC | Maurya Empire | Early Cholas Early Pandyan Kingdom Satavahana dynasty Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||
Culture | Preclassical Hinduism[c] - "Hindu Synthesis"[d] (ca. 200 BC - 300 AD)[e][f] Epics - Puranas - Ramayana - Mahabharata - Bhagavad Gita - Brahma Sutras - Smarta Tradition Mahayana Buddhism | Sangam period (continued) (300 BC – 200 AD) | ||||
2nd century BC | Indo-Greek Kingdom | Shunga Empire Maha-Meghavahana Dynasty | Early Cholas Early Pandyan Kingdom Satavahana dynasty Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | |||
1st century BC | ||||||
1st century AD | Indo-Scythians | Kuninda Kingdom | ||||
2nd century | Kushan Empire | |||||
3rd century | Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom | Kushan Empire | Western Satraps | Kamarupa kingdom | Kalabhra dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |
Culture | "Golden Age of Hinduism"(ca. AD 320-650)[g] Puranas Co-existence of Hinduism and Buddhism | |||||
4th century | Kidarites | Gupta Empire Varman dynasty | Kalabhra dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Kadamba Dynasty Western Ganga Dynasty | |||
5th century | Hephthalite Empire | Alchon Huns | Kalabhra dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Vishnukundina | |||
6th century | Nezak Huns Kabul Shahi | Maitraka | Adivasi (tribes) | Badami Chalukyas Kalabhra dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | ||
Culture | Late-Classical Hinduism (ca. AD 650-1100)[h] Advaita Vedanta - Tantra Decline of Buddhism in India | |||||
7th century | Indo-Sassanids | Vakataka dynasty Empire of Harsha | Mlechchha dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Pandyan Kingdom(Revival) Pallava | |
8th century | Kabul Shahi | Pala Empire | Pandyan Kingdom Kalachuri | |||
9th century | Gurjara-Pratihara | Rashtrakuta dynasty Pandyan Kingdom Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai | ||||
10th century | Ghaznavids | Pala dynasty Kamboja-Pala dynasty | Kalyani Chalukyas Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai Rashtrakuta | |||
References and sources for table References
Sources
| ||||||