Struve Geodetic Arc
| Struve Geodetic Arc | |
|---|---|
 The northernmost station of the Struve Geodetic Arc is located in Fuglenes, Norway. | |
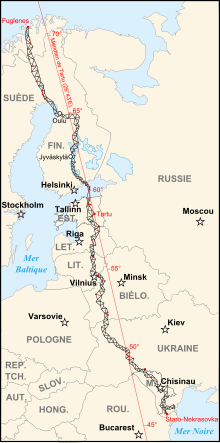 Map of the Struve Geodetic Arc where red points identify the World Heritage Sites. | |
| General information | |
| Type | Ensemble of memorable sites |
| Country | Estonia, Belarus, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Moldova, Russia, Sweden & Ukraine |
| Coordinates | 59°3′28″N 26°20′16″E / 59.05778°N 26.33778°E / 59.05778; 26.33778Coordinates: 59°3′28″N 26°20′16″E / 59.05778°N 26.33778°E / 59.05778; 26.33778 |
| Opened | Geodetic Arc |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect | Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve |
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
| Official name | Struve Geodetic Arc |
| Criteria | ii, iii, vi |
| Reference | 1187 |
| Inscription | 2005 (29th Session) |

Tartu Old Observatory, the first point of the arc.

Point Z that is situated on Hogland, Russia.

The commemorative plaque of the arc in Felshtyn, Ukraine

The Geodetic Point in Rudi, Moldova
The Struve Geodetic Arc is a chain of survey triangulations stretching from Hammerfest in Norway to the Black Sea, through ten countries and over 2,820 km, which yielded the first accurate measurement of a meridian.[1]
The chain was established and used by the German-born Russian scientist Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve in the years 1816 to 1855 to establish the exact size and shape of the earth. At that time, the chain passed merely through two countries: Union of Sweden-Norway and the Russian Empire. The Arc's first point is located in Tartu Observatory in Estonia, where Struve conducted much of his research.[1]
In 2005, the chain was inscribed on the World Heritage List as a memorable ensemble of the chain made up of 34 commemorative plaques or built obelisks out of the original 265 main station points which are marked by drilled holes in rock, iron crosses, cairns, others.[1]
Measurement of the triangulation chain comprises 258 main triangles and 265 geodetic vertices. The northernmost point is located near Hammerfest in Norway and the southernmost point near the Black Sea in Ukraine. This inscription is located in ten countries, the most of any UNESCO World Heritage.[1]
Contents
1 Chain
1.1 Norway
1.2 Sweden
1.3 Finland
1.4 Russia
1.5 Estonia
1.6 Latvia
1.7 Lithuania
1.8 Belarus
1.9 Moldova
1.10 Ukraine
2 Results
2.1 Historical
2.2 Modern
3 See also
4 References
5 External links
Chain
Norway
- Fuglenes in Hammerfest (70°40′12″N 23°39′48″E / 70.67000°N 23.66333°E / 70.67000; 23.66333)[1]
- Raipas in Alta (69°56′19″N 23°21′37″E / 69.93861°N 23.36028°E / 69.93861; 23.36028)[1]
- Luvdiidcohkka in Kautokeino (69°39′52″N 23°36′08″E / 69.66444°N 23.60222°E / 69.66444; 23.60222)[1]
- Baelljasvarri in Kautokeino (69°01′43″N 23°18′19″E / 69.02861°N 23.30528°E / 69.02861; 23.30528)[1]
Sweden
- "Pajtas-vaara" (Tynnyrilaki) in Kiruna
- "Kerrojupukka" (Jupukka) in Pajala
Pullinki in Övertorneå
- "Perra-vaara" (Perävaara) in Haparanda
Finland
- Stuor-Oivi (currently Stuorrahanoaivi) in Enontekiö (68°40′57″N 22°44′45″E / 68.68250°N 22.74583°E / 68.68250; 22.74583)
- Avasaksa (currently Aavasaksa) in Ylitornio (66°23′52″N 23°43′31″E / 66.39778°N 23.72528°E / 66.39778; 23.72528)
- Torneå (currently Alatornion kirkko) in Tornio (65°49′48″N 24°09′26″E / 65.83000°N 24.15722°E / 65.83000; 24.15722)
- Puolakka (currently Oravivuori) in Korpilahti (61°55′36″N 25°32′01″E / 61.92667°N 25.53361°E / 61.92667; 25.53361)
- Porlom II (currently Tornikallio) in Lapinjärvi (60°42′17″N 26°00′12″E / 60.70472°N 26.00333°E / 60.70472; 26.00333)
- Svartvira (currently Mustaviiri) in Pyhtää (60°16′35″N 26°36′12″E / 60.27639°N 26.60333°E / 60.27639; 26.60333)
[2]
Russia
- "Mäki-päälys" (Mäkipäällys (Finland 1917/1920-1940) in Hogland (Suursaari)
- "Hogland, Z" (Gogland, Tochka Z) in Hogland (60°5′9.8″N 26°57′37.5″E / 60.086056°N 26.960417°E / 60.086056; 26.960417)
Estonia
- "Woibifer" (Võivere) in Väike-Maarja Parish (59°03′28″N 26°20′16″E / 59.05778°N 26.33778°E / 59.05778; 26.33778)
- "Katko" (Simuna) in Väike-Maarja Parish (59°02′54″N 26°24′51″E / 59.04833°N 26.41417°E / 59.04833; 26.41417)
- "Dorpat" (Tartu Old Observatory) in Tartu. (58°22′43.64″N 26°43′12.61″E / 58.3787889°N 26.7201694°E / 58.3787889; 26.7201694)
Latvia
- "Sestu-Kalns" (Ziestu) in Ērgļu novads (56°50′24″N 25°38′12″E / 56.84000°N 25.63667°E / 56.84000; 25.63667)
- "Jacobstadt" in Jēkabpils (56°30′05″N 25°51′24″E / 56.50139°N 25.85667°E / 56.50139; 25.85667)
Lithuania
- "Karischki" (Gireišiai) in Panemunėlis (55°54′09″N 25°26′12″E / 55.90250°N 25.43667°E / 55.90250; 25.43667)
- "Meschkanzi" (Meškonys) in Nemenčinė (54°55′51″N 25°19′00″E / 54.93083°N 25.31667°E / 54.93083; 25.31667)
- "Beresnäki" (Paliepiukai) in Nemėžis (54°38′04″N 25°25′45″E / 54.63444°N 25.42917°E / 54.63444; 25.42917)
Belarus
19 topographic points of the Struve Geodetic Arc are located in Belarus.[3]
- "Tupischki" (Tupishki) in Ashmyany district (54°17′30″N 26°2′43″E / 54.29167°N 26.04528°E / 54.29167; 26.04528)
- "Lopati" (Lopaty) in Zelva district (53°33′38″N 24°52′11″E / 53.56056°N 24.86972°E / 53.56056; 24.86972)
- "Ossownitza" (Ossovnitsa) in Ivanovo district (52°17′22″N 25°38′58″E / 52.28944°N 25.64944°E / 52.28944; 25.64944)
- "Tchekutsk" (Chekutsk) in Ivanovo district (52°12′28″N 25°33′23″E / 52.20778°N 25.55639°E / 52.20778; 25.55639)
- "Leskowitschi" (Leskovichi) in Ivanovo district (52°9′39″N 25°34′17″E / 52.16083°N 25.57139°E / 52.16083; 25.57139)
Moldova
- "Rudi" near Rudi village, Soroca district (48°19′08″N 27°52′36″E / 48.31889°N 27.87667°E / 48.31889; 27.87667)
Ukraine
- Katerynivka in Antonivka, Khmelnytsky Oblast (49°33′57″N 26°45′22″E / 49.56583°N 26.75611°E / 49.56583; 26.75611 )
- Felshtyn in Hvardiiske, Khmelnytsky Oblast (49°19′48″N 26°40′55″E / 49.33000°N 26.68194°E / 49.33000; 26.68194 )
- Baranivka in Baranivka, Khmelnytsky Oblast (49°08′55″N 26°59′30″E / 49.14861°N 26.99167°E / 49.14861; 26.99167 )
- Staro-Nekrasivka (Stara Nekrasivka) in Nekrasivka, Odesa Oblast (45°19′54″N 28°55′41″E / 45.33167°N 28.92806°E / 45.33167; 28.92806 )
Results
Historical
At publication in 1858, the flattening of the earth was estimated at one part in 294.26. The earth's equatorial radius was estimated at 6,378,360.7 metres.[1]
In 2005 the work was repeated using satellite navigation. The new flattening estimate was one part in 298.257 222 101 and the equatorial radius was 6,378,136.8 metres.[1]
An earlier survey, in 1740, had given flattening at one part in 178 and an equatorial radius of 6,396,800 metres.[1]
Modern
Northernmost point: Hammerfest (Fuglenes): 70° 40′ 11.23″ N[1]
Southernmost point: Ismail (Staro-Nekrassowka): 45° 20′ 02.94″ N[1]
Difference in Geodetic Latitude: 25° 20′ 08.29″[1]
Distance in kilometres: 2,821.853 ± 0.012[1]
See also
- Meridian arc
- Paris meridian
References
^ abcdefghijklmno Norwegian Directorate for Cultural Heritage,Dronningensg 13, P.O.Box 8196, Dep. 0034, Oslo, Norway (2005), Norwegian Points on The Struve Geodetic Arc (pamphlet)
^ "Mapscroll". Mapscroll.fi. Archived from the original on 18 February 2012. Retrieved 8 November 2012..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Landmarks, historic and cultural, and natural sites of the Republic of Belarus on the UNESCO World Heritage List". Land of Ancestors. National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Retrieved 12 October 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Struve Geodetic Arc. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Struve Geodetic Arc. |
- Listing on UNESCO website
- A UNESCO article about the chain
- FIG – Proposal to UNESCO for the Struve Geodetic Arc to become a World Heritage Monument
- J.R. Smith. The Struve Geodetic Arc
- Latvia Struve arc webpage
- Estonian souvenir sheet and first day cover dedicated to Struve and Struve Geodetic Arc (2011)





