Low back pain
| Low back pain | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Lower back pain, lumbago |
 | |
| Low back pain is a common and costly complaint. | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Orthopedics, rheumatology, rehabilitation medicine |
| Usual onset | 20 to 40 years of age[1] |
| Duration | ~65% get better in 6 weeks[2] |
| Types | Acute (less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), chronic (more than 12 weeks)[3] |
| Causes | Usually non-specific, occasionally significant underlying cause[1][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Medical imaging (if red flags )[5] |
| Treatment | Continued normal activity, non-medication based treatments, NSAIDs[2][6] |
| Frequency | ~25% in any given month[7][8] |
Low back pain (LBP) is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back.[4]Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling.[4] Low back pain may be classified by duration as acute (pain lasting less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks).[3] The condition may be further classified by the underlying cause as either mechanical, non-mechanical, or referred pain.[5] The symptoms of low back pain usually improve within a few weeks from the time they start, with 40–90% of people completely better by six weeks.[2]
In most episodes of low back pain, a specific underlying cause is not identified or even looked for, with the pain believed to be due to mechanical problems such as muscle or joint strain.[1][4] If the pain does not go away with conservative treatment or if it is accompanied by "red flags" such as unexplained weight loss, fever, or significant problems with feeling or movement, further testing may be needed to look for a serious underlying problem.[5] In most cases, imaging tools such as X-ray computed tomography are not useful and carry their own risks.[9][10] Despite this, the use of imaging in low back pain has increased.[11] Some low back pain is caused by damaged intervertebral discs, and the straight leg raise test is useful to identify this cause.[5] In those with chronic pain, the pain processing system may malfunction, causing large amounts of pain in response to non-serious events.[12]
Initial management with non–medication based treatments is recommended.[6]NSAIDs are recommended if these are not sufficiently effective.[6] Normal activity should be continued as much as the pain allows.[2] Medications are recommended for the duration that they are helpful.[13] A number of other options are available for those who do not improve with usual treatment. Opioids may be useful if simple pain medications are not enough, but they are not generally recommended due to side effects.[4][13] Surgery may be beneficial for those with disc-related chronic pain and disability or spinal stenosis.[14][15] No clear benefit has been found for other cases of non-specific low back pain.[14] Low back pain often affects mood, which may be improved by counseling or antidepressants.[13][16] Additionally, there are many alternative medicine therapies, including the Alexander technique and herbal remedies, but there is not enough evidence to recommend them confidently.[17] The evidence for chiropractic care[18] and spinal manipulation is mixed.[17][19][20][21]
Approximately 9–12% of people (632 million) have LBP at any given point in time, and nearly 25% report having it at some point over any one-month period.[7][8] About 40% of people have LBP at some point in their lives,[7] with estimates as high as 80% among people in the developed world.[22] Difficulty most often begins between 20 and 40 years of age.[1] Men and women are equally affected.[4] Low back pain is more common among people aged between 40 and 80 years, with the overall number of individuals affected expected to increase as the population ages.[7]
 Play media
Play mediaVideo explanation
.mw-parser-output .toclimit-2 .toclevel-1 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-3 .toclevel-2 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-4 .toclevel-3 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-5 .toclevel-4 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-6 .toclevel-5 ul,.mw-parser-output .toclimit-7 .toclevel-6 ul{display:none}
Contents
1 Signs and symptoms
2 Causes
3 Pathophysiology
3.1 Back structures
3.2 Pain sensation
4 Diagnosis
4.1 Classification
4.2 Red flags
4.3 Tests
5 Prevention
6 Management
6.1 Physical management
6.2 Medications
6.3 Surgery
6.4 Alternative medicine
7 Prognosis
8 Epidemiology
9 History
10 Society and culture
11 Research
12 References
13 External links
Signs and symptoms
In the common presentation of acute low back pain, pain develops after movements that involve lifting, twisting, or forward-bending. The symptoms may start soon after the movements or upon waking up the following morning. The description of the symptoms may range from tenderness at a particular point to diffuse pain. It may or may not worsen with certain movements, such as raising a leg, or positions, such as sitting or standing. Pain radiating down the legs (known as sciatica) may be present. The first experience of acute low back pain is typically between the ages of 20 and 40. This is often a person's first reason to see a medical professional as an adult.[1] Recurrent episodes occur in more than half of people[23] with the repeated episodes being generally more painful than the first.[1]
Other problems may occur along with low back pain. Chronic low back pain is associated with sleep problems, including a greater amount of time needed to fall asleep, disturbances during sleep, a shorter duration of sleep, and less satisfaction with sleep.[24] In addition, a majority of those with chronic low back pain show symptoms of depression[13] or anxiety.[17]
Causes

A herniated disc as seen on MRI, one possible cause of low back pain
Low back pain is not a specific disease but rather a complaint that may be caused by a large number of underlying problems of varying levels of seriousness.[25] The majority of LBP does not have a clear cause[1] but is believed to be the result of non-serious muscle or skeletal issues such as sprains or strains.[26] Obesity, smoking, weight gain during pregnancy, stress, poor physical condition, poor posture and poor sleeping position may also contribute to low back pain.[26] A full list of possible causes includes many less common conditions.[5] Physical causes may include osteoarthritis, degeneration of the discs between the vertebrae or a spinal disc herniation, broken vertebra(e) (such as from osteoporosis) or, rarely, an infection or tumor of the spine.[27]
Women may have acute low back pain from medical conditions affecting the female reproductive system, including endometriosis, ovarian cysts, ovarian cancer, or uterine fibroids.[28] Nearly half of all pregnant women report pain in the lower back or sacral area during pregnancy, due to changes in their posture and center of gravity causing muscle and ligament strain.[29]
Low back pain can be broadly classified into four main categories:
- Musculoskeletal – mechanical (including muscle strain, muscle spasm, or osteoarthritis); herniated nucleus pulposus, herniated disk; spinal stenosis; or compression fracture
- Inflammatory – HLA-B27 associated arthritis including ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease
- Malignancy – bone metastasis from lung, breast, prostate, thyroid, among others
- Infectious – osteomyelitis; abscess
Pathophysiology
Back structures
@media all and (max-width:720px){.mw-parser-output .tmulti>.thumbinner{width:100%!important;max-width:none!important}.mw-parser-output .tmulti .tsingle{float:none!important;max-width:none!important;width:100%!important;text-align:center}}


The lumbar (or lower back) region is made up of five vertebrae (L1–L5), sometimes including the sacrum. In between these vertebrae are fibrocartilaginous discs, which act as cushions, preventing the vertebrae from rubbing together while at the same time protecting the spinal cord. Nerves come from and go to the spinal cord through specific openings between the vertebrae, providing the skin with sensations and messages to muscles. Stability of the spine is provided by the ligaments and muscles of the back and abdomen. Small joints called facet joints limit and direct the motion of the spine.[30]
The multifidus muscles run up and down along the back of the spine, and are important for keeping the spine straight and stable during many common movements such as sitting, walking and lifting.[12] A problem with these muscles is often found in someone with chronic low back pain, because the back pain causes the person to use the back muscles improperly in trying to avoid the pain.[31] The problem with the multifidus muscles continues even after the pain goes away, and is probably an important reason why the pain comes back.[31] Teaching people with chronic low back pain how to use these muscles is recommended as part of a recovery program.[31]
An intervertebral disc has a gelatinous core surrounded by a fibrous ring.[32] When in its normal, uninjured state, most of the disc is not served by either the circulatory or nervous systems – blood and nerves only run to the outside of the disc.[32] Specialized cells that can survive without direct blood supply are in the inside of the disc.[32] Over time, the discs lose flexibility and the ability to absorb physical forces.[25] This decreased ability to handle physical forces increases stresses on other parts of the spine, causing the ligaments of the spine to thicken and bony growths to develop on the vertebrae.[25] As a result, there is less space through which the spinal cord and nerve roots may pass.[25] When a disc degenerates as a result of injury or disease, the makeup of a disc changes: blood vessels and nerves may grow into its interior and/or herniated disc material can push directly on a nerve root.[32] Any of these changes may result in back pain.[32]
Pain sensation
Pain is generally an unpleasant feeling in response to an event that either damages or can potentially damage the body's tissues. There are four main steps in the process of feeling pain: transduction, transmission, perception, and modulation.[12] The nerve cells that detect pain have cell bodies located in the dorsal root ganglia and fibers that transmit these signals to the spinal cord.[33] The process of pain sensation starts when the pain-causing event triggers the endings of appropriate sensory nerve cells. This type of cell converts the event into an electrical signal by transduction. Several different types of nerve fibers carry out the transmission of the electrical signal from the transducing cell to the posterior horn of spinal cord, from there to the brain stem, and then from the brain stem to the various parts of the brain such as the thalamus and the limbic system. In the brain, the pain signals are processed and given context in the process of pain perception. Through modulation, the brain can modify the sending of further nerve impulses by decreasing or increasing the release of neurotransmitters.[12]
Parts of the pain sensation and processing system may not function properly; creating the feeling of pain when no outside cause exists, signaling too much pain from a particular cause, or signaling pain from a normally non-painful event. Additionally, the pain modulation mechanisms may not function properly. These phenomena are involved in chronic pain.[12]
Diagnosis
As the structure of the back is complex and the reporting of pain is subjective and affected by social factors, the diagnosis of low back pain is not straightforward.[5] While most low back pain is caused by muscle and joint problems, this cause must be separated from neurological problems, spinal tumors, fracture of the spine, and infections, among others.[3][1]
Classification
There are a number of ways to classify low back pain with no consensus that any one method is best.[5] There are three general types of low back pain by cause: mechanical back pain (including nonspecific musculoskeletal strains, herniated discs, compressed nerve roots, degenerative discs or joint disease, and broken vertebra), non-mechanical back pain (tumors, inflammatory conditions such as spondyloarthritis, and infections), and referred pain from internal organs (gallbladder disease, kidney stones, kidney infections, and aortic aneurysm, among others).[5] Mechanical or musculoskeletal problems underlie most cases (around 90% or more),[5][34] and of those, most (around 75%) do not have a specific cause identified, but are thought to be due to muscle strain or injury to ligaments.[5][34] Rarely, complaints of low back pain result from systemic or psychological problems, such as fibromyalgia and somatoform disorders.[34]
Low back pain may be classified based on the signs and symptoms. Diffuse pain that does not change in response to particular movements, and is localized to the lower back without radiating beyond the buttocks, is classified as nonspecific, the most common classification.[5] Pain that radiates down the leg below the knee, is located on one side (in the case of disc herniation), or is on both sides (in spinal stenosis), and changes in severity in response to certain positions or maneuvers is radicular, making up 7% of cases.[5] Pain that is accompanied by red flags such as trauma, fever, a history of cancer or significant muscle weakness may indicate a more serious underlying problem and is classified as needing urgent or specialized attention.[5]
The symptoms can also be classified by duration as acute, sub-chronic (also known as sub-acute), or chronic. The specific duration required to meet each of these is not universally agreed upon, but generally pain lasting less than six weeks is classified as acute, pain lasting six to twelve weeks is sub-chronic, and more than twelve weeks is chronic.[3] Management and prognosis may change based on the duration of symptoms.
Red flags
| Red flag[35] | Possible cause[1] |
|---|---|
| Previous history of cancer | Cancer |
Unintentional weight loss | |
| Loss of bladder or bowel control | Cauda equina syndrome |
| Significant motor weakness or sensory problems | |
| Loss of sensation in the buttocks (saddle anesthesia) | |
| Significant trauma related to age | Fracture |
| Chronic corticosteroid use | |
Osteoporosis | |
| Severe pain after lumbar surgery in past year | Infection |
| Fever | |
| Urinary tract infection | |
Immunosuppression | |
Intravenous drug use |
The presence of certain signs, termed red flags, indicate the need for further testing to look for more serious underlying problems, which may require immediate or specific treatment.[5][36] The presence of a red flag does not mean that there is a significant problem. It is only suggestive,[37][38] and most people with red flags have no serious underlying problem.[3][1] If no red flags are present, performing diagnostic imaging or laboratory testing in the first four weeks after the start of the symptoms has not been shown to be useful.[5]
The usefulness of many red flags are poorly supported by evidence.[39][40] The most useful for detecting a fracture are: older age, corticosteroid use, and significant trauma especially if it results in skin markings.[39] The best determinant of the presence of cancer is a history of the same.[39]
With other causes ruled out, people with non-specific low back pain are typically treated symptomatically, without exact determination of the cause.[3][1] Efforts to uncover factors that might complicate the diagnosis, such as depression, substance abuse, or an agenda concerning insurance payments may be helpful.[5]
Tests

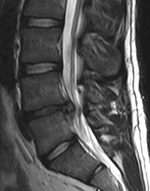
Imaging is indicated when there are red flags, ongoing neurological symptoms that do not resolve, or ongoing or worsening pain.[5] In particular, early use of imaging (either MRI or CT) is recommended for suspected cancer, infection, or cauda equina syndrome.[5] MRI is slightly better than CT for identifying disc disease; the two technologies are equally useful for diagnosing spinal stenosis.[5] Only a few physical diagnostic tests are helpful.[5] The straight leg raise test is almost always positive in those with disc herniation.[5]Lumbar provocative discography may be useful to identify a specific disc causing pain in those with chronic high levels of low back pain.[41] Similarly, therapeutic procedures such as nerve blocks can be used to determine a specific source of pain.[5] Some evidence supports the use of facet joint injections, transforminal epidural injections and sacroilliac injections as diagnostic tests.[5] Most other physical tests, such as evaluating for scoliosis, muscle weakness or wasting, and impaired reflexes, are of little use.[5]
Complaints of low back pain are one of the most common reasons people visit doctors.[9][42] For pain that has lasted only a few weeks, the pain is likely to subside on its own.[43] Thus, if a person's medical history and physical examination do not suggest a specific disease as the cause, medical societies advise against imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.[42] Individuals may want such tests but, unless red flags are present,[10][44] they are unnecessary health care.[9][43] Routine imaging increases costs, is associated with higher rates of surgery with no overall benefit,[45][46] and the radiation used may be harmful to one's health.[45] Fewer than 1% of imaging tests identify the cause of the problem.[9] Imaging may also detect harmless abnormalities, encouraging people to request further unnecessary testing or to worry.[9] Even so, MRI scans of the lumbar region increased by more than 300% among United States Medicare beneficiaries from 1994 to 2006.[11]
Prevention
Exercise appears to be useful for preventing low back pain.[47] Exercise is also probably effective in preventing recurrences in those with pain that has lasted more than six weeks.[1][48] Medium-firm mattresses are more beneficial for chronic pain than firm mattresses.[49] There is little to no evidence that back belts are any more helpful in preventing low back pain than education about proper lifting techniques.[47][50]Shoe insoles do not help prevent low back pain.[47][51]
Management
Management of low back pain depends on which of the three general categories is the cause: mechanical problems, non-mechanical problems, or referred pain.[52] For acute pain that is causing only mild to moderate problems, the goals are to restore normal function, return the individual to work, and minimize pain. The condition is normally not serious, resolves without much being done, and recovery is helped by attempting to return to normal activities as soon as possible within the limits of pain.[3] Providing individuals with coping skills through reassurance of these facts is useful in speeding recovery.[1] For those with sub-chronic or chronic low back pain, multidisciplinary treatment programs may help.[53] Initial management with non–medication based treatments is recommended, with NSAIDs used if these are not sufficiently effective.[6]
Physical management
Increasing general physical activity has been recommended, but no clear relationship to pain or disability has been found when used for the treatment of an acute episode of pain.[48][54] For acute pain, low- to moderate-quality evidence supports walking.[55] Treatment according to McKenzie method is somewhat effective for recurrent acute low back pain, but its benefit in the short term does not appear significant.[1] There is tentative evidence to support the use of heat therapy for acute and sub-chronic low back pain[56] but little evidence for the use of either heat or cold therapy in chronic pain.[57] Weak evidence suggests that back belts might decrease the number of missed workdays, but there is nothing to suggest that they will help with the pain.[50] Ultrasound and shock wave therapies do not appear effective and therefore are not recommended.[58][59] Lumbar traction lacks effectiveness as an intervention for radicular low back pain.[60]
Exercise therapy is effective in decreasing pain and improving function for those with chronic low back pain.[50] It also appears to reduce recurrence rates for as long as six months after the completion of program[61] and improves long-term function.[57] There is no evidence that one particular type of exercise therapy is more effective than another.[62] The Alexander technique appears useful for chronic back pain,[63] and there is tentative evidence to support the use of yoga.[64]Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) has not been found to be effective in chronic low back pain.[65] Evidence for the use of shoe insoles as a treatment is inconclusive.[51]Peripheral nerve stimulation, a minimally-invasive procedure, may be useful in cases of chronic low back pain that do not respond to other measures, although the evidence supporting it is not conclusive, and it is not effective for pain that radiates into the leg.[66]
Medications
The management of low back pain often includes medications for the duration that they are beneficial. With the first episode of low back pain the hope is a complete cure; however, if the problem becomes chronic, the goals may change to pain management and the recovery of as much function as possible. As pain medications are only somewhat effective, expectations regarding their benefit may differ from reality, and this can lead to decreased satisfaction.[13]
The medication typically recommended first are NSAIDs (though not aspirin) or skeletal muscle relaxants and these are enough for most people.[13][6] Benefits with NSAIDs; however, is often small.[67] High-quality reviews have found acetaminophen (paracetamol) to be no more effective than placebo at improving pain, quality of life, or function.[68][69] NSAIDs are more effective for acute episodes than acetaminophen; however, they carry a greater risk of side effects including: kidney failure, stomach ulcers and possibly heart problems. Thus, NSAIDs are a second choice to acetaminophen, recommended only when the pain is not handled by the latter. NSAIDs are available in several different classes; there is no evidence to support the use of COX-2 inhibitors over any other class of NSAIDs with respect to benefits.[70][13][71] With respect to safety naproxen may be best.[72]Muscle relaxants may be beneficial.[13]
If the pain is still not managed adequately, short term use of opioids such as morphine may be useful.[73][13] These medications carry a risk of addiction, may have negative interactions with other drugs, and have a greater risk of side effects, including dizziness, nausea, and constipation.[13] The effect of long term use of opioids for lower back pain is unknown.[74] Opioid treatment for chronic low back pain increases the risk for lifetime illicit drug use.[75] Specialist groups advise against general long-term use of opioids for chronic low back pain.[13][76] As of 2016, the CDC has released a guideline for prescribed opioid use in the management of chronic pain.[77] It states that opioid use is not the preferred treatment when managing chronic pain due to the excessive risks involved. If prescribed, a person and their clinician should have a realistic plan to discontinue its use in the event that the risks outweigh the benefit.[77]
For older people with chronic pain, opioids may be used in those for whom NSAIDs present too great a risk, including those with diabetes, stomach or heart problems. They may also be useful for a select group of people with neuropathic pain.[78]
Antidepressants may be effective for treating chronic pain associated with symptoms of depression, but they have a risk of side effects.[13] Although the antiseizure drugs gabapentin, pregabalin, and topiramate are sometimes used for chronic low back pain evidence does not support a benefit.[79] Systemic oral steroids have not been shown to be useful in low back pain.[1][13] Facet joint injections and steroid injections into the discs have not been found to be effective in those with persistent, non-radiating pain; however, they may be considered for those with persistent sciatic pain.[80]Epidural corticosteroid injections provide a slight and questionable short-term improvement in those with sciatica but are of no long term benefit.[81] There are also concerns of potential side effects.[82]
Surgery
Surgery may be useful in those with a herniated disc that is causing significant pain radiating into the leg, significant leg weakness, bladder problems, or loss of bowel control.[14] It may also be useful in those with spinal stenosis.[15] In the absence of these issues, there is no clear evidence of a benefit from surgery.[14]
Discectomy (the partial removal of a disc that is causing leg pain) can provide pain relief sooner than nonsurgical treatments.[14] Discectomy has better outcomes at one year but not at four to ten years.[14] The less invasive microdiscectomy has not been shown to result in a different outcome than regular discectomy.[14] For most other conditions, there is not enough evidence to provide recommendations for surgical options.[14] The long-term effect surgery has on degenerative disc disease is not clear.[14] Less invasive surgical options have improved recovery times, but evidence regarding effectiveness is insufficient.[14]
For those with pain localized to the lower back due to disc degeneration, fair evidence supports spinal fusion as equal to intensive physical therapy and slightly better than low-intensity nonsurgical measures.[15] Fusion may be considered for those with low back pain from acquired displaced vertebra that does not improve with conservative treatment,[14] although only a few of those who have spinal fusion experience good results.[15] There are a number of different surgical procedures to achieve fusion, with no clear evidence of one being better than the others.[83] Adding spinal implant devices during fusion increases the risks but provides no added improvement in pain or function.[11]
Alternative medicine
It is unclear if among those with non-chronic back pain alternative treatments are useful.[84] For chiropractic care or spinal manipulation therapy (SMT) it is unclear if it improves outcomes more or less than other treatments.[18] Some reviews find that SMT results in equal or better improvements in pain and function when compared with other commonly used interventions for short, intermediate, and long-term follow-up;[19][20][85] other reviews find it to be no more effective in reducing pain than either inert interventions, sham manipulation, or other treatments, and conclude that adding SMT to other treatments does improve outcomes.[17][21] National guidelines reach different conclusions, with some not recommending spinal manipulation, some describing manipulation as optional, and others recommending a short course for those who do not improve with other treatments.[3] A 2017 review recommended spinal manipulation based on low quality evidence.[6]Manipulation under anaesthesia, or medically assisted manipulation, has not enough evidence to make any confident recommendation.[86]
Acupuncture is no better than placebo, usual care, or sham acupuncture for nonspecific acute pain or sub-chronic pain.[87] For those with chronic pain, it improves pain a little more than no treatment and about the same as medications, but it does not help with disability.[87] This pain benefit is only present right after treatment and not at follow-up.[87] Acupuncture may be a reasonable method to try for those with chronic pain that does not respond to other treatments like conservative care and medications.[1][88]
Massage therapy does not appear to provide much benefit for acute low back pain.[1] A 2015 Cochrane review found that for acute low back pain massage therapy was better than no treatment for pain only in the short-term.[89] There was no effect for improving function.[89] For chronic low back pain massage therapy was no better than no treatment for both pain and function, though only in the short-term.[89] The overall quality of the evidence was low and the authors conclude that massage therapy is generally not an effective treatment for low back pain.[89]
Prolotherapy – the practice of injecting solutions into joints (or other areas) to cause inflammation and thereby stimulate the body's healing response – has not been found to be effective by itself, although it may be helpful when added to another therapy.[17]
Herbal medicines, as a whole, are poorly supported by evidence.[90] The herbal treatments Devil's claw and white willow may reduce the number of individuals reporting high levels of pain; however, for those taking pain relievers, this difference is not significant.[17]Capsicum, in the form of either a gel or a plaster cast, has been found to reduce pain and increase function.[17]
Behavioral therapy may be useful for chronic pain.[16] There are several types available, including operant conditioning, which uses reinforcement to reduce undesirable behaviors and increase desirable behaviors; cognitive behavioral therapy, which helps people identify and correct negative thinking and behavior; and respondent conditioning, which can modify an individual's physiological response to pain.[17] The benefit however is small.[91] Medical providers may develop an integrated program of behavioral therapies.[17] The evidence is inconclusive as to whether mindfulness-based stress reduction reduces chronic back pain intensity or associated disability, although it suggests that it may be useful in improving the acceptance of existing pain.[92][93]
Tentative evidence supports neuroreflexotherapy (NRT), in which small pieces of metal are placed just under the skin of the ear and back, for non-specific low back pain.[94][95]
Prognosis
Overall, the outcome for acute low back pain is positive. Pain and disability usually improve a great deal in the first six weeks, with complete recovery reported by 40 to 90%.[2] In those who still have symptoms after six weeks, improvement is generally slower with only small gains up to one year. At one year, pain and disability levels are low to minimal in most people. Distress, previous low back pain, and job satisfaction are predictors of long-term outcome after an episode of acute pain.[2] Certain psychological problems such as depression, or unhappiness due to loss of employment may prolong the episode of low back pain.[13] Following a first episode of back pain, recurrences occur in more than half of people.[23]
For persistent low back pain, the short-term outcome is also positive, with improvement in the first six weeks but very little improvement after that. At one year, those with chronic low back pain usually continue to have moderate pain and disability.[2] People at higher risk of long-term disability include those with poor coping skills or with fear of activity (2.5 times more likely to have poor outcomes at one year),[96] those with a poor ability to cope with pain, functional impairments, poor general health, or a significant psychiatric or psychological component to the pain (Waddell's signs).[96]
Epidemiology
Low back pain that lasts at least one day and limits activity is a common complaint.[7] Globally, about 40% of people have LBP at some point in their lives,[7] with estimates as high as 80% of people in the developed world.[22] Approximately 9 to 12% of people (632 million) have LBP at any given point in time, and nearly one quarter (23.2%) report having it at some point over any one-month period.[7][8] Difficulty most often begins between 20 and 40 years of age.[1] Low back pain is more common among people aged 40–80 years, with the overall number of individuals affected expected to increase as the population ages.[7]
It is not clear whether men or women have higher rates of low back pain.[7][8] A 2012 review reported a rate of 9.6% among males and 8.7% among females.[8] Another 2012 review found a higher rate in females than males, which the reviewers felt was possibly due to greater rates of pains due to osteoporosis, menstruation, and pregnancy among women, or possibly because women were more willing to report pain than men.[7] An estimated 70% of women experience back pain during pregnancy with the rate being higher the further along in pregnancy.[97] Current smokers – and especially those who are adolescents – are more likely to have low back pain than former smokers, and former smokers are more likely to have low back pain than those who have never smoked.[98]
History

Harvey Williams Cushing, 1920s
Low back pain has been with humans since at least the Bronze Age. The oldest known surgical treatise – the Edwin Smith Papyrus, dating to about 1500 BCE – describes a diagnostic test and treatment for a vertebral sprain. Hippocrates (c. 460 BCE – c. 370 BCE) was the first to use a term for sciatic pain and low back pain; Galen (active mid to late second century CE) described the concept in some detail. Physicians through the end of the first millennium did not attempt back surgery and recommended watchful waiting. Through the Medieval period, folk medicine practitioners provided treatments for back pain based on the belief that it was caused by spirits.[99]
At the start of the 20th century, physicians thought low back pain was caused by inflammation of or damage to the nerves,[99] with neuralgia and neuritis frequently mentioned by them in the medical literature of the time.[100] The popularity of such proposed causes decreased during the 20th century.[100] In the early 20th century, American neurosurgeon Harvey Williams Cushing increased the acceptance of surgical treatments for low back pain.[14] In the 1920s and 1930s, new theories of the cause arose, with physicians proposing a combination of nervous system and psychological disorders such as nerve weakness (neurasthenia) and female hysteria.[99] Muscular rheumatism (now called fibromyalgia) was also cited with increasing frequency.[100]
Emerging technologies such as X-rays gave physicians new diagnostic tools, revealing the intervertebral disc as a source for back pain in some cases. In 1938, orthopedic surgeon Joseph S. Barr reported on cases of disc-related sciatica improved or cured with back surgery.[100] As a result of this work, in the 1940s, the vertebral disc model of low back pain took over,[99] dominating the literature through the 1980s, aiding further by the rise of new imaging technologies such as CT and MRI.[100] The discussion subsided as research showed disc problems to be a relatively uncommon cause of the pain. Since then, physicians have come to realize that it is unlikely that a specific cause for low back pain can be identified in many cases and question the need to find one at all as most of the time symptoms resolve within 6 to 12 weeks regardless of treatment.[99]
Society and culture
Low back pain results in large economic costs. In the United States, it is the most common type of pain in adults, responsible for a large number of missed work days, and is the most common musculoskeletal complaint seen in the emergency department.[25] In 1998, it was estimated to be responsible for $90 billion in annual health care costs, with 5% of individuals incurring most (75%) of the costs.[25] Between 1990 and 2001 there was a more than twofold increase in spinal fusion surgeries in the US, despite the fact that there were no changes to the indications for surgery or new evidence of greater usefulness.[11] Further costs occur in the form of lost income and productivity, with low back pain responsible for 40% of all missed work days in the United States.[101] Low back pain causes disability in a larger percentage of the workforce in Canada, Great Britain, the Netherlands and Sweden than in the US or Germany.[101]
Workers who experience acute low back pain as a result of a work injury may be asked by their employers to have x-rays.[102] As in other cases, testing is not indicated unless red flags are present.[102] An employer's concern about legal liability is not a medical indication and should not be used to justify medical testing when it is not indicated.[102] There should be no legal reason for encouraging people to have tests which a health care provider determines are not indicated.[102]
Research
Total disc replacement is an experimental option,[32] but no significant evidence supports its use over lumbar fusion.[14] Researchers are investigating the possibility of growing new intervertebral structures through the use of injected human growth factors, implanted substances, cell therapy, and tissue engineering.[32]
References
^ abcdefghijklmnopqr Casazza, BA (15 February 2012). "Diagnosis and treatment of acute low back pain". American Family Physician. 85 (4): 343–50. PMID 22335313..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abcdefg Menezes Costa Lda, C; Maher, CG; Hancock, MJ; McAuley, JH; Herbert, RD; Costa, LO (7 August 2012). "The prognosis of acute and persistent low-back pain: a meta-analysis". CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association Journal. 184 (11): E613–24. doi:10.1503/cmaj.111271. PMC 3414626. PMID 22586331.
^ abcdefgh Koes BW, van Tulder M, Lin CW, Macedo LG, McAuley J, Maher C (December 2010). "An updated overview of clinical guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care". European Spine Journal. 19 (12): 2075–94. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1502-y. PMC 2997201. PMID 20602122.
^ abcdef "Low Back Pain Fact Sheet". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 3 November 2015. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2016.
^ abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwx Manusov EG (September 2012). "Evaluation and diagnosis of low back pain". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 471–9. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.003. PMID 22958556.
^ abcdef Qaseem, A; Wilt, TJ; McLean, RM; Forciea, MA; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of, Physicians. (4 April 2017). "Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 166 (7): 514–530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367. PMID 28192789.
^ abcdefghij Hoy D, Bain C, Williams G, et al. (June 2012). "A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain". Arthritis Rheum. 64 (6): 2028–37. doi:10.1002/art.34347. PMID 22231424.
^ abcde Vos, T (15 December 2012). "Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010". Lancet. 380 (9859): 2163–96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. PMID 23245607.
^ abcde "Use of imaging studies for low back pain: percentage of members with a primary diagnosis of low back pain who did not have an imaging study (plain x-ray, MRI, CT scan) within 28 days of the diagnosis". —. 2013. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2013.
^ ab Chou, R; Fu, R; Carrino, JA; Deyo, RA (7 February 2009). "Imaging strategies for low-back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis". Lancet. 373 (9662): 463–72. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60172-0. PMID 19200918.
^ abcd Deyo, RA; Mirza, SK; Turner, JA; Martin, BI (2009). "Overtreating Chronic Back Pain: Time to Back Off?". Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine : JABFM. 22 (1): 62–8. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2009.01.080102. PMC 2729142. PMID 19124635.
^ abcde Salzberg L (September 2012). "The physiology of low back pain". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 487–98. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.014. PMID 22958558.
^ abcdefghijklmn Miller SM (September 2012). "Low back pain: pharmacologic management". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 499–510. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.005. PMC 494876. PMID 22958559.
^ abcdefghijklm Manusov, EG (September 2012). "Surgical treatment of low back pain". Primary Care. 39 (3): 525–31. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.010. PMID 22958562.
^ abcd Chou R, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Resnick DK, Shaffer WO, Loeser JD (May 2009). "Surgery for low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society Clinical Practice Guideline". Spine. 34 (10): 1094–109. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a105fc. PMID 19363455.
^ ab Henschke N, Ostelo RW, van Tulder MW, et al. (2010). "Behavioural treatment for chronic low-back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (7): CD002014. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD002014.pub3. PMID 20614428.
^ abcdefghi Marlowe D (September 2012). "Complementary and alternative medicine treatments for low back pain". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 533–46. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.008. PMID 22958563.
^ ab Walker, BF; French, SD; Grant, W; Green, S (1 February 2011). "A Cochrane review of combined chiropractic interventions for low-back pain". Spine. 36 (3): 230–42. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318202ac73. PMID 21248591.
^ ab Dagenais, S; Gay, RE; Tricco, AC; Freeman, MD; Mayer, JM (2010). "NASS Contemporary Concepts in Spine Care: spinal manipulation therapy for acute low back pain". The Spine Journal. 10 (10): 918–40. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2010.07.389. PMID 20869008.
^ ab Rubinstein SM, van Middelkoop M, Assendelft WJ, de Boer MR, van Tulder MW (2011). Rubinstein SM, ed. "Spinal manipulative therapy for chronic low-back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD008112. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008112.pub2. PMID 21328304.
^ ab Rubinstein SM, Terwee CB, Assendelft WJ, de Boer MR, van Tulder MW (12 September 2012). "Spinal manipulative therapy for acute low-back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 9 (9): CD008880. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008880.pub2. hdl:1871/48563. PMC 2716152. PMID 22972127.
^ ab Vinod Malhotra; Yao, Fun-Sun F.; Fontes, Manuel da Costa (2011). Yao and Artusio's Anesthesiology: Problem-Oriented Patient Management. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. Chapter 49. ISBN 978-1-4511-0265-9. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
^ ab Stanton, TR; Latimer, J; Maher, CG; Hancock, MJ (April 2010). "How do we define the condition 'recurrent low back pain'? A systematic review". European Spine Journal. 19 (4): 533–9. doi:10.1007/s00586-009-1214-3. PMC 2899839. PMID 19921522.
^ Kelly GA, Blake C, Power CK, O'keeffe D, Fullen BM (February 2011). "The association between chronic low back pain and sleep: a systematic review". Clin J Pain. 27 (2): 169–81. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e3181f3bdd5. PMID 20842008.
^ abcdef Borczuk, Pierre (July 2013). "An Evidence-Based Approach to the Evaluation and Treatment of Low Back Pin in the Emergency Department". Emergency Medicine Practice. 15 (7). Archived from the original on 14 August 2013.
^ ab "Low Back Pain Fact Sheet". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. National Institute of Health. Archived from the original on 19 July 2013. Retrieved 12 July 2013.
^ "Fast Facts About Back Pain". National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. National Institute of Health. September 2009. Archived from the original on 5 June 2013. Retrieved 10 June 2013.
^ "Low back pain – acute". U.S. Department of Health and Human Services – National Institutes of Health. Archived from the original on 1 April 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2013.
^ Majchrzycki M, Mrozikiewicz PM, Kocur P, et al. (November 2010). "[Low back pain in pregnant women]". Ginekol. Pol. (in Polish). 81 (11): 851–5. PMID 21365902.
^ Floyd, R., & Thompson, Clem. (2008). Manual of structural kinesiology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Humanities/Social Sciences/Languages.
^ abc Freedman MD, Woodham MA, Woodham AW (March 2010). "The role of the lumbar multifidus in chronic low back pain: a review". PM&R. 2 (2): 142–6. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2009.11.006. PMID 20193941.
^ abcdefg Hughes SP, Freemont AJ, Hukins DW, McGregor AH, Roberts S (October 2012). "The pathogenesis of degeneration of the intervertebral disc and emerging therapies in the management of back pain" (PDF). J Bone Joint Surg Br. 94 (10): 1298–304. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.94B10.28986. PMID 23015552. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 25 June 2013.
^ Patel, NB (2010). "Chapter 3: Physiology of Pain". In Kopf A, Patel NB. Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 26 May 2017.CS1 maint: Uses editors parameter (link)
^ abc Cohen SP, Argoff CE, Carragee EJ (2008). "Management of low back pain". BMJ. 337: a2718. doi:10.1136/bmj.a2718. PMID 19103627.
^ Davis PC, Wippold II FJ, Cornelius RS, et al. (2011). "American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria – Low Back Pain" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 December 2012.
^ North American Spine Society (February 2013), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, North American Spine Society, retrieved 25 March 2013, which cites
Chou R, Qaseem A, Snow V, Casey D, Cross JT Jr, Shekelle P, Owens DK, Clinical Efficacy Assessment Subcommittee of the American College of Physicians, American College of Physicians, American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guidelines Panel (Oct 2, 2007). "Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain: a joint clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society". Annals of Internal Medicine. 147 (7): 478–91. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-147-7-200710020-00006. PMID 17909209.
Forseen, SE; Corey, AS (Oct 2012). "Clinical decision support and acute low back pain: evidence-based order sets". Journal of the American College of Radiology : JACR. 9 (10): 704–712.e4. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2012.02.014. PMID 23025864.
^ Williams CM, Henschke N, Maher CG, et al. (2013). "Red flags to screen for vertebral fracture in patients presenting with low-back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 1 (1): CD008643. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008643.pub2. PMID 23440831.
^ Henschke N, Maher CG, Ostelo RW, de Vet HC, Macaskill P, Irwig L (2013). "Red flags to screen for malignancy in patients with low-back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2 (2): CD008686. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008686.pub2. PMID 23450586.
^ abc Downie A, Williams CM, Henschke N, Hancock MJ, Ostelo RW, de Vet HC, Macaskill P, Irwig L, van Tulder MW, Koes BW, Maher CG (11 December 2013). "Red flags to screen for malignancy and fracture in patients with low back pain: systematic review". BMJ. 347 (dec11 1): f7095. doi:10.1136/bmj.f7095. PMC 3898572. PMID 24335669.
^ Williams, CM; Henschke, N; Maher, CG; van Tulder, MW; Koes, BW; Macaskill, P; Irwig, L (31 January 2013). "Red flags to screen for vertebral fracture in patients presenting with low-back pain". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD008643. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008643.pub2. PMID 23440831.
^ Manchikanti L, Glaser SE, Wolfer L, Derby R, Cohen SP (2009). "Systematic review of lumbar discography as a diagnostic test for chronic low back pain". Pain Physician. 12 (3): 541–59. PMID 19461822. Archived from the original on 5 October 2013.
^ ab American Academy of Family Physicians, "Ten Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American Academy of Family Physicians, archived from the original on 10 February 2013, retrieved 5 September 2012
^ ab American College of Physicians, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American College of Physicians, archived from the original on 1 September 2013, retrieved 5 September 2013
^ Crownover BK, Bepko JL (April 2013). "Appropriate and safe use of diagnostic imaging". Am Fam Physician. 87 (7): 494–501. PMID 23547591.
^ ab Chou R, Qaseem A, Owens DK, Shekelle P, Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians (1 February 2011). "Diagnostic imaging for low back pain: advice for high-value health care from the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 154 (3): 181–9. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-154-3-201102010-00008. PMID 21282698.
^ Flynn TW, Smith B, Chou R (November 2011). "Appropriate use of diagnostic imaging in low back pain: a reminder that unnecessary imaging may do as much harm as good". J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 41 (11): 838–46. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3618. PMID 21642763.
^ abc Steffens, Daniel; Maher, Chris G.; Pereira, Leani S. M.; Stevens, Matthew L; Oliveira, Vinicius C.; Chapple, Meredith; Teixeira-Salmela, Luci F.; Hancock, Mark J. (11 January 2016). "Prevention of Low Back Pain". JAMA Internal Medicine. 176 (2): 199–208. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7431. PMID 26752509.
^ ab Choi BK, Verbeek JH, Tam WW, Jiang JY (2010). Choi, Brian KL, ed. "Exercises for prevention of recurrences of low-back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD006555. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006555.pub2. PMID 20091596.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ Chou R, Qaseem A, Snow V, et al. (October 2007). "Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain: a joint clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society". Annals of Internal Medicine. 147 (7): 478–91. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-147-7-200710020-00006. PMID 17909209.
^ abc Guild DG (September 2012). "Mechanical therapy for low back pain". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 511–6. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.006. PMID 22958560.
^ ab Sahar T, Cohen MJ, Uval-Ne'eman V, et al. (April 2009). "Insoles for prevention and treatment of back pain: a systematic review within the framework of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group". Spine. 34 (9): 924–33. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31819f29be. PMID 19359999.
^ Sprouse R (September 2012). "Treatment: current treatment recommendations for acute and chronic undifferentiated low back pain". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 481–6. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.004. PMID 22958557.
^ Momsen AM, Rasmussen JO, Nielsen CV, Iversen MD, Lund H (November 2012). "Multidisciplinary team care in rehabilitation: an overview of reviews". J Rehabil Med. 44 (11): 901–12. doi:10.2340/16501977-1040. PMID 23026978.
^ Hendrick P, Milosavljevic S, Hale L, et al. (March 2011). "The relationship between physical activity and low back pain outcomes: a systematic review of observational studies". Eur Spine J. 20 (3): 464–74. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1616-2. PMC 3048226. PMID 21053026.
^ Hendrick P, Te Wake AM, Tikkisetty AS, Wulff L, Yap C, Milosavljevic S (October 2010). "The effectiveness of walking as an intervention for low back pain: a systematic review". Eur Spine J. 19 (10): 1613–20. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1412-z. PMC 2989236. PMID 20414688.
^ French, SD.; Cameron, M.; Walker, BF.; Reggars, JW.; Esterman, AJ. (2006). "Superficial heat or cold for low back pain". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD004750. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004750.pub2. PMID 16437495.
^ ab van Middelkoop M, Rubinstein SM, Kuijpers T, Verhagen AP, Ostelo R, Koes BW, van Tulder MW (2011). "A systematic review on the effectiveness of physical and rehabilitation interventions for chronic non-specific low back pain". Eur Spine J. 20 (1): 19–39. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1518-3. PMC 3036018. PMID 20640863.
^ Seco J, Kovacs FM, Urrutia G (October 2011). "The efficacy, safety, effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound and shock wave therapies for low back pain: a systematic review". Spine J. 11 (10): 966–77. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2011.02.002. PMID 21482199.
^ Ebadi, S.; Henschke, N.; Nakhostin Ansari, N.; Fallah, E.; van Tulder, MW. (2014). "Therapeutic ultrasound for chronic low-back pain". Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 3 (3): CD009169. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009169.pub2. PMID 24627326.
^ Chou, Roger; Deyo, Richard; Friedly, Janna; Skelly, Andrea; Hashimoto, Robin; Weimer, Melissa; Fu, Rochelle; Dana, Tracy; Kraegel, Paul (2016). Noninvasive Treatments for Low Back Pain. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US). PMID 26985522.
^ Smith C, Grimmer-Somers K (2010). "The treatment effect of exercise programmes for chronic low back pain". J Eval Clin Pract. 16 (3): 484–91. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2753.2009.01174.x. PMID 20438611.
^ van Middelkoop M, Rubinstein SM, Verhagen AP, Ostelo RW, Koes BW, van Tulder MW (2010). "Exercise therapy for chronic nonspecific low-back pain". Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 24 (2): 193–204. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2010.01.002. PMID 20227641.
^ Woodman, JP; Moore, NR (January 2012). "Evidence for the effectiveness of Alexander Technique lessons in medical and health-related conditions: a systematic review". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 66 (1): 98–112. doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2011.02817.x. PMID 22171910.
^ Posadzki, P; Ernst, E (September 2011). "Yoga for low back pain: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials". Clinical Rheumatology. 30 (9): 1257–62. doi:10.1007/s10067-011-1764-8. PMID 21590293.
^ Dubinsky, R. M.; Miyasaki, J. (2009). "Assessment: Efficacy of transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation in the treatment of pain in neurologic disorders (an evidence-based review): Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 74 (2): 173–6. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c918fc. PMID 20042705.
^ Nizard J, Raoul S, Nguyen JP, Lefaucheur JP (October 2012). "Invasive stimulation therapies for the treatment of refractory pain". Discov Med. 14 (77): 237–46. PMID 23114579.
^ Machado, GC; Maher, CG; Ferreira, PH; Oday, R (2017). "Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for spinal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 76 (7): annrheumdis–2016–210597. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210597. PMID 28153830.
^ Saragiotto, BT; Machado, GC; et al. (June 2016). "Paracetamol for low back pain". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (6): CD012230. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012230. PMID 27271789.
^ Machado, GC; Maher, CG; Ferreira, PH; Pinheiro, MB; Lin, CW; Day, RO; McLachlan, AJ; Ferreira, ML (31 March 2015). "Efficacy and safety of paracetamol for spinal pain and osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo controlled trials". BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). 350: h1225. doi:10.1136/bmj.h1225. PMC 4381278. PMID 25828856.
^ Machado, Gustavo C; Maher, Chris G; Ferreira, Paulo H; Day, Richard O; Pinheiro, Marina B; Ferreira, Manuela L (2 February 2017). "Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for spinal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 76 (7): annrheumdis–2016–210597. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210597. PMID 28153830.
^ Enthoven, WT; Roelofs, PD; Deyo, RA; van Tulder, MW; Koes, BW (10 February 2016). "Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for chronic low back pain". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2: CD012087. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012087. PMID 26863524.
^ Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' (CNT) Collaboration, Bhala N, Emberson J, Merhi A, Abramson S, Arber N, Baron JA, Bombardier C, Cannon C, Farkouh ME, FitzGerald GA, Goss P, Halls H, Hawk E, Hawkey C, Hennekens C, Hochberg M, Holland LE, Kearney PM, Laine L, Lanas A, Lance P, Laupacis A, Oates J, Patrono C, Schnitzer TJ, Solomon S, Tugwell P, Wilson K, Wittes J, Baigent C (Aug 31, 2013). "Vascular and upper gastrointestinal effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: meta-analyses of individual participant data from randomised trials". Lancet. 382 (9894): 769–79. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60900-9. PMC 3778977. PMID 23726390.
^ Chaparro, LE; Furlan, AD; Deshpande, A; Mailis-Gagnon, A; Atlas, S; Turk, DC (Apr 1, 2014). "Opioids compared with placebo or other treatments for chronic low back pain: an update of the Cochrane Review". Spine. 39 (7): 556–63. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000000249. PMID 24480962.
^ Abdel Shaheed, C; Maher, CG; Williams, KA; Day, R; McLachlan, AJ (1 July 2016). "Efficacy, Tolerability, and Dose-Dependent Effects of Opioid Analgesics for Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". JAMA Internal Medicine. 176 (7): 958–68. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.1251. PMID 27213267.
^ Shmagel, Anna; Krebs, Erin; Ensrud, Kristine; Foley, Robert (2016-09-01). "Illicit Substance Use in US Adults With Chronic Low Back Pain". SPINE. 41 (17): 1372–1377. doi:10.1097/brs.0000000000001702. ISSN 0362-2436. PMC 5002230. PMID 27438382.
^ Franklin, G. M. (29 September 2014). "Opioids for chronic noncancer pain: A position paper of the American Academy of Neurology". Neurology. 83 (14): 1277–1284. doi:10.1212/WNL.0000000000000839. PMID 25267983.
^ ab Dowell, Deborah; Haegerich, Tamara M.; Chou, Roger (2016). "CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain — United States, 2016". MMWR. Recommendations and Reports. 65 (1): 1–49. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6501e1. ISSN 1057-5987. PMID 26987082.
^ de Leon-Casasola OA (March 2013). "Opioids for chronic pain: new evidence, new strategies, safe prescribing". Am. J. Med. 126 (3 Suppl 1): S3–11. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.11.011. PMID 23414718.
^ Enke, Oliver; New, Heather A.; New, Charles H.; Mathieson, Stephanie; McLachlan, Andrew J.; Latimer, Jane; Maher, Christopher G.; Lin, C.-W. Christine (2 July 2018). "Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 190 (26): E786–E793. doi:10.1503/cmaj.171333. PMC 6028270. PMID 29970367.
^ Chou R, Loeser JD, Owens DK, Rosenquist RW, Atlas SJ, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Grabois M, Murphy DR, Resnick DK, Stanos SP, Shaffer WO, Wall EM, American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guideline Panel (2009). "Interventional therapies, surgery, and interdisciplinary rehabilitation for low back pain: An evidence-based clinical practice guideline from the American Pain Society". Spine. 34 (10): 1066–77. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a1390d. PMID 19363457.
^ Pinto, RZ; Maher, CG; Ferreira, ML; Hancock, M; Oliveira, VC; McLachlan, AJ; Koes, B; Ferreira, PH (18 December 2012). "Epidural corticosteroid injections in the management of sciatica: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Annals of Internal Medicine. 157 (12): 865–77. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-157-12-201212180-00564. PMID 23362516.
^ "Epidural Corticosteroid Injection: Drug Safety Communication - Risk of Rare But Serious Neurologic Problems". FDA. 23 April 2014. Archived from the original on 24 April 2014. Retrieved 24 April 2014.
^ Lee, CS; Hwang, CJ; Lee, DH; Kim, YT; Lee, HS (March 2011). "Fusion rates of instrumented lumbar spinal arthrodesis according to surgical approach: a systematic review of randomized trials". Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery. 3 (1): 39–47. doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.39. PMC 3042168. PMID 21369477.
^ Rothberg, S; Friedman, BW (January 2017). "Complementary therapies in addition to medication for patients with nonchronic, nonradicular low back pain: a systematic review". The American Journal of Emergency Medicine. 35 (1): 55–61. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2016.10.001. PMID 27751598.
^ Paige, Neil M.; Miake-Lye, Isomi M.; Booth, Marika Suttorp; Beroes, Jessica M.; Mardian, Aram S.; Dougherty, Paul; Branson, Richard; Tang, Baron; Morton, Sally C.; Shekelle, Paul G. (11 April 2017). "Association of Spinal Manipulative Therapy With Clinical Benefit and Harm for Acute Low Back Pain". JAMA. 317 (14): 1451–1460. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.3086. PMC 5470352. PMID 28399251.
^ Dagenais, S; Mayer, J; Wooley, J; Haldeman, S (2008). "Evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain with medicine-assisted manipulation". The Spine Journal. 8 (1): 142–9. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2007.09.010. PMID 18164462.
^ abc Furlan AD, Yazdi F, Tsertsvadze A, Gross A, Van Tulder M, Santaguida L, Gagnier J, Ammendolia C, Dryden T, Doucette S, Skidmore B, Daniel R, Ostermann T, Tsouros S (2012). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy, cost-effectiveness, and safety of selected complementary and alternative medicine for neck and low-back pain". Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2012: 1–61. doi:10.1155/2012/953139. PMC 3236015. PMID 22203884.
^ Lin CW, Haas M, Maher CG, Machado LA, van Tulder MW (July 2011). "Cost-effectiveness of guideline-endorsed treatments for low back pain: a systematic review". Eur Spine J. 20 (7): 1024–38. doi:10.1007/s00586-010-1676-3. PMC 3176706. PMID 21229367.
^ abcd Furlan, Andrea D.; Giraldo, Mario; Baskwill, Amanda; Irvin, Emma; Imamura, Marta (1 September 2015). "Massage for low-back pain". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (9): CD001929. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001929.pub3. ISSN 1469-493X. PMID 26329399.
^ Gagnier, JJ; Oltean, H; van Tulder, MW; Berman, BM; Bombardier, C; Robbins, CB (January 2016). "Herbal Medicine for Low Back Pain: A Cochrane Review". Spine. 41 (2): 116–33. doi:10.1097/brs.0000000000001310. PMID 26630428.
^ Cherkin, DC; Herman, PM (1 April 2018). "Cognitive and Mind-Body Therapies for Chronic Low Back Pain and Neck Pain: Effectiveness and Value". JAMA Internal Medicine. 178 (4): 556–557. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.0113. PMID 29507946.
^ Cramer H, Haller H, Lauche R, Dobos G (2012). "Mindfulness-based stress reduction for low back pain. A systematic review". BMC Complement Altern Med. 12: 162. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-162. PMC 3520871. PMID 23009599.
^ Anheyer, D; Haller, H; Barth, J; Lauche, R; Dobos, G; Cramer, H (6 June 2017). "Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for Treating Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis". Annals of Internal Medicine. 166 (11): 799–807. doi:10.7326/M16-1997. PMID 28437793.
^ Urrútia G, Burton K, Morral A, Bonfill X, Zanoli G (March 2005). "Neuroreflexotherapy for nonspecific low back pain: a systematic review". Spine. 30 (6): E148–53. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000155575.85223.14. PMID 15770167.
^ Marlowe, D (September 2012). "Complementary and alternative medicine treatments for low back pain". Primary Care. 39 (3): 533–46. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.008. PMID 22958563.
^ ab Chou, R; Shekelle, P (2010). "Will this patient develop persistent disabling low back pain?". JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 303 (13): 1295–302. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.344. PMID 20371789.
^ Cunningham, F (2009). Williams Obstetrics (23 ed.). McGraw Hill Professional. p. 210. ISBN 9780071702850. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
^ Shiri R, Karppinen J, Leino-Arjas P, Solovieva S, Viikari-Juntura E (January 2010). "The association between smoking and low back pain: a meta-analysis". Am. J. Med. 123 (1): 87.e7–35. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2009.05.028. PMID 20102998.
^ abcde Maharty DC (September 2012). "The history of lower back pain: a look "back" through the centuries". Prim. Care. 39 (3): 463–70. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2012.06.002. PMID 22958555.
^ abcde Lutz GK, Butzlaff M, Schultz-Venrath U (August 2003). "Looking back on back pain: trial and error of diagnoses in the 20th century". Spine. 28 (16): 1899–905. doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000083365.41261.CF. PMID 12923482.
^ ab Manchikanti L, Singh V, Datta S, Cohen SP, Hirsch JA, ASIPP (2009). "Comprehensive review of epidemiology, scope, and impact of spinal pain". Pain Physician. 12 (4): E35–70. PMID 19668291.CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
^ abcd American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (February 2014), "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, archived from the original on 11 September 2014, retrieved 24 February 2014, which cites
Talmage, J; Belcourt, R; Galper, J; et al. (2011). "Low back disorders". In Kurt T. Hegmann. Occupational medicine practice guidelines : evaluation and management of common health problems and functional recovery in workers (3rd ed.). Elk Grove Village, IL: American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. pp. 336, 373, 376–377. ISBN 978-0615452272.
External links
| Classification | D
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
Back and spine at Curlie