Heathrow Airport
Heathrow Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | Heathrow Airport Holdings | ||||||||||||||
| Operator | Heathrow Airport Limited | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | London, United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||
| Location | Hillingdon, London, England, United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||
Hub for | British Airways | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 83 ft / 25 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 51°28′39″N 000°27′41″W / 51.47750°N 0.46139°W / 51.47750; -0.46139Coordinates: 51°28′39″N 000°27′41″W / 51.47750°N 0.46139°W / 51.47750; -0.46139 | ||||||||||||||
| Website | www.heathrow.com | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
 LHR Show map of Greater London  LHR Show map of the United Kingdom  LHR Show map of Europe | |||||||||||||||
Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2017) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Sources: Statistics from the UK Civil Aviation Authority[1] | |||||||||||||||
Heathrow Airport (also known as London Heathrow)[2] (IATA: LHR, ICAO: EGLL) is a major international airport in London, United Kingdom. Heathrow is the second busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic, as well as the busiest airport in Europe by passenger traffic, and the seventh busiest airport in the world by total passenger traffic. It is one of six international airports serving Greater London. In 2017, it handled a record 78.0 million passengers, a 3.1% increase from 2016.[1]
Heathrow lies 14 miles (23 km) west of Central London,[3] and has two parallel east–west runways along with four operational terminals on a site that covers 12.27 square kilometres (4.74 sq mi). The airport is owned and operated by Heathrow Airport Holdings, which itself is owned by FGP TopCo Limited, an international consortium led by Ferrovial that also includes Qatar Holding LLC, Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec, GIC Private Limited, Alinda Capital Partners, China Investment Corporation and Universities Superannuation Scheme (USS).[4] London Heathrow is the primary hub for British Airways and the primary operating base for Virgin Atlantic.
In September 2012, the UK government established the Airports Commission, an independent commission chaired by Sir Howard Davies to examine various options for increasing capacity at UK airports. In July 2015, the commission backed a third runway at Heathrow, which the government approved in October 2016.[5][6][7]
Contents
1 Location
2 History
3 Operations
3.1 Facilities
3.2 Flight movements
3.3 Regulation
3.4 Security
4 Terminals
4.1 Terminal 1 (defunct)
4.2 Terminal 2
4.3 Terminal 3
4.4 Terminal 4
4.5 Terminal 5
4.6 Terminal assignments
5 Airlines and destinations
5.1 Passenger
5.2 Cargo
6 Traffic and statistics
6.1 Overview
6.2 Annual traffic statistics
6.3 Busiest routes
7 Other facilities
8 Access
8.1 Public transport
8.1.1 Train
8.1.2 Bus and coach
8.2 Inter-terminal transport
8.3 Hotel access
8.4 Taxi
8.5 Car
8.6 Bicycle
9 Incidents and accidents
9.1 Terrorism and security incidents
9.2 Other incidents
10 Future expansion and plans
10.1 Runway and terminal expansion
10.2 New transport proposals
10.3 Heathrow City
11 See also
12 Notes
13 References
13.1 Citations
13.2 Bibliography
14 External links
Location

A Qantas Boeing 747-400 on approach to London Heathrow 27L runway[8]
Heathrow is 14 mi (23 km) west of central London,[3] near the south end of the London Borough of Hillingdon on a parcel of land that is designated part of the Metropolitan Green Belt. The airport is surrounded by the villages of Harlington, Harmondsworth, Longford and Cranford to the north and by Hounslow and Hatton to the east. To the south lie Bedfont and Stanwell while to the west Heathrow is separated from Slough in Berkshire by the M25 motorway. Heathrow falls entirely under the Twickenham postcode area, with the postcode TW6.
As the airport is located west of London and as its runways run east–west, an airliner's landing approach is usually directly over the conurbation of London when the wind is from the west, which is most of the time.
Along with Gatwick, Stansted, Luton, Southend and London City, Heathrow is one of six airports with scheduled services serving the London area.
History

Aerial photo of Heathrow Airport from the 1950s, before the terminals were built
Heathrow Airport originated in 1929 as a small airfield (Great West Aerodrome) on land south-east of the hamlet of Heathrow from which the airport takes its name. At that time there were farms, market gardens and orchards there: there was a "Heathrow Farm" about where Terminal 1 is now, a "Heathrow Hall" and a "Heathrow House". This hamlet was largely along a country lane (Heathrow Road) which ran roughly along the east and south edges of the present central terminals area.
Development of the whole Heathrow area as a very much larger airport began in 1944: it was stated to be for long-distance military aircraft bound for the Far East. But by the time the airfield was nearing completion, World War II had ended. The government continued to develop the airport as a civil airport. The airport was opened on 25 March 1946 as London Airport and was renamed Heathrow Airport in 1966. The masterplan[clarification needed] for the airport was designed by Sir Frederick Gibberd, who designed the original terminals and central area buildings, including the original control tower and the multi-faith chapel of St George's.
Operations
Facilities

Central waiting area in Terminal 5

Concorde G-BOAB in storage at Heathrow

Four aircraft on the approach to Heathrow runway 09L

Heathrow's control tower

British Airways aircraft at Terminal 5C
Heathrow Airport is used by over 80 airlines flying to 185 destinations in 84 countries. The airport is the primary hub of British Airways and is a base for Virgin Atlantic. It has four passenger terminals (numbered 2 to 5) and a cargo terminal. Of Heathrow's 73.4 million passengers in 2014, 93% were international travellers; the remaining 7% were bound for (or arriving from) places in the UK.[9] The busiest single destination in passenger numbers is New York, with over 3 million passengers flying between Heathrow and JFK Airport in 2013.[10]
In the 1950s, Heathrow had six runways, arranged in three pairs at different angles in the shape of a hexagram with the permanent passenger terminal in the middle and the older terminal along the north edge of the field; two of its runways would always be within 30° of the wind direction. As the required length for runways has grown, Heathrow now has only two parallel runways running east–west. These are extended versions of the two east–west runways from the original hexagram. From the air, almost all of the original runways can still be seen, incorporated into the present system of taxiways. North of the northern runway and the former taxiway and aprons, now the site of extensive car parks, is the entrance to the access tunnel and the site of Heathrow's unofficial "gate guardian". For many years the home of a 40% scale model of a British Airways Concorde, G-CONC, the site has been occupied by a model of an Emirates Airbus A380 since 2008.[11]
Heathrow Airport has Anglican, Catholic, Free Church, Hindu, Jewish, Muslim and Sikh chaplains. There is a multi-faith prayer room and counselling room in each terminal, in addition to St. George's Interdenominational Chapel in an underground vault adjacent to the old control tower, where Christian services take place. The chaplains organise and lead prayers at certain times in the prayer room.[12]
The airport has its own resident press corps, consisting of six photographers and one TV crew, serving all the major newspapers and television stations around the world.[13]
Most of Heathrow's internal roads are initial letter coded by area: N in the north (e.g. Newall Road), E in the east (e.g. Elmdon Road), S in the south (e.g. Stratford Road), W in the west (e.g. Walrus Road), C in the centre (e.g. Camborne Road).
Flight movements
Aircraft destined for Heathrow are usually routed to one of four holding points.
Air traffic controllers at Heathrow Approach Control (based in Swanwick, Hampshire) then guide the aircraft to their final approach, merging aircraft from the four holds into a single stream of traffic, sometimes as close as 2.5 nautical miles (4.6 km; 2.9 mi) apart. Considerable use is made of continuous descent approach techniques to minimize the environmental effects of incoming aircraft, particularly at night.[14] Once an aircraft is established on its final approach, control is handed over to Heathrow Tower.
When runway alternation was introduced, aircraft generated significantly more noise on departure than when landing, so a preference for westerly operations during daylight was introduced, which continues to this day.[15] In this mode, aircraft depart towards the west and approach from the east over London, thereby minimizing the impact of noise on the most densely populated areas. Heathrow's two runways generally operate in segregated mode, whereby arriving aircraft are allocated to one runway and departing aircraft to the other. To further reduce noise nuisance to people beneath the approach and departure routes, the use of runways 27R and 27L is swapped at 15:00 each day if the wind is from the west. When landings are easterly there is no alternation; 09L remains the landing runway and 09R the departure runway due to the legacy of the now rescinded Cranford Agreement, pending taxiway works to allow the roles to be reversed. Occasionally, landings are allowed on the nominated departure runway, to help reduce airborne delays and to position landing aircraft closer to their terminal, reducing taxi times.
Night-time flights at Heathrow are subject to restrictions. Between 23:00 and 04:00, the noisiest aircraft (rated QC/8 and QC/16) cannot be scheduled for operation. In addition, during the night quota period (23:30–06:00) there are four limits:
- A limit on the number of flights allowed;
- A Quota Count system which limits the total amount of noise permitted, but allows operators to choose to operate fewer noisy aircraft or a greater number of quieter planes;[16]
- QC/4 aircraft cannot be scheduled for operation.
- A voluntary agreement with the airlines that no early morning arrivals will be scheduled to land before 04:30.
A trial of "noise relief zones" ran from December 2012 to March 2013, which concentrated approach flight paths into defined areas compared with the existing paths which were spread out. The zones used alternated weekly, meaning residents in the "no-fly" areas received respite from aircraft noise for set periods.[17] However, it was concluded that some residents in other areas experienced a significant disbenefit as a result of the trial and that it should therefore not be taken forward in its current form. Heathrow received more than 25,000 noise complaints in just three months over the summer of 2016, but around half were made by the same ten people.[18]
Regulation
Until it was required to sell Gatwick and Stansted Airports, Heathrow Airport Holdings held a dominant position in the London aviation market, and has been heavily regulated by the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) as to how much it can charge airlines to land. The annual increase in landing charge per passenger was capped at inflation minus 3% until 1 April 2003. From 2003 to 2007 charges increased by inflation plus 6.5% per year, taking the fee to £9.28 per passenger in 2007. In March 2008, the CAA announced that the charge would be allowed to increase by 23.5% to £12.80 from 1 April 2008 and by inflation plus 7.5% for each of the following four years.[19] In April 2013, the CAA announced a proposal for Heathrow to charge fees calculated by inflation minus 1.3%, continuing until 2019.[20] Whilst the cost of landing at Heathrow is determined by the CAA and Heathrow Airport Holdings, the allocation of landing slots to airlines is carried out by Airport Co-ordination Limited (ACL).[21]
Until 2008, air traffic between Heathrow and the United States was strictly governed by the countries' bilateral Bermuda II treaty. The treaty originally allowed only British Airways, Pan Am and TWA to fly from Heathrow to the US. In 1991, PAA and TWA sold their rights to United Airlines and American Airlines respectively, while Virgin Atlantic was added to the list of airlines allowed to operate on these routes. The Bermuda bilateral agreement conflicted with the Right of Establishment of the United Kingdom in relation to its EU membership, and as a consequence the UK was ordered to drop the agreement in 2004. A new "open skies" agreement was signed by the United States and the European Union on 30 April 2007 and came into effect on 30 March 2008. Shortly afterwards, additional US airlines, including Northwest Airlines, Continental Airlines, US Airways and Delta Air Lines started services to Heathrow.
The airport has been criticized in recent years for overcrowding and delays;[22] according to Heathrow Airport Holdings, Heathrow's facilities were originally designed to accommodate 55 million passengers annually. The number of passengers using the airport reached a record 70 million in 2012.[23] In 2007 the airport was voted the world's least favorite, alongside Chicago O'Hare, in a TripAdvisor survey.[24] However, the opening of Terminal 5 in 2008 has relieved some pressure on terminal facilities, increasing the airport's terminal capacity to 90 million passengers per year. A tie-up is also in place with McLaren Applied Technologies to optimize the general procedure, reducing delays and pollution.[25]
With only two runways, operating at over 98% of their capacity, Heathrow has little room for more flights, although the increasing use of larger aircraft such as the Airbus A380 will allow some increase in passenger numbers. It is difficult for existing airlines to obtain landing slots to enable them to increase their services from the airport, or for new airlines to start operations.[26] To increase the number of flights, Heathrow Airport Holdings has proposed using the existing two runways in 'mixed mode' whereby aircraft would be allowed to take off and land on the same runway. This would increase the airport's capacity from its current 480,000 movements per year to as many as 550,000 according to British Airways CEO Willie Walsh.[27] Heathrow Airport Holdings has also proposed building a third runway to the north of the airport, which would significantly increase traffic capacity (see Future expansion below).[28]
Security
Policing of the airport is the responsibility of the aviation security unit of the Metropolitan Police, although the army, including armored vehicles of the Household Cavalry, has occasionally been deployed at the airport during periods of heightened security.
Full body scanners are now used at the airport, and passengers who object to their use after being selected are required to submit to a hand search in a private room.[29] The scanners display passengers' bodies as a cartoon-style figure, with indicators showing where concealed items may be.[29] The new imagery was introduced initially as a trial in September 2011 following complaints over privacy.[30]
Terminals
The airport has 4 active terminals. Terminal 1 is a disused terminal that was closed in 2015. It formerly housed Star Alliance airlines along with some British Airways destinations. Terminal 2, the newest terminal formerly served Virgin Atlantic Little Red and now houses Star Alliance members along with Aer Lingus, Eurowings, the new Flybe, and Icelandair. Terminal 3 houses Oneworld and some SkyTeam members, Virgin Atlantic, Delta Air Lines, Garuda Indonesia, Middle East Airlines, all new airlines, and few other unaffiliated members with the exception of Iberia, Malaysia Airlines and Qatar Airways. Terminal 4 serves SkyTeam, Malaysia Airlines and Qatar Airways, and most unaffiliated members. It also formerly operated Air India as well, who have joined Star Alliance in Terminal 2. Terminal 5 houses the International Airlines Group-British Airways and Iberia.
Terminal 1 (defunct)
Terminal 1 opened in 1968 and was inaugurated by Queen Elizabeth II in April 1969.[31][32] Before Terminal 5 opened, Terminal 1 was the Heathrow base for British Airways' (BA) domestic and European network and for a few of its long haul routes. The acquisition of British Midland International (BMI) in 2012 by BA's owner International Airlines Group meant British Airways took over BMI's short-haul and medium-haul destinations from the terminal.[33] Terminal 1 was also the main base for most Star Alliance members, some Star Alliance members were also based at Terminal 3.
Terminal 1 closed at the end of June 2015. Its site is being used for an extension to Terminal 2,[34] which opened in June 2014. A number of newer boarding gates used by Terminal 1 had been built as part of the Terminal 2 development and are being retained as part of Terminal 2.[35][36] The last tenants along with British Airways were El Al, Icelandair, the one who moved to Terminal 2 on 25 March 2015, and LATAM Brasil, the third one to move in to Terminal 3 on 27 May, 2015. British Airways was the last operator in Terminal 1. Two flights of this carrier, one departing to Hannover and one arriving from Baku, marked the terminal closure on 29 June 2015. British Airways operations have been relocated to Terminals 3 and 5.[37]
Terminal 2

Terminal 2 central departures area
The airport's newest terminal, officially known as the Queen's Terminal, was opened on 4 June 2014.[38][39] Designed by Spanish architect Luis Vidal, it was built on the site that had been occupied by the original Terminal 2 and the Queens Building.[40][41] The main complex was completed in November 2013 and underwent six months of testing before opening to passengers. It includes a satellite pier (T2B), a 1,340-space car park, an energy center[clarification needed] and a cooling station to generate chilled water. There are 52 shops and 17 bars and restaurants.[42]
Terminal 2 is used by all Star Alliance members which fly from Heathrow (consolidating the airlines under Star Alliance's co-location policy "Move Under One Roof"). Aer Lingus, Eurowings, Flybe and Icelandair also operate from the terminal. Tianjin Airlines is a possible new member at Terminal 2. The airlines moved from their original locations over a six-month period, with only 10% of flights operating from there in the first six weeks (United Airlines' transatlantic flights) to avoid the opening problems seen at Terminal 5. On 4 June 2014, United Airlines became the first airline to move into Terminal 2 from Terminals 1 and 4 followed by All Nippon Airways, Air Canada and Air China from Terminal 3. Air New Zealand, Asiana Airlines, Croatia Airlines, LOT Polish Airlines, South African Airways, and TAP Air Portugal were the last airlines to move in on 22 October 2014 from Terminal 1.[43] Development will continue at the terminal to increase capacity in preparation for the closure of Terminal 3 in 2019.[44]
The original Terminal 2 opened as the Europa Building in 1955 and was the airport's oldest terminal. It had an area of 49,654 m2 (534,470 sq ft) and was designed to handle around 1.2 million passengers annually. In its final years it accommodated up to 8 million. A total of 316 million passengers passed through the terminal in its lifetime. The building was demolished in 2010, along with the Queens Building which had housed airline company offices.[45]
Terminal 3

Terminal 3 bird's-eye view
Terminal 3 opened as the Oceanic Terminal on 13 November 1961 to handle flight departures for long-haul routes for foreign carriers to the United States, Asia and other Far Eastern destinations.[46] At this time the airport had a direct helicopter service to Central London from the gardens on the roof of the terminal building. Renamed Terminal 3 in 1968, it was expanded in 1970 with the addition of an arrivals building. Other facilities added included the UK's first moving walkways. In 2006, the new £105 million Pier 6 was completed[47] to accommodate the Airbus A380 superjumbo; Emirates and Qantas operate regular flights from Terminal 3 using the Airbus A380.
Redevelopment of Terminal 3's forecourt by the addition of a new four-lane drop-off area and a large pedestrianised plaza, complete with canopy to the front of the terminal building, was completed in 2007. These improvements were intended to improve passengers' experience, reduce traffic congestion and improve security.[48] As part of this project, Virgin Atlantic was assigned its own dedicated check-in area, known as 'Zone A', which features a large sculpture and atrium.
As of 2013[update], Terminal 3 has an area of 98,962 m2 (1,065,220 sq ft) and in 2011 it handled 19.8 million passengers on 104,100 flights.[49] Terminal 3 is home to Oneworld members with the exception of Iberia, which uses Terminal 5, Malaysia Airlines and Qatar Airways which use Terminal 4, SkyTeam members Delta Air Lines, Garuda Indonesia, Middle East Airlines, all new airlines and a few unaffiliated carriers.
Terminal 4

Terminal 4 bird's-eye view
Opened in 1986, Terminal 4 is situated to the south of the southern runway next to the cargo terminal and is connected to Terminals 2 and 3 by the Heathrow Cargo Tunnel. The terminal has an area of 105,481 m2 (1,135,390 sq ft) and is now home to the SkyTeam alliance, with the exception of Garuda Indonesia, Delta Air Lines, and Middle East Airlines, which use Terminal 3, Oneworld carriers Malaysia Airlines and Qatar Airways, and to most unaffiliated carriers. It has undergone a £200m upgrade to enable it to accommodate 45 airlines with an upgraded forecourt to reduce traffic congestion and improve security. Most flights that go to Terminal 4 are flights coming from Asia and North Africa, as well as a few flights to Europe. An extended check-in area with renovated piers and departure lounges and a new baggage system were installed, and two new stands were built to accommodate the Airbus A380; Etihad Airways, Korean Air, Malaysia Airlines and Qatar Airways operate regular A380 flights.[50]EL AL operates some regular Boeing 747 flights.
Terminal 5

Terminal 5 bird's-eye view
Terminal 5 lies between the northern and southern runways at the western end of the Heathrow site and was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 14 March 2008,[51] some 19 years after its inception. It opened to the public on 27 March 2008, and British Airways and its partner company Iberia have exclusive use of this terminal. The first passenger to enter Terminal 5 was a UK ex-pat from Kenya who passed through security at 04:30 on the day. He was presented with a boarding pass by the British Airways CEO Willie Walsh for the first departing flight, BA302 to Paris. During the two weeks after its opening, operations were disrupted by problems with the terminal's IT systems, coupled with insufficient testing and staff training, which caused over 500 flights to be cancelled.[52] Until March 2012, Terminal 5 was exclusively used by British Airways as its global hub; however, because of the merger, on 25 March Iberia's operations at Heathrow were moved to the terminal, making it the home of International Airlines Group.[53]
Built at a cost of £4.3 billion, the terminal consists of a four-story main terminal building (Concourse A) and two satellite buildings linked to the main terminal by an underground people mover transit system. The second satellite (Concourse C), includes dedicated aircraft stands for the Airbus A380. It became fully operational on 1 June 2011. Terminal 5 was voted Skytrax World's Best Airport Terminal 2014 in the Annual World Airport Awards.[54]
The main terminal building (Concourse A) has an area of 300,000 square metres (3,200,000 sq ft) while Concourse B covers 60,000 square metres (650,000 sq ft).[55] It has 60 aircraft stands and capacity for 30 million passengers annually as well as more than 100 shops and restaurants.[56]
A further building, designated Concourse D and of similar size to Concourse C, may yet be built to the east of the existing site, providing up to another 16 stands. Following British Airways' merger with Iberia, this may become a priority since the combined business will require accommodation at Heathrow under one roof to maximise the cost savings envisaged under the deal. A proposal for Concourse D featured in Heathrow's most recent capital investment plan.
The transport network around the airport has been extended to cope with the increase in passenger numbers. A dedicated motorway spur links the terminal to the M25 (between junctions 14 and 15). The terminal has a 3,800 space multi-story car park. A more distant long-stay car park for business passengers is connected to the terminal by a personal rapid transit system, which became operational in the spring of 2011.[57] New branches of both the Heathrow Express and the Underground's Piccadilly line serve a new shared Heathrow Terminal 5 station.
Terminal assignments
As of September 2018, Heathrow's four passenger terminals are assigned as follows:[58]
| Terminal | Airlines and alliances |
|---|---|
Terminal 2 | Star Alliance and a few non aligned airlines |
| Terminal 3 | Oneworld (except Malaysia Airlines, Qatar Airways, Iberia and most British Airways destinations), Virgin Atlantic, Delta Air Lines, Garuda Indonesia, Middle East Airlines and several non-aligned airlines |
| Terminal 4 | SkyTeam (except Delta Air Lines, Garuda Indonesia and Middle East Airlines), Malaysia Airlines, Qatar Airways and most non-aligned airlines |
| Terminal 5 | British Airways (most destinations, except those at Terminal 3) and Iberia |
Following the opening of Terminal 5 in March 2008, a complex programme of terminal moves was implemented. This saw many airlines move so as to be grouped in terminals by airline alliance as far as possible.[59]
Following the opening of Phase 1 of the new Terminal 2 in June 2014, all Star Alliance member airlines[60] (with the exception of new member Air India which moved in early 2017) along with Aer Lingus and Germanwings relocated to Terminal 2 in a phased process completed on 22 October 2014. Additionally, by 30 June 2015 all airlines left Terminal 1 in preparation for its demolition to make room for the construction of Phase 2 of Terminal 2.[61] Some other airlines made further minor moves at a later point, e.g. Air India moving from Terminal 4 to the other Star Alliance carriers in Terminal 2[62] or Delta Air Lines merging all departures in Terminal 3 instead of a split between Terminals 3 and 4.[63]
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
The following airlines operate regular scheduled passenger flights at London Heathrow Airport:[64]
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aegean Airlines | Athens |
| Aer Lingus | Belfast–City, Cork, Dublin, Shannon |
| Aeroflot | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Aeroméxico | Mexico City |
| Air Algérie | Algiers |
| Air Astana | Astana |
Air Canada[65] | Calgary, Halifax, Montréal–Trudeau, Ottawa, St. John's, Toronto–Pearson, Vancouver |
| Air China | Beijing–Capital, Chengdu (begins 2 April 2019)[66] |
Air France[67] | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Air India | Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Delhi, Mumbai |
| Air Malta | Malta |
| Air Mauritius | Mauritius |
| Air New Zealand | Auckland, Los Angeles |
| Air Serbia | Belgrade |
| Alitalia | Milan–Linate, Rome–Fiumicino |
| All Nippon Airways | Tokyo–Haneda |
American Airlines[68] | Charlotte, Chicago–O'Hare, Dallas/Fort Worth, Los Angeles, Miami, New York–JFK, Philadelphia, Raleigh/Durham Seasonal: Phoenix–Sky Harbor (begins 31 March 2019)[69] |
| Asiana Airlines | Seoul–Incheon |
| Austrian Airlines | Vienna |
| Avianca | Bogotá |
| Azerbaijan Airlines | Baku |
| Beijing Capital Airlines | Qingdao |
| Biman Bangladesh Airlines | Dhaka, Sylhet |
British Airways[70] | Aberdeen, Abu Dhabi, Abuja, Accra, Amman–Queen Alia, Amsterdam, Athens, Atlanta, Austin, Bahrain, Baltimore, Bengaluru, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Barcelona, Basel/Mulhouse/Freiburg, Beijing–Capital, Beirut, Belfast–City, Berlin–Tegel, Bilbao (ends 31 March 2019),[71]Billund, Bologna, Boston, Brussels, Bucharest–Otopeni, Budapest, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Cairo, Cape Town, Chennai, Chicago–O'Hare, Copenhagen, Dallas/Fort Worth, Delhi, Denver, Doha, Dubai–International, Dublin, Durban, Düsseldorf, Edinburgh, Frankfurt, Geneva, Gibraltar, Glasgow-International, Gothenburg, Gran Canaria, Grand Cayman, Hamburg, Hanover, Helsinki, Hong Kong, Houston–Intercontinental, Hyderabad, Innsbruck, Inverness, Istanbul–Atatürk (ends 29 December 2018),[72]Istanbul–Havalimanı (begins 1 January 2019),[73]Jeddah, Johannesburg–OR Tambo, Kyiv–Boryspil, Kraków, Kuala Lumpur–International, Kuwait City, Lagos, Larnaca, Las Vegas, Leeds/Bradford, Lisbon, Los Angeles, Luxembourg, Lyon, Madrid, Mahé Island, Málaga, Manchester, Marseille, Mexico City, Miami, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Montréal–Trudeau, Moscow–Domodedovo, Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Mumbai, Munich, Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta, Nashville, Nassau, New Orleans, New York–JFK, Newark, Newcastle upon Tyne, Nice, Osaka–Kansai (resumes 1 April 2019),[74]Oslo–Gardermoen, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Philadelphia, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Pisa, Pittsburgh (begins 2 April 2019),[75]Prague, Reykjavík–Keflavík, Rio de Janeiro–Galeão, Riyadh, Rome–Fiumicino, Saint Petersburg, San Diego, San Francisco, San Jose (CA), Santiago de Chile, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Seattle/Tacoma, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Singapore, Sofia, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Sydney, Tallinn (ends 29 March 2019),[76]Tel Aviv–Ben Gurion, Tenerife-South, Tokyo–Haneda, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto–Pearson, Toulouse, Valencia (begins 31 March 2019),[77]Vancouver, Venice, Vienna, Warsaw–Chopin, Washington–Dulles, Zagreb, Zürich Seasonal: Bastia (begins 25 May 2019),[78]Brindisi, Calgary, Chania, Charleston (begins 4 April 2019),[79]Corfu, Faro, Figari, Grenoble, Ibiza, Kalamata, Kefalonia, Ljubljana (begins 15 July 2019),[80]Marrakesh, Montpellier (resumes 11 July 2018),[81]Muscat, Mykonos, Nantes, Olbia, Palermo, Palma de Mallorca, Preveza/Lefkada (begins 26 May 2019),[78]Pula, Salzburg, Santorini, Split, Zakynthos |
| Brussels Airlines | Brussels |
| Bulgaria Air | Sofia |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| China Eastern Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong |
China Southern Airlines[82] | Guangzhou, Sanya, Wuhan |
| Croatia Airlines | Zagreb Seasonal: Split |
Delta Air Lines[83] | Atlanta, Boston, Detroit, Minneapolis/St. Paul, New York–JFK Seasonal: Portland (OR), Salt Lake City |
| EgyptAir | Cairo Seasonal: Luxor |
| El Al | Tel Aviv–Ben Gurion |
| Emirates | Dubai–International |
| Ethiopian Airlines | Addis Ababa |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi |
| Eurowings | Berlin-Tegel, Cologne/Bonn, Düsseldorf, Hamburg, Stuttgart |
| EVA Air | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Flybe | Aberdeen, Edinburgh, Newquay (begins 31 March 2019)[84] |
| Garuda Indonesia | Jakarta-Soekarno-Hatta (resumes 13 December 2018)[85] |
| Gulf Air | Bahrain |
| Hainan Airlines | Changsha |
| Iberia | Madrid |
| Icelandair | Reykjavík–Keflavík |
| Iran Air | Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| Japan Airlines | Tokyo–Haneda |
| Jet Airways | Delhi, Mumbai |
| Kenya Airways | Nairobi–Kenyatta |
KLM[86] | Amsterdam |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| Kuwait Airways | Kuwait City |
| LATAM Brasil | São Paulo–Guarulhos |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
Lufthansa[87] | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Malaysia Airlines | Kuala Lumpur–International |
| Middle East Airlines | Beirut |
| Oman Air | Muscat |
| Pakistan International Airlines | Islamabad, Karachi, Lahore |
| Philippine Airlines | Manila |
Qantas[88] | Melbourne, Perth, Singapore, Sydney |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca, Rabat |
| Royal Brunei Airlines | Bandar Seri Begawan |
| Royal Jordanian | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Saudia | Jeddah, Riyadh Seasonal: Medina |
| Scandinavian Airlines | Copenhagen, Oslo–Gardermoen, Stavanger, Stockholm–Arlanda |
| Shenzhen Airlines | Shenzhen |
| Singapore Airlines | Singapore |
| South African Airways | Johannesburg–OR Tambo |
| SriLankan Airlines | Colombo |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Geneva, Zürich Seasonal: Sion |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon |
| TAROM | Bucharest–Otopeni |
| Thai Airways | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi |
| Tianjin Airlines | Chongqing, Tianjin, Xi'an |
| Tunisair | Tunis |
| Turkish Airlines | İstanbul–Atatürk (ends 31 December 2018),[89]Istanbul–Havalimanı (begins 1 January 2019)[89] |
| Turkmenistan Airlines | Ashgabat |
United Airlines[90] | Chicago–O'Hare, Houston–Intercontinental, Los Angeles, Newark, San Francisco, Washington–Dulles Seasonal: Denver |
| Uzbekistan Airways | Tashkent |
| Vietnam Airlines | Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City |
Virgin Atlantic[91] | Atlanta, Boston, Delhi, Dubai–International (ends 31 March 2019),[92]Hong Kong, Johannesburg–OR Tambo, Lagos, Las Vegas (begins 31 March 2019),[93]Los Angeles, Miami, New York–JFK, Newark, San Francisco, Seattle/Tacoma, Shanghai–Pudong, Washington–Dulles Seasonal: Barbados |
| Vueling | A Coruña, Barcelona |
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| AirBridgeCargo Airlines | Leipzig/Halle, Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Cathay Pacific Cargo | Delhi, Hong Kong, Milan–Malpensa, Mumbai, Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| DHL Aviation | Amsterdam, Brussels, East Midlands, Frankfurt, Leipzig/Halle, Luton, Madrid–Barajas, Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Emirates SkyCargo | Dubai–Al Maktoum |
| Ethiopian Airlines Cargo | Addis Ababa, Lagos |
| Korean Air Cargo | Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Seoul–Incheon |
| Qatar Airways Cargo | Basel, Doha |
| Royal Air Maroc Cargo | Casablanca |
| Royal Jordanian Cargo | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Singapore Airlines Cargo | Amsterdam, Sharjah, Singapore |
Traffic and statistics

British Airways Boeing 747-400 in Oneworld livery at Heathrow Airport
Overview

Development of passenger numbers, aircraft movements and air freight between 1986 and 2014
When ranked by passenger traffic, Heathrow is the sixth busiest internationally, behind Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Beijing Capital International Airport, Dubai International Airport, Chicago's O'Hare International Airport, and Tokyo Haneda Airport, for the 12 months ending December 2015.[94]
In 2015, Heathrow was the busiest airport in Europe in total passenger traffic, with 14% more passengers than Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport[95] and 22% more than Istanbul Atatürk Airport.[96] Heathrow was the fourth busiest European airport by cargo traffic in 2013, after Frankfurt Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol.[97]
Annual traffic statistics
| Year | Passengers handled[a] | Passenger % Change | Cargo (tonnes) | Cargo % Change | Aircraft movements | Aircraft % Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 | 31,675,779 | 537,131 | 315,753 | |||
| 1987 | 35,079,755 | 574,116 | 329,977 | |||
| 1988 | 37,840,503 | 642,147 | 351,592 | |||
| 1989 | 39,881,922 | 686,170 | 368,429 | |||
| 1990 | 42,950,512 | 695,347 | 390,372 | |||
| 1991 | 40,494,575 | 654,625 | 381,724 | |||
| 1992 | 45,242,591 | 754,770 | 406,481 | |||
| 1993 | 47,899,081 | 846,486 | 411,173 | |||
| 1994 | 51,713,366 | 962,738 | 424,557 | |||
| 1995 | 54,461,597 | 1,031,639 | 434,525 | |||
| 1996 | 56,049,706 | 1,040,486 | 440,343 | |||
| 1997 | 58,185,398 | 1,156,104 | 440,631 | |||
| 1998 | 60,683,988 | 1,208,893 | 451,382 | |||
| 1999 | 62,268,292 | 1,265,495 | 458,300 | |||
| 2000 | 64,618,254 | 1,306,905 | 466,799 | |||
| 2001 | 60,764,924 | 1,180,306 | 463,567 | |||
| 2002 | 63,362,097 | 1,234,940 | 466,545 | |||
| 2003 | 63,495,367 | 1,223,439 | 463,650 | |||
| 2004 | 67,342,743 | 1,325,173 | 476,001 | |||
| 2005 | 67,913,153 | 1,305,686 | 477,887 | |||
| 2006 | 67,527,923 | 1,264,129 | 477,048 | |||
| 2007 | 68,066,028 | 1,310,987 | 481,476 | |||
| 2008 | 67,054,745 | 1,397,054 | 478,693 | |||
| 2009 | 66,036,957 | 1,277,650 | 466,393 | |||
| 2010 | 65,881,660 | 1,472,988 | 454,823 | |||
| 2011 | 69,433,230 | 1,484,351 | 480,906 | |||
| 2012 | 70,037,417 | 1,464,390 | 475,176 | |||
| 2013 | 72,367,054 | 1,422,939 | 471,936 | |||
| 2014 | 73,405,330 | 1,498,906 | 472,802 | |||
| 2015 | 74,985,748 | 1,496,551 | 474,087 | |||
| 2016 | 75,711,130 | 1,541,029 | 474,963 | |||
| 2017 | 78,047,278 | 1,698,455 | 476,186 |
Busiest routes
Heathrow Airport processed 78,047,278 passengers in 2017.[1]New York's John F. Kennedy International Airport was the most popular route with 2,945,744 passengers.[98] The table below shows the 40 busiest international routes at the airport in 2017.
| Rank | Airport | Total passengers | Change 2016 / 17 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2,945,744 | ||
| 2 | 2,873,011 | ||
| 3 | 1,803,497 | ||
| 4 | 1,689,924 | ||
| 5 | 1,600,587 | ||
| 6 | 1,588,805 | ||
| 7 | 1,501,134 | ||
| 8 | 1,382,478 | ||
| 9 | 1,287,225 | ||
| 10 | 1,234,806 | ||
| 11 | 1,207,929 | ||
| 12 | 1,190,441 | ||
| 13 | 1,139,638 | ||
| 14 | 1,062,328 | ||
| 15 | 1,056,478 | ||
| 16 | 1,047,947 | ||
| 17 | 1,023,509 | ||
| 18 | 1,021,532 | ||
| 19 | 1,020,678 | ||
| 20 | 1,013,192 | ||
| 21 | 1,009,584 | ||
| 22 | 1,004,473 | ||
| 23 | 985,148 | ||
| 24 | 982,928 | ||
| 25 | 976,106 | ||
| 26 | 963,977 | ||
| 27 | 954,716 | ||
| 28 | 865,043 | ||
| 29 | 850,446 | ||
| 30 | 845,634 | ||
| 31 | 814,124 | ||
| 32 | 807,858 | ||
| 33 | 779,203 | ||
| 34 | 761,330 | ||
| 35 | 741,486 | ||
| 36 | 714,261 | ||
| 37 | 692,039 | ||
| 38 | 683,777 | ||
| 39 | 679,409 | ||
| 40 | 677,113 |
| Rank | Airport | Total passengers | Change 2016 / 17 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Edinburgh | 1,179,758 | |
| 2 | Glasgow | 909,117 | |
| 3 | Belfast-City | 691,552 | |
| 4 | Manchester | 665,203 | |
| 5 | Aberdeen | 622,034 | |
| 6 | Newcastle | 491,597 | |
| 7 | Leeds Bradford | 162,042 | |
| 8 | Inverness | 79,065 |
Other facilities

The Compass Centre, the head office of Heathrow Airport Holdings
The head office of Heathrow Airport Holdings (formerly BAA Limited) is located in the Compass Centre by Heathrow's northern runway, a building that previously served as a British Airways flight crew centre.[100] The World Business Centre Heathrow consists of three buildings. 1 World Business Centre houses offices of Heathrow Airport Holdings, Heathrow Airport itself, and Scandinavian Airlines.[101] Previously International Airlines Group had its head office in 2 World Business Centre.[102][103]
At one time the British Airways head office was located within Heathrow Airport at Speedbird House[104] before the completion of Waterside, the current BA head office in Harmondsworth, in June 1998.[105]
To the north of the airfield lies the Northern Perimeter Road, along which most of Heathrow's car rental agencies are based, and Bath Road, which runs parallel to it, but outside the airport campus. This is nicknamed "The Strip" by locals, because of its continuous line of airport hotels.
Access
Public transport

Heathrow Airport tube and rail stations
Train

Heathrow Express train at Paddington station
Heathrow Express: a non-stop service direct to London's Paddington station; trains leave every 15 minutes for the 15-minute journey (21 minutes to/from Terminal 5). Trains depart from Heathrow Terminal 5 station or Heathrow Central station (Terminals 2 & 3). A Heathrow Express transfer service operates between Terminal 4 and Heathrow Central to connect with services from London and Terminal 5.
TfL Rail: a stopping service to Paddington calling at up to five National Rail stations en route – trains leave every 30 minutes for the 27-minute journey.[106] Calls at Hayes & Harlington for connecting trains to Reading. It will be extended in December 2019 to Abbey Wood and Shenfield via the Elizabeth line. (Operated by Heathrow Connect until May 2018.)
London Underground (Piccadilly line): four stations serve the airport: Terminal 2 & 3, Terminal 4 and Terminal 5 serve the passenger terminals; and Hatton Cross the maintenance areas. The usual journey time from Heathrow Central to Central London is around 40–50 minutes.[107]
Bus and coach
Many buses and coaches operate from the large Heathrow Central bus station serving Terminals 2 and 3, and also from bus stations at Terminals 4 and 5.
Inter-terminal transport
All terminals lie within the Heathrow Free Travel Zone with free travel between the terminals. Terminals 2 and 3 are within walking distance of each other. Transfers from Terminals 2 and 3 to Terminal 4 and 5 are provided by Heathrow Express trains.[108] Transfer between Terminals 4 and 5 is provided by London Buses routes 482 and 490.[109]
Transit passengers remaining airside are provided with free dedicated transfer buses between terminals.
ULTra Personal Rapid Transport opened in April 2011 to shuttle passengers between Terminal 5 and the business car park at a speed of up to 40 km/h (25 mph). There are 21 small transportation pods that can each carry up to four adults, two children, and their luggage. The pods are battery-powered and run on a four-kilometre track. The capsules run on demand. The provider claims a 95% availability rate and no accidents so far.[110] Plans to use the same technology to connect Terminals 2 and 3 to remote car parks were included in the draft 2014–2019 five-year master plan but have since been deferred due to other priorities.[111]
Hotel access
The Hotel Hoppa bus network connects all terminals to major hotels in the area.[112]
Taxi
Taxis are available at all terminals.[113]
Car

Entrance at the southern end of the M4 Motorway spur, showing a scale model of Concorde, replaced since 2008 by the Emirates A380 scale model.[114]
Heathrow is accessible via the nearby M4 motorway or A4 road (Terminals 2–3), the M25 motorway (Terminals 4 and 5) and the A30 road (Terminal 4). There are drop-off and pick-up areas at all terminals and short-[115] and long-stay[116] multi-storey car parks. All the Heathrow forecourts are drop-off only.[117] There are further car parks, not run by Heathrow Airport Holdings, just outside the airport: the most recognisable is the National Car Parks facility, although there are many other options; these car parks are connected to the terminals by shuttle buses.
Four parallel tunnels under the northern runway connect the M4 Heathrow spur and the A4 road to Terminals 2–3. The two larger tunnels are each two lanes wide and are used for motorised traffic. The two smaller tunnels were originally reserved for pedestrians and bicycles; to increase traffic capacity the cycle lanes have been modified to each take a single lane of cars, although bicycles still have priority over cars. Pedestrian access to the smaller tunnels has been discontinued, with the free bus services being used instead.
Bicycle
There are (mainly off-road) bicycle routes to some of the terminals.[118] Free bicycle parking places are available in car parks 1 and 1A, at Terminal 4, and to the North and South of Terminal 5's Interchange Plaza. It is worth noting travelers are not allowed to cycle through the main tunnel to access Terminals 2 and 3 (Terminal 1 closed in 2015).[119]
Incidents and accidents
- On 3 March 1948, Sabena Douglas DC3 OO-AWH crashed in fog. Three crew and 19 of the 22 passengers on board died.[120]
- On 31 October 1950, BEA Vickers Viking G-AHPN crashed at Heathrow after hitting the runway during a go-around. Three crew and 25 passengers died.[121]
- On 16 January 1955, BEA Vickers Viscount G-AMOK crashed into barriers whilst taking off in fog from a disused runway strip parallel to the desired runway. There were 2 injuries.[122]
- On 22 June 1955, BOAC de Havilland Dove G-ALTM crashed just short of the runway during a filming flight, when the pilot shut-down the incorrect engine. There were no casualties.[123]
- On 1 October 1956, XA897, an Avro Vulcan strategic bomber of the Royal Air Force, crashed at Heathrow after an approach in bad weather. The Vulcan was the first to be delivered to the RAF, and was returning from a demonstration flight to Australia and New Zealand. The pilot and co-pilot ejected and survived, but the four other occupants were killed.[124]
- On 7 January 1960, Vickers Viscount G-AOHU of BEA was damaged beyond economic repair when the nose wheel collapsed on landing. A fire then developed and burnt out the fuselage. There were no casualties among the 59 people on board.[125]
- On 27 October 1965, BEA Vickers Vanguard G-APEE, flying from Edinburgh, crashed on Runway 28R while attempting to land in poor visibility. All 30 passengers and six crew on board died.[126][127]
- On 8 April 1968, BOAC Flight 712 Boeing 707 G-ARWE, departing for Australia via Singapore, suffered an engine fire just after take-off. The engine fell from the wing into a nearby gravel pit in Staines, before the plane managed to perform an emergency landing with the wing on fire. However, the plane was consumed by fire once on the ground. Five people – four passengers and a flight attendant – died, while 122 survived. The flight attendant, Barbara Harrison, who helped with the evacuation, was posthumously awarded the George Cross.[128]
- On 3 July 1968, the port flap operating rod of G-AMAD, an Airspeed Ambassador operated by BKS Air Transport failed due to fatigue, thereby allowing the port flaps to retract. This resulted in a rolling movement to port which could not be controlled during the approach, causing the aircraft to contact the grass and swerve towards the terminal building. It hit two parked British European Airways Hawker Siddeley Trident aircraft, burst into flames and came to rest against the ground floor of the terminal building. Six of the eight crew died, as did eight horses on board. Trident G-ARPT was written off,[129] and Trident G-ARPI was badly damaged, but subsequently repaired, only to be lost in the Staines crash in 1972.
- On 22 January 1970, Vickers Viscount G-AWXI of British Midland was damaged beyond economic repair when an engine caught fire on take-off. A successful emergency landing was made at Heathrow.[130]
- On 18 June 1972, Trident G-ARPI, operating as BEA548, crashed in a field close to the Crooked Billet Public House, Staines, two minutes after taking off. All 118 passengers and crew on board died.[131]

British Airways Flight 38 which crash landed just short of the runway on 17 January 2008
- On 8 December 1996, a KLM Cityhopper Fokker 50, PH-KVK, operating as KLM483 from Rotterdam, suffered a main gear collapse after landing on runway 09R. The aircraft's touchdown was normal, right mainwheel first. About 5 seconds after all the landing gear were in ground contact the left main landing gear collapsed and the aircraft left wing tip, left propeller and the rear left portion of the fuselage contacted the runway. The aircraft veered to the left coming to rest on the hard surface clear of the runway in Block 81.[132][133]
- On 5 November 1997, a Virgin Atlantic Airbus A340-300, G-VSKY, made an emergency landing following an undercarriage malfunction. Part of the undercarriage collapsed on landing, and both aircraft and runway were damaged. Recommendations made as a result of the accident included one that aircraft cabin door simulators should more accurately reproduce operating characteristics in an emergency, and another that cockpit voice recorders should have a two-hour duration in aircraft registered before April 1998.[134]
- On 17 January 2008, a British Airways Boeing 777-236ER, G-YMMM, operating flight BA038 from Beijing, crash-landed at Heathrow. The aircraft landed on grass short of the south runway, then slid to the edge of the runway and stopped on the threshold, leading to 18 minor injuries. The aircraft was later found to have suffered loss of thrust caused by fuel icing.[135]
Terrorism and security incidents
- On 8 June 1968, James Earl Ray, the man convicted of 4 April 1968 assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr., was captured and arrested at Heathrow Airport while attempting to leave the United Kingdom on a false Canadian passport.[136]
- On 6 September 1970, El Al Flight 219 experienced an attempted hijack by two PFLP members. One hijacker was killed and the other was subdued as the plane made an emergency landing at Heathrow Airport.
- On 19 May 1974, the IRA planted a series of bombs in the Terminal 1 car park. Two people were injured by the explosions.[137]
- On 26 November 1983, the Brink's-Mat robbery occurred, in which 6,800 gold bars worth nearly £26 million were taken from a vault near Heathrow. Only a small amount of the gold was recovered, and only two men were convicted of the crime.[138]
- On 17 April 1986, semtex explosives were found in the bag of a pregnant Irishwoman attempting to board an El Al flight. The explosives had been given to her by her Jordanian boyfriend and father of her unborn child Nizar Hindawi. The incident became known as the Hindawi Affair.[139]
- On 21 December 1988, Pan Am Flight 103 from Heathrow to New York JFK was blown up over Lockerbie, Scotland, killing all 259 on board and 11 other people on the ground. This also still remains the deadliest attack on a US aircraft.[140]
- In 1994, over a six-day period, Heathrow was targeted three times (8, 10, and 13 March) by the IRA, which fired 12 mortars. Heathrow was a symbolic target due to its importance to the UK economy, and much disruption was caused when areas of the airport were closed over the period. The gravity of the incident was heightened by the fact that the Queen was being flown back to Heathrow by the RAF on 10 March.[141]
- In March 2002, thieves stole US$3 million that had arrived on a South African Airways flight.[142]
- In February 2003, the British Army was deployed to Heathrow along with 1,000 police officers in response to intelligence reports suggesting that al-Qaeda terrorists might launch surface-to-air missile attacks at British or American airliners.[143]
- On 17 May 2004, Scotland Yard's Flying Squad foiled an attempt by seven men to steal £40 million in gold bullion and a similar quantity of cash from the Swissport warehouse at Heathrow.[144]
- On 10 August 2006, the airport became the focus of changes in security protocol, following the revelation of a supposed al-Qaeda terrorist plot. New security rules were put in force immediately, causing additional restrictions in regards to carrying liquids onto flights. This caused longer queues and wait times at security. These included the prohibition of carry-on luggage (except essential items such as travel documents and medication) and all liquids – although this rule was later relaxed to allow the carrying on board of liquid medications and baby milk, if they were tasted first by passengers at the security checkpoint.[145]
- On 25 February 2008, Greenpeace activists protesting against the planned third runway managed to cross the tarmac and climb atop a British Airways Airbus A320, which had just arrived from Manchester Airport. At about 09:45 GMT the protesters unveiled a "Climate Emergency – No Third Runway" banner over the aircraft's tailfin. By 11:00 GMT four arrests had been made.[146]
- On 13 March 2008, a man with a rucksack scaled the perimeter fence onto runway 27R, and ran across the grounds, resulting in his subsequent arrest. A controlled explosion of his bag took place, although nothing suspicious was found, and the Metropolitan Police later said that the incident had not been terrorism related.[147]
- On 13 July 2015, thirteen activists belonging to the climate change protest group Plane Stupid managed to break through the perimeter fence and get onto the northern runway. They chained themselves together in protest, disrupting hundreds of flights. All were eventually arrested.[148][149]
Other incidents
- Flights from Heathrow were suspended from midday Thursday 15 April 2010 to 22:00 Tuesday 20 April 2010 due to risk of jet engines being damaged by volcanic ash in the upper atmosphere caused by the eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland.[150]
- On 18 December 2010, 'heavy' (9 cm, according to the Heathrow Winter Resilience Enquiry)[151] snowfall caused the closure of the entire airport, causing one of the largest incidents at Heathrow of all time. 4,000 flights were cancelled over five days and 9,500 passengers spent the night at Heathrow on 18 December following the initial snowfall.[152] The problems were caused not only by snow on the runways, but also by snow and ice on the 198 parking stands which were all occupied by aircraft.[153]
- On 12 July 2013, the ELT on an Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 787 Dreamliner parked at Heathrow airport caught fire due to a short circuit.[154] There were no passengers aboard and no injuries.[155][156]
- On 14 February 2018, 2 airside vehicles, a BA engineering vehicle and a Heathrow airside operation vehicle, crashed on a taxiway near Terminal 5. The driver of the BA vehicle died from cardiac arrest and the other driver sustained a broken shoulder. The airport remained opened, although 20+ flights were delayed. This incident was referred to the health and safety executive and no arrests were made by the Metropolitan Police.[157]
Future expansion and plans
Runway and terminal expansion

British Airways aircraft queuing for take-off
In January 2009, the Transport Secretary at the time, Geoff Hoon announced that the British government supported the expansion of Heathrow by building a third 2,200-metre (7,200 ft) runway and a sixth terminal building.[158] This decision followed the 2003 white paper on the future of air transport in the UK,[159] and a public consultation in November 2007.[160] This was a controversial decision which met with widespread opposition because of the expected greenhouse gas emissions, impact on local communities, as well as noise and air pollution concerns.[161]
Prior to the 2010 general election, the Conservative and Liberal Democrat parties announced that they would prevent the construction of any third runway or further material expansion of the airport's operating capacity. The Mayor of London, then Boris Johnson, took the position that London needs more airport capacity, favouring the construction of an entirely new airport in the Thames Estuary rather than expanding Heathrow.[162] After the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition took power, it was announced that the third runway expansion was cancelled.[163] Two years later, leading Conservatives were reported to have changed their minds on the subject.[164]
Another proposal for expanding Heathrow's capacity was the Heathrow Hub, which aims to extend both runways to a total length of about 7,000 metres and divide them into four so that they each provide two, full length runways, allowing simultaneous take-offs and landings while decreasing noise levels.[165][166]
In July 2013, the airport submitted three new proposals for expansion to the Airports Commission, which was established to review airport capacity in the southeast of England. The Airports Commission was chaired by Sir Howard Davies who, at the time of his appointment was in the employ of GIC Private Limited (formerly known as Government Investment Corporation of Singapore) and a member of its International Advisory Board. GIC Private Limited was then (2012), as it remains today, one of Heathrow's principal owners. Sir Howard Davies resigned these positions upon confirmation of his appointment to lead the Airports Commission, although it has been observed that he failed to identify these interests when invited to complete the Airports Commission's register of interests. Each of the three proposals that were to be considered by Sir Howard Davies's commission involved the construction of a third runway, either to the north, northwest or southwest of the airport.[167]
The commission released its interim report in December 2013, shortlisting three options: the north-west third runway option at Heathrow, extending an existing runway at Heathrow, and a second runway at Gatwick Airport. After this report was published, the government confirmed that no options had been ruled out for airport expansion in the South-east and that a new runway would not be built at Heathrow before 2015.[168] The full report was published on 1 July 2015, and backed a third, north-west, runway at Heathrow.[169]
Reaction to the report was generally negative, particularly from London Mayor Boris Johnson. One senior Conservative told Channel 4: "Howard Davies has dumped an utter steaming pile of poo on the Prime Minister's desk."[170] On 25 October 2016, the government confirmed that Heathrow would be allowed to build a third runway; however, a final decision would not be taken until winter of 2017/18, after consultations and government votes. The earliest opening year would be 2025. On 5 June 2018 Cabinet approved the third runway, with a full vote planned for Parliament.[171] On 25 June 2018, the House of Commons voted 415-119 in favor of the Third Runway.[172] The bill received support from most MPs in the Conservative and Labour Parties.[173] A judicial review against the decision is being launched by four London local authorities affected by the expansion—Wandsworth, Richmond, Hillingdon and Hammersmith and Fulham—in partnership with Greenpeace and London mayor Sadiq Khan.[174] Khan previously stated he would take legal action if it were passed by Parliament.[175]
New transport proposals
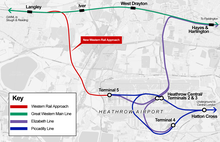
One of the transport projects being considered is the Western Rail Approach to Heathrow
Currently, all rail connections with Heathrow airport run along an east-west alignment to and from central London, and a number of schemes have been proposed over the years to develop new rail transport links with other parts of London and with stations outside the city.[176] This mainline rail service is due to be extended to central London and Essex when the Elizabeth line, currently under construction, opens in 2019.[177]
A 2009 proposal to create a southern link with London Waterloo via the Waterloo–Reading line was abandoned in 2011 due to lack of funding and difficulties with a high number of level crossings on the route into London,[178][179] and a plan to link Heathrow to the planned High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line (with a new station, Heathrow Hub) was also dropped from the HS2 plans in March 2015.[180][181][182]
Among other schemes that have been considered is a rapid transport link between Heathrow and Gatwick Airports, known as Heathwick, which would allow the airports to operate jointly as an airline hub;[183][184] In 2018, the Department for Transport began to invite proposals for privately funded rail links to Heathrow Airport.[185] Projects being considered under this initiative include:
- the Western Rail Approach to Heathrow, a proposal for a spur from the Great Western Main Line to link Heathrow to Reading, Slough, the South West, South Wales and the West Midlands;[186]
Heathrow Southern Railway, a similar scheme to the abandoned Airtrack proposal, which would connect Terminal 5 station with Chertsey or Virginia Water, Staines, London Waterloo Guildford and Clapham Junction;[187]
HS4Air, a proposal for a new high-speed railway line which would link HS2 to the High Speed 1 line and the Channel Tunnel via a southern route, with stations at Heathrow and Gatwick Airports.[188]
Heathrow City
The Mayor of London's office and Transport for London commissioned plans in the event of Heathrow's closure—to replace it by a large built-up area.[189][190][191][192] Some of the plans seem to show terminal 5, or part of it, kept as a shopping centre.
See also
- Airports of London
- Heathrow Worldwide Distribution Centre
- Hello Goodbye (TV series)
- List of airports in the United Kingdom and the British Crown Dependencies
Notes
^ Number of passengers including domestic, international and transit
References
Citations
^ abcd "Aircraft and passenger traffic data from UK airports". UK Civil Aviation Authority. 11 February 2018. Retrieved 11 March 2018..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Nats | Ais - Home". Nats-uk.ead-it.com. Retrieved 24 September 2017.
^ ab "London Heathrow – EGLL". NATS Aeronautical Information Service. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
^ "Company information". Retrieved 4 March 2016.
^ Calder, Simon (1 July 2015). "Heathrow Airport expansion: Commission report backs third runway". The Independent. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Andrew Simms (1 July 2015). "Forget Heathrow expansion, Davies report should tackle frequent flyers". the Guardian. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Third runway at Heathrow cleared for takeoff by ministers". BBC News. 25 October 2016. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Myrtle Avenue, Hounslow". Google Maps. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
^ "Facts and figures". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
^ "International Air Passenger Traffic To and From Reporting Airports for 2013" (PDF). Civil Aviation Authority. p. 68. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 July 2015. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
^ "Heathrow Concorde model removed". BBC News. 30 March 2007. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Prayer and Worship". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 27 January 2013.
^ "Heathrow's hidden gems". CNN. 13 July 2007. Retrieved 21 April 2011.
^ BAA Heathrow (2004–2005). "Flight Evaluation Report 2004/05" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 November 2005. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
^ During periods of westerly operation, aircraft continue to fly in a westerly direction with an easterly tailwind component of up to 5 knots (9.3 km/h; 5.8 mph), if the runway is dry and there is no significant crosswind.
^ "Noise limits". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 27 January 2013.
^ "Heathrow begins trial of noise relief zones". BBC News. 4 December 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Hugh Morris (1 November 2016). "Half of Heathrow's 25,000 noise complaints made by the same 10 people". The Telegraph. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "IATA attacks higher landing charges at British airports". Agence France-Presse. 12 March 2008. Archived from the original on 2 November 2013. Retrieved 14 March 2008.
^ "Heathrow and Gatwick face new airline fee caps". BBC News. 30 April 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Economic Regulation of Heathrow and Gatwick Airports 2008–2013". Civil Aviation Authority. 11 March 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "BA boss joins attack on Heathrow". BBC News. 1 August 2007. Retrieved 28 October 2007.
^ "Heathrow airport hits record 70 million passengers". BBC News. 18 February 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2013.
^ Millward, David (30 October 2007). "Heathrow voted world's least favourite airport". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
^ "Work Smarter: McLaren". Wired. 1 March 2010. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Airport Coordination Ltd (February 2002). "Submission to the CAA Regarding Peak Periods at Heathrow" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 February 2008. Retrieved 13 January 2008.
^ "BA pushes for 'mixed mode' at Heathrow". UK Airport News. Archived from the original on 12 December 2007. Retrieved 31 May 2008.
^ Webster, Ben (7 August 2007). "Heathrow is defeated in its attempt to ban environmental campaigners". The Times. London. Retrieved 9 August 2007.
(subscription required)
^ ab "Security (body) scanners". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Airport body scanners: Heathrow trials new 'privacy friendly' security technology". Daily Mail. London. 5 September 2011. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow - Heathrow bids farewell to Terminal 1" (Press release). Heathrow. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Above Us The Skies: The Story Of BAA – 1991 (Michael Donne – BAA plc), p. 40
^ Walton, John (31 May 2012). "British Airways takes over, rebrands BMI lounge at Heathrow T1". Australian Business Traveller. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Terminal One deserted ahead of closure next month". ITV News. 28 May 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Calder, Simon (23 January 2015). "Heathrow and Gatwick: Terminal confusion at London's airports". The Independent. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Paylor, Anne (29 June 2015). "London Heathrow turns out the lights in Terminal 1". Air Transport World. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Mellon, James (30 June 2015). "Heathrow shuts doors on Terminal 1 flights". London: Flightglobal. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Blachly, Linda (4 June 2014). "United is first airline to fly out of Heathrow Airport's new T2". Air Transport World. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Terminal 2 named Queen's Terminal". BBC News. 14 June 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow airport's new Terminal 2 opens to passengers". BBC News. 23 November 2009. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Hofmann, Kurt (28 May 2014). "New London Heathrow T2 opening set for June 4". Air Transport World. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "The new Terminal 2: Only one year to go" (Press release). Heathrow Airport. 4 June 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow's Terminal 2 to be opened in stages". BBC News. 3 June 2014. Retrieved 4 June 2014.
^ "Heathrow Terminal One deserted ahead of closure next month". ITV News. 28 May 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Demolition work begins at Heathrow's Terminal 2". BBC News. 29 April 2010. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Our history". Heathrow Airport Holdings. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Debut A380 flight lands in London". BBC News. 18 March 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "BAA Heathrow unveils plans to re-develop Terminal 3" (Press release). BAA. 15 February 2007. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow facts and figures". Heathrow Airport Limited. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Terminal 4's £100m new check-in area reaches the top" (Press release). BAA. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Queen opens new Heathrow Terminal". BBC News. 14 March 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "British Airways reveals what went wrong with Terminal 5". Computer Weekly. 14 May 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Iberia to move to Heathrow T5". Business Traveller. 8 February 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Andy, Ivy (1 January 2012). "Londen Heathrow". Vliegveld Londen (in Dutch). Vliegveld Londen. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Terminal 5" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2011.
^ "Heathrow Terminal 5: The Vital Statistics". Sky News. 15 March 2008. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2011.
^ "ULTra PRT – FAQ". ATS ULTra. 2010. Archived from the original on 16 June 2010. Retrieved 1 July 2010.
^ heathrowairport.com – Heathrow destinations and airlines retrieved 3 September 2018
^ "Heathrow looks ahead", Airports (Key Publishing), September/October 2007, p. 30.
^ "Terminal 2 opens as the Star Alliance terminal at London Heathrow Airport". World Airline News. 4 June 2014.
^ "London Heathrow Airport bids farewell to Terminal 1". BBC News. 29 June 2015.
^ "Air India re-locates at Heathrow T2 - Business Traveller – The leading magazine for frequent flyers". Business Traveler. 26 January 2017. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Delta to move all Heathrow services to Terminal 3 - Business Traveller – The leading magazine for frequent flyers". Business Traveler. 22 August 2016. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow destinations list". Retrieved 6 June 2018.
^ "Flight Schedules - Air Canada". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ https://www.airchina.co.uk/CAOnline/dyn/air/booking/availability
^ "Air France flight schedule". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ "Flight schedules and notifications". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ http://s21.q4cdn.com/616071541/files/doc_news/2018/08/American-Airlines-Expands-European-Footprint-and-Modifies-Asia-Service-GUIDE-082118.pdf
^ "British Airways - Timetables". Retrieved 21 August 2018.
^ "British Airways cambia la ruta Bilbao-Londres de Heathrow a Gatwick". Deia. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
^ https://www.britishairways.com/travel/flightops/public/en_gb
^ https://www.britishairways.com/travel/flightops/public/en_gb
^ 25 September 2018 by Tom Otley (25 September 2018). "British Airways confirms Osaka route". Businesstraveller.com. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ "British Airways - British Airways Steels With Deal With New Route To Pittsburgh". Mediacentre.britishairways.com. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ Author LondonAirTravel (2 November 2018). "British Airways Suspends London Heathrow - Tallinn – London Air Travel". Londonairtravel.com. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
^ "British Airways Trade Support - AskBA". Britishairways.com. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
^ ab "British Airways - SUMMER SCHEDULE SHAPES UP". Mediacentre.britishairways.com. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ http://www.mediacentre.britishairways.com/pressrelease/details/86/2018-247/10207?ref=Home
^ http://mediacentre.britishairways.com/pressrelease/details/86/2018-247/10366?ref=Home
^ http://mediacentre.britishairways.com/pressrelease/details/86/2018-247/10366?ref=Home
^ "China Southern Airlines timetable". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ "Delta Flight Status". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ https://www.cornwallairportnewquay.com/press/press-releases/cornwall-airport-newquay-gains-heathrow-connection
^ "Garuda Indonesia delays London Heathrow resumption to Dec 2018". Routesonline. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
^ "Timetable - KLM.com". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ "Timetable - Lufthansa". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ "Timetables | Qantas". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ ab "Turkish Airlines to fully move to Istanbul New in late 4Q18". ch-aviation.com. 16 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ "United Flight Schedules". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ "Flight Schedules | Virgin Atlantic". Retrieved 13 October 2018.
^ 27 June 2018 by Becky Ambury (27 June 2018). "Virgin Atlantic to end Dubai to London Heathrow flights". Businesstraveller.com. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ 16 May 2018 by Tom Otley (16 May 2018). "Virgin to launch London Heathrow to Las Vegas flights". Businesstraveller.com. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ "Passenger Traffic for the last 12 months". ACI. 11 April 2016. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Investor Relations - Paris Airports Traffic". Aeroports De Paris. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Turkish Airport Statistics". DHMI. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Cargo Traffic 2013 Final". Airports Council International. 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ ab "Airport Data 2017". UK Civil Aviation Authority. 3 March 2017. Tables 12.1(XLS) and 12.2 (XLS). Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Domestic Air Pax Traffic Route Analysis" (PDF). UK Civil Aviation Authority. 3 March 2017. Tables 12.1(XLS) and 12.2 (XLS). Retrieved 18 May 2018.
^ "Explore Our Working World". British Airways. 3 March 2006. Archived from the original on 3 March 2006.
^ "World Business Centre Heathrow". thearoragroup.com. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "IAG – International Airlines Group – Investor Relations Team". Iairgroup.com. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "IAG – International Airlines Group – About Us". Iairgroup.com. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "World Airline Directory." Flight International. 26 March – 1 April 1997. 58. "Speedbird House, PO Box 10, London Heathrow Airport, Hounslow, Middlesex, TW6 2JA, UK."
^ McKellar, Susie and Penny Sparke. "The Contemporary Office." Interior Design and Identity. Manchester University Press, 2004. 200. Retrieved from Google Books on 12 February 2010.
ISBN 0-7190-6729-4,
ISBN 978-0-7190-6729-7.
^ "Best Way to Get from Heathrow to London". www.autoeurope.com. Auto Europe. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Airport trains". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Travel between terminals – Heathrow terminal transfers". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Heathrow Free Travel Zone Heathrow Airport
^ "Heathrow to Debut Futuristic Travel Pods". PopSci.com.au. 27 January 2009. Retrieved 27 January 2009.
^ "My Pods". Futureairports. 2014 (1): 61.
^ Home Hotel Hoppa
^ "Heathrow: Airport taxi". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Emirates launches A380 model at LHR". Business Traveller. 24 July 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Short Stay Parking". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Long Stay Parking". Heathrow Airport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow parking picking up and dropping off information". www.heathrow.com. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Transport for London free maps 'London Cycling Guide 6' covers Terminals 1, 2 & 3 while 'London Cycling Guide 9' covers Terminal 4 (as of the June 2007 revision).
^ Cycling and Motorcycling map Archived 11 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
^ Hamilton, Fiona (3 March 2003). "On This Day The Times 3 March 1948". The Times. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
(subscription required)
^ "Aviation Safety Network G-AHPN". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "ICAO Aircraft Accident Digest No 7, Page 46" (PDF). ICAO. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Flight 13 January 1956, Civil Aviation". Flightglobal. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Blackman, Tony (2007). Vulcan Test Pilot: My Experiences in the Cockpit of a Cold War Icon. London: Grub Street.
ISBN 978-1-904943-88-4. p. 142.
^ "Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "ASN Aircraft accident description Vickers 951 Vanguard G-APEE – London–Heathrow Airport (LHR)". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Night the sky turned to flames". The Scotsman. Edinburgh. 1 December 2005. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Women awarded the George Cross". Stephen-stratford.com. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Aviation Safety Network G-AMAD". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Accident description". Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "1972: UK's worst air crash kills 118". BBC News. 18 June 1972. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Huge delays after Heathrow crash-landing". The Independent. London. 9 December 1996. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Accident description". Aviation Safety Net. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Symonds, Tom (3 August 2000). "Pilots praised for crash landing". BBC News. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Symonds, Tom (4 September 2008). "'Ice in fuel' caused BA jet crash". BBC News. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Borrell, Clive (28 June 1968). "Ramon Sneyd denies that he killed Dr King". The Times. London. p. 2.
(subscription required)
^ "Heathrow Airport History". Milesfaster.co.uk. Retrieved 31 May 2008.
^ "Brinks Mat gold". BBC News. 15 April 2000. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Reynolds, Paul (16 December 2002). "Assad engages politics of politeness". BBC News. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "1988: Jumbo jet crashes onto Lockerbie". BBC News. 21 December 1988. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Henderson, Scott (1998). Silent Swift Superb: The Story of the Vickers VC10. Newcastle-upon-Tyne: Scoval. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-901125-02-3.
^ "$3m heist at Heathrow". BBC News. 19 March 2002. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Archive index at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Flying Squad foils £80m robbery". BBC News. 18 May 2004. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Batty, David; Oliver, Mark (10 August 2006). "'Mass murder terror plot' uncovered". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Climate protest on Heathrow plane". BBC News. 25 February 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Man arrested over Heathrow alert". BBC News. 13 March 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Dron, Alan (13 July 2015). "London Heathrow cancels flights due to protests over third runway". Air Transport World. Archived from the original on 15 July 2015.
^ "Heathrow Airport climate change protest delays flights". BBC News. 13 July 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Icelandic volcanic ash alert grounds UK flights". BBC News. 15 April 2010. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Winter Resilience Enquiry" (PDF).
^ "BAA launches inquiry into Heathrow Airport snow chaos". BBC News. 23 December 2010. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "De-icing Aircraft Parking Stands". Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Plane on fire at Heathrow airport was Boeing Dreamliner-TV". Reuters. 12 July 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow shut after Boeing Dreamliner 787 fire". BBC News. 12 July 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ AAIB aircraft accident report
2/2015
^ "Man dies in Heathrow Airport vehicle crash". BBC News. BBC. 14 February 2018. Retrieved 3 July 2018.
^ "Britain's Transport Infrastructure: Adding Capacity at Heathrow: Decisions Following Consultation, January 2009" (PDF). Department of Transport. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 May 2010. Retrieved 16 January 2009.
^ "The Future of Air Transport" (PDF). 1 December 2003.
^ "Industry backs third Heathrow runway as consultation opens". Flight International. 22 November 2007. Archived from the original on 26 December 2007. Retrieved 8 December 2007.
^ Needham, Duncan (27 October 2014). "Maplin: the Treasury and London's third airport in the 1970s". History & Policy. History & Policy. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow's new runway". BBC News. 15 January 2009. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow third runway plans scrapped by new government". BBC News. 12 May 2010. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Helm, Toby; Doward, Jamie (24 March 2012). "Top Tories admit: we got it wrong on third runway". The Observer. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Parker, Andrew; Jacobs, Rose (10 March 2013). "Pilot plots longer Heathrow runways". Financial Times. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "CPS paper – Double Upon Heathrow – July 2013" (PDF). Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow submits third runway options to Davies Commission". BBC News. 17 July 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Airports Commission reveals expansion shortlist". BBC News. 17 December 2013. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Airports Commission releases final report". gov.uk. 1 July 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Blackhurst, Chris (1 July 2015). "Heathrow expansion: This final 'conclusion' has simply fanned the airport flames". The Independent. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Heathrow Airport: Cabinet approves new runway plan". BBC News. 5 June 2018.
^ Davidson, Lynn (26 June 2018). "Heathrow Airport third runway wins Parliament vote after protesters force lockdown and MPs shout 'Where's Boris?'". Thesun.co.uk. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ Sparrow, Andrew; Rawlinson, Kevin (25 June 2018). "House of Commons backs third runway for Heathrow airport – as it happened | Politics". The Guardian. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ "Heathrow expansion plans approved for take-off after Commons vote".
^ "Heathrow third runway: Sadiq Khan backs legal challenge - BBC News". BBC News. Bbc.co.uk. 21 June 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
^ Coogan, Matthew A. (2000). Improving Public Transportation Access to Large Airports. Leigh Fisher Associates, Transportation Research Board, Transit Cooperative Research Program. p. 66. ISBN 9780309066594. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ Blow, Christopher J. (2013). "15. Public transport interchanges". Airport Terminals: Butterworth Architecture Library of Planning and Design. Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 90–92. ISBN 9781483145051. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ "Heathrow Airtrack Waterloo rail link shelved by BAA". BBC News London. 11 April 2011. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Samuel, A. (11 April 2011). "Heathrow: 'No option but to withdraw proposed Airtrack link to Staines'". Rail News from Rail.co. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2011.
^ Oakeshott, Isabel; Gourlay, Chris (4 January 2009). "Heathrow train plan to allay environmental fears". The Times. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
(subscription required)
^ "High Speed Rail: Investing in Britain's Future". Department for Transport. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "HS2: Heathrow spur plans dropped by transport minister". BBC News. 10 March 2015.
^ "Heathrow and Gatwick airports: Ministers mull rail link". BBC News. 8 October 2011. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Commons, The Committee Office, House of. "House of Commons - Transport Committee: Written evidence from Interlinking Transit Solutions Ltd (AS 115)". www.publications.parliament.uk. Retrieved 1 July 2017.
^ Morby, Aaron (8 May 2018). "DfT tests appetite for £2.3bn Heathrow rail links | Construction Enquirer". www.constructionenquirer.com. Construction Enquirer. Archived from the original on 12 September 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ MCINTYRE, FIONA. "Private partner wanted for £900M Heathrow rail link". New Civil Engineer. Archived from the original on 12 September 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
^ "Proposed Route - Heathrow Southern Railway". Heathrow Southern Railway. Retrieved 22 August 2018.
^ Nolan, Tara. "HS4Air: The UK needs a strategic plan for its transport infrastructure". Global Railway Review.
^ Cockroft, Steph (16 July 2014). "Heathrow City, 190,000-home town that would open if airport closes". Daily Mail. London. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ "Drones and homes replace runways in 'Heathrow City' plans". Financial Times. London.
^ "'Heathrow City' designs set out". Express & Star. 15 July 2014. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
^ Crerar, Pippa (5 December 2013). "Vision of a new London borough on site of abandoned Heathrow is revealed". London Evening Standard. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
Bibliography
- Cotton, Jonathan; Mills, John & Clegg, Gillian. (1986) Archaeology in West Middlesex. Uxbridge: London Borough of Hillingdon
ISBN 0-907869-07-6
- Gallop, Alan. (2005) Time Flies: Heathrow At 60. Stroud: Sutton Publishing
ISBN 0-7509-3840-4
- Halpenny, Bruce B. (1992) Action Stations Vol.8: Military Airfields of Greater London.
ISBN 1-85260-431-X
- Sherwood, Philip. (1990) The History of Heathrow. Uxbridge: London Borough of Hillingdon
ISBN 0-907869-27-0
- Sherwood, Philip (editor). (1993) The Villages of Harmondsworth. West Middlesex Family History Society,
ISBN 0 9511476 2 5
- Sherwood, Philip. (1999) Heathrow: 2000 Years of History. Stroud: Sutton Publishing
ISBN 0-7509-2132-3
- Sherwood, Philip. (2006) Around Heathrow Past & Present. Sutton Publishing
ISBN 0-7509-4135-9
- (Contains many pairs of photographs, old (or in one case a painting), and new, each pair made from the same viewpoint.)
- Sherwood, Philip. (2009) Heathrow: 2000 Years of History. Stroud: The History Press
ISBN 978-0750921329
- Sherwood, Philip. (2012) Around Heathrow Through Time. Amberley Publishing,
ISBN 978-1-4456-0846-4
- Sherwood, Tim. (1999) Coming in to Land: A Short History of Hounslow, Hanworth and Heston Aerodromes 1911–1946. Heritage Publications (Hounslow Library)
ISBN 1-899144-30-7
- Smith, Graham. (2003) Taking to the Skies: the Story of British Aviation 1903–1939. Countryside
ISBN 1-85306-815-2
- Smith, Ron. (2002) British Built Aircraft Vol.1. Greater London: Tempus
ISBN 0-7524-2770-9
- Sturtivant, Ray. (1995) Fairey Aircraft: in Old Photographs. Alan Sutton
ISBN 0-7509-1135-2
- Taylor, H.A. (1974) Fairey Aircraft since 1915. Putnam
ISBN 0-370-00065-X. - Taylor, John WR. (1997) Fairey Aviation: Archive Photographs. Chalford
ISBN 0-7524-0684-1
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to London Heathrow Airport. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Heathrow Airport. |
- Official website
- Heathrow Airport Consultative Committee
- Detailed maps of taxiways, stands etc
The building of Heathrow Video at the Internet Archive
- Heathrow Air Watch – Information on pollution levels around Heathrow
London Heathrow airport data (at Airportsdata.net)