New Zealand general election, 2008
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 120 seats (plus 2 overhang seats) in the New Zealand House of Representatives 62 seats were needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Opinion polls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 2,376,480 (79.46%) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2008 New Zealand general election was held on 8 November 2008 to determine the composition of the 49th New Zealand parliament. The conservative National Party, headed by its parliamentary leader John Key, won the largest share of votes and seats, ending nine years of government by the social-democratic Labour Party, led by Helen Clark. Key announced a week later that he would lead a National minority government with confidence-and-supply support from the ACT, United Future and Māori parties. The Governor-General swore Key in as New Zealand's 38th Prime Minister on 19 November 2008. This marked an end to nine years of Labour Party government, and the beginning of the Fifth National Government of New Zealand which would govern for 9 years, until its loss to the Labour Party in the 2017 general election.
The Green Party became the third-largest party in Parliament, with nine seats. The ACT Party came joint-fourth (in terms of seats), increasing their number of seats from two to five, and reversing some of their losses from the 2005 election. The Māori Party also won five seats – out of the seven Māori seats – creating an overhang of two seats. The New Zealand First party, which had seven MPs in the previous parliament, failed to win any electorates or pass the 5 per cent MMP threshold, and therefore won no seats in the new parliament.
In his victory speech, John Key announced the readiness of the ACT, Maori Party and United Future parties to co-operate with the National Party to form the next government, the Fifth National Government of New Zealand. In her concession speech, Helen Clark announced her resignation as the parliamentary leader of the Labour Party. She had led the party since 1993, and had served as prime minister since the 1999 election.
Contents
1 Results
1.1 Parliamentary parties
1.2 Non-parliamentary parties
1.3 Votes summary
1.4 Electorate results
1.5 List results
1.5.1 Unsuccessful list candidates
2 Dates
3 Political parties
3.1 Contesting parties
3.2 Non-contesting parties
3.3 Retiring MPs
4 MPs who lost their seats
4.1 New Zealand First
4.2 United Future Party
4.3 Labour Party
4.4 Independents
5 Voter enrolment and turnout
6 Issues
6.1 Electoral Finance Act
6.2 Economic conditions
6.3 Taxation
6.4 Trust
7 Electorates
7.1 Boundary changes
7.2 Situation after 2005
7.3 Seats that changed hands
7.4 New seats won by incumbent MPs
7.5 New MPs in vacated seats
8 Opinion polling
9 Coalition preferences during the campaign
10 Candidates
11 See also
12 Notes
13 Further reading
14 External links
Results
The Labour government failed to secure a fourth consecutive term, after the National Party entered into support agreements with the ACT, United Future and Māori parties, resulting in a National minority government.[1]
The Chief Electoral Officer released the official results on 22 November 2008.[2]
Parliamentary parties
| party | votes | % of votes | seats | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | change | electorate | list | total | change | |||
National | 1,053,398 | 44.93 | +5.83 | 41 | 17 | 58 | +10 | |
Labour | 796,880 | 33.99 | −7.11 | 21 | 22 | 43 | −7 | |
Green | 157,613 | 6.72 | +1.42 | 0 | 9 | 9 | +3 | |
ACT | 85,496 | 3.65 | +2.14 | 1 | 4 | 5 | +3 | |
Māori | 55,980 | 2.39 | +0.27 | 5 | 0 | 5 | +1 | |
Progressive | 21,241 | 0.91 | −0.25 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
United Future | 20,497 | 0.87 | −1.80 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −2 | |
| other parties | 153,461 | 6.55 | +5.23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −7a | |
total | 2,344,566 | 100.00 | 70 | 52 | 122 | +1b | ||
National minority government | 1,159,391 | 49.45 | 43 | 21 | 64 | +14 | ||
| Opposition parties | 1,031,714 | 44.00 | 27 | 31 | 58 | -7 | ||
| party informal votes | 11,970c | |||||||
| disallowed special votes | 19,517c | |||||||
| disallowed ordinary votes | 427c | |||||||
| total votes cast | 2,376,480 | |||||||
| turnout | 79.46d | -1.46 | ||||||
a The loss of seven seats by 'other parties' shown here compared to the 2005 election result was mostly due to NZ First failing to clear the MMP threshold while two independents, Gordon Copeland and Taito Phillip Field, who had split from their parties since the 2005 election lost their seats.
b The Māori Party gained two overhang seats (increasing parliament's size from 120 to 122 seats) by virtue of gaining more electorate seats than their party vote would have otherwise given them. This was one more overhang seat than in 2005.
c"Party Votes and Turnout by Electorate". Chief Electoral Office, New Zealand Ministry of Justice. Retrieved 29 November 2008..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
dThe turnout is given as a percentage of those enrolled to vote. In New Zealand, enrolment is compulsory, though voting is not. "New Zealand General Election 2008 – Official Results". Elections New Zealand. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
Non-parliamentary parties
Party vote percentage
National (44.93%)
Labour (33.99%)
Green (6.72%)
NZ First (4.07%)
ACT (3.65%)
Māori (2.39%)
New Zealand Progressive Party (0.91%)
United Future New Zealand (0.87%)
Other (2.47%)
| Party | Votes | % | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
New Zealand First | 95,356 | 4.07 | -1.65 | |
Bill and Ben | 13,016 | 0.56 | ||
Kiwi Party | 12,755 | 0.54 | ||
Legalise Cannabis | 9,515 | 0.41 | +0.16 | |
New Zealand Pacific | 8,640 | 0.37 | ||
Family Party | 8,176 | 0.35 | ||
Alliance | 1,909 | 0.08 | +0.01 | |
Democrats for Social Credit | 1,208 | 0.05 | ±0.00 | |
Libertarianz | 1,176 | 0.05 | +0.01 | |
Workers Party of New Zealand | 932 | 0.04 | ||
Residents Action Movement | 465 | 0.02 | ||
Republic of NZ | 313 | 0.01 | -0.01 | |
| Minor parties, total | 153,461 | 6.51 | +5.32 | |
Votes summary
Electorate results

Party affiliation of the winning electorate candidates.
While the National Party has dominated rural seats since 1938, it achieved a clean sweep this year. The 19 general electorates which Labour retained all have a predominantly urban character, excluding Waimakariri, a predominantly urban area but with a significant rural population, resulting in a Labour MP narrowly elected but National winning the party vote commandingly. Palmerston North remains the only provincial city with a Labour MP. The two seats of Hamilton (considered "bellwether" seats as their demographic profile closely resembles that of the country as a whole[3]) both went to National.
The table below shows the results of the 2008 general election:
Key:
National | Labour | NZ First |
ACT | United Future | Māori |
| Electorate | Incumbent | Winner | Majority | Runner up | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Auckland Central | Judith Tizard | Nikki Kaye | 1,497 | Judith Tizard | |||
Bay of Plenty | Tony Ryall | 17,604 | Carol Devoy-Heena | ||||
Botany | New electorate | Pansy Wong | 10,872 | Koro Tawa | |||
Christchurch Central | Tim Barnett | Brendon Burns | 935 | Nicky Wagner† | |||
Christchurch East | Lianne Dalziel | 5,765 | Aaron Gilmore† | ||||
Clutha-Southland | Bill English | 15,475 | Don Pryde | ||||
Coromandel | Sandra Goudie | 14,560 | Hugh Kininmonth | ||||
Dunedin North | Pete Hodgson | 7,155 | Michael Woodhouse† | ||||
Dunedin South | David Benson-Pope | Clare Curran | 6,449 | Conway Powell | |||
East Coast | Anne Tolley | 6,413 | Moana Mackey† | ||||
East Coast Bays | Murray McCully | 13,974 | Vivienne Goldsmith | ||||
Epsom | Rodney Hide | 12,882 | Richard Worth† | ||||
Hamilton East | David Bennett | 8,820 | Sue Moroney† | ||||
Hamilton West | Martin Gallagher | Tim Macindoe | 1,618 | Martin Gallagher | |||
Helensville | John Key | 20,547 | Darien Fenton† | ||||
Hunua | Paul Hutchison | 15,858 | Jordan Carter | ||||
Hutt South | Trevor Mallard | 4,086 | Paul Quinn† | ||||
Ilam | Gerry Brownlee | 11,893 | Sam Yau | ||||
Invercargill | Eric Roy | 6,664 | Lesley Soper | ||||
Kaikoura | Colin King | 11,077 | Brian McNamara | ||||
Mana | Winnie Laban | 6,155 | Hekia Parata† | ||||
Māngere | Taito Phillip Field | William Sio | 7,126 | Taito Phillip Field (Pacific) | |||
Manukau East | Ross Robertson | 12,445 | Kanwal Singh Bakshi† | ||||
Manurewa | George Hawkins | 6,726 | Cam Calder | ||||
Maungakiekie | Mark Gosche | Sam Lotu-Iiga | 1,942 | Carol Beaumont† | |||
Mount Albert | Helen Clark | 10,351 | Ravi Masuku | ||||
Mount Roskill | Phil Goff | 6,418 | Jackie Blue† | ||||
Napier | Chris Tremain | 9,018 | Russell Fairbrother | ||||
Nelson | Nick Smith | 8,471 | Maryan Street† | ||||
New Lynn | David Cunliffe | 4,025 | Tim Groser† | ||||
New Plymouth | Harry Duynhoven | Jonathan Young | 105 | Harry Duynhoven | |||
North Shore | Wayne Mapp | 14,574 | Phil Twyford† | ||||
Northcote | Jonathan Coleman | 9,360 | Hamish McCracken | ||||
Northland | John Carter | 10,054 | Shane Jones† | ||||
Ōhariu | Peter Dunne | 1,006 | Charles Chauvel† | ||||
Ōtaki | Darren Hughes | Nathan Guy | 1,354 | Darren Hughes† | |||
Pakuranga | Maurice Williamson | 13,906 | Brian Kelly | ||||
Palmerston North | Steve Maharey | Iain Lees-Galloway | 1,117 | Malcolm Plimmer | |||
Papakura | New electorate | Judith Collins | 10,277 | Dave Hereora | |||
Port Hills | New electorate | Ruth Dyson | 3,452 | Terry Heffernan | |||
Rangitata | New electorate | Jo Goodhew | 8,112 | Julian Blanchard | |||
Rangitīkei | Simon Power | 12,042 | Jills Burney | ||||
Rimutaka | Paul Swain | Chris Hipkins | 753 | Richard Whiteside | |||
Rodney | Lockwood Smith | 15,635 | Conor Roberts | ||||
Rongotai | Annette King | 9,020 | Chris Finlayson† | ||||
Rotorua | Steve Chadwick | Todd McClay | 5,065 | Steve Chadwick† | |||
Selwyn | New electorate | Amy Adams | 11,075 | David Coates | |||
Tāmaki | Allan Peachey | 17,020 | Josephine Bartley | ||||
Taranaki-King Country | Shane Ardern | 15,618 | Renée van de Weert | ||||
Taupō | Mark Burton | Louise Upston | 6,445 | Mark Burton | |||
Tauranga | Bob Clarkson | Simon Bridges | 11,742 | Winston Peters | |||
Te Atatū | Chris Carter | 5,298 | Tau Henare† | ||||
Tukituki | Craig Foss | 7,811 | Rick Barker† | ||||
Waikato | Lindsay Tisch | 12,850 | Jacinda Ardern† | ||||
Waimakariri | Clayton Cosgrove | 390 | Kate Wilkinson† | ||||
Wairarapa | John Hayes | 6,758 | Denise MacKenzie | ||||
Waitakere | Lynne Pillay | Paula Bennett | 632 | Lynne Pillay† | |||
Waitaki | New electorate | Jacqui Dean | 11,039 | David Parker† | |||
Wellington Central | Marian Hobbs | Grant Robertson | 1,904 | Stephen Franks | |||
West Coast-Tasman | Damien O'Connor | Chris Auchinvole | 971 | Damien O'Connor | |||
Whanganui | Chester Borrows | 6,333 | Hamish McDouall | ||||
Whangarei | Phil Heatley | 14,663 | Paul Chalmers | ||||
Wigram | Jim Anderton | 4,767 | Marc Alexander | ||||
Māori Electorates | |||||||
Hauraki-Waikato | New electorate | Nanaia Mahuta | 888 | Angeline Greensill | |||
Ikaroa-Rāwhiti | Parekura Horomia | 1,645 | Derek Fox | ||||
Tāmaki Makaurau | Pita Sharples | 7,540 | Louisa Wall | ||||
Te Tai Hauāuru | Tariana Turia | 7,817 | Errol Mason | ||||
Te Tai Tokerau | Hone Harawira | 6,308 | Kelvin Davis† | ||||
Te Tai Tonga | Mahara Okeroa | Rahui Katene | 1,049 | Mahara Okeroa | |||
Waiariki | Te Ururoa Flavell | 6,812 | Mita Ririnui† | ||||
- ^† These people entered Parliament at the election as list MPs
List results

Highest polling party in each electorate.
National | Labour | Green | ACT |
David Carter (09) Chris Finlayson (14) Tim Groser (15) Steven Joyce (16) Georgina te Heuheu (17) Richard Worth (25)1 Tau Henare (26) Kate Wilkinson (30) Hekia Parata (36) Melissa Lee (37) Kanwaljit Singh Bakshi (38) Nicky Wagner (43) Jackie Blue (45) Katrina Shanks (46) Paul Quinn (48) Michael Woodhouse (49) Aaron Gilmore (56) | Michael Cullen (02)1 Maryan Street (09) Rajen Prasad (12) Shane Jones (16) David Parker (17) Darren Hughes (19)1 Jacinda Ardern (20) Raymond Huo (21) Sue Moroney (22) Mita Ririnui (23) Moana Mackey (25) Phil Twyford (26) Charles Chauvel (27) Carol Beaumont (28) Kelvin Davis (29) Steve Chadwick (30) Ashraf Choudhary (31) Lynne Pillay (32) Darien Fenton (33) Rick Barker (34) Carmel Sepuloni (35) Stuart Nash (36) | Jeanette Fitzsimons (01)1 Russel Norman (02) Sue Bradford (03)1 Metiria Turei (04) Sue Kedgley (05) Keith Locke (06) Kevin Hague (07) Catherine Delahunty (08) Kennedy Graham (09) | Heather Roy (02) Roger Douglas (03) John Boscawen (04) David Garrett (05)1 |
Unsuccessful list candidates
National | Cam Calder2, Conway Powell, Stephen Franks, Marc Alexander, Mita Harris, Terry Heffernan, Ravi Musuku, Richard Whiteside, Paul O'Brien, Youngshin Watkins, Hamuera Mitchell, Viv Gurrey, Dugald McLean, Simon O'Connor | |
Labour | Damien O'Connor2, Judith Tizard, Mark Burton, Mahara Okeroa, Martin Gallagher, Dave Hereora, Louisa Wall2, Lesley Soper, Hamish McCracken, Erin Ebborn-Gillespie, Errol Mason, Chris Yoo, Josephine Bartley, Don Pryde, Michael Wood, Farida Sultana, Denise MacKenzie, Julian Blanchard, Hamish McDouall, Anjum Rahmen, Susan Zhu, Kate Sutton, Conor Roberts, Koro Tawa, Jills Angus-Burney Rangitikei, Vivienne Goldsmith, Eamon Daly, Brian Kelly, Jordan Carter, Tracey Dorreen, Renee van de Weert, Anne Pankhurst, David Coates, Hugh Kinnimonth, Carol Devoy-Heena, Raj Thandi | |
Green | David Clendon2, Gareth Hughes2, Steffan Browning, Mojo Mathers, Mike Ward, Quentin Duthie, Mikaere Curtis, Richard Leckinger, Jeanette Elley, Virginia Horrocks, Donna Wynd, David Hay, Dianne Mellor, James Redwood, Lisa Er, Jan McLauchlan, Lizzie Gillett, Rayna Fahey, Craig Carson, Richard Tindall, Paul Doherty, Michael Woodcok, Pieter Watson, Bevan Tipene, Peter Taylor, Karen Summerhays, Mua Strickson-Pua, Gary Stewart, Dale Stevens, Brett Stansfield, James Shaw, Raewyn Saville, Denise Roche, Rebecca Redwood, Linda Persson, Rawiri Paratene, Lawrence O'Halloran, John Milnes, Alan Liefting, Martin Leiding, Dora Langsbury, Fiona Kenworthy, Jim Kebbell, Alan Johnson, Wendy Harper, Rob Hamill, Rachel Grimwood, Tim Gow, Xavier Goldie, Michael Gilchrist, Ryan Garland, Shane Gallagher, Zachary Dorner, Kath Dewar, Peter Cooper, Joseph Burston, Oliver Briggs | |
NZ First | Winston Peters, Peter Brown, Ron Mark, Doug Woolerton, Barbara Stewart, Pita Paraone, Le-Aufa'amulia Asenati Lole-Taylor, Edwin Perry, Steven Campbell, Brendan Horan, Melanie Mark-Shadbolt David Scott, Tracey Martin, Dail Jones, Brent Catchpole, Helen Mulford-Tyler, Craig McNair, Joseph Gregory, Douglas Nabbs, John Hall, Graham Odering, Linda King | |
ACT | Hilary Calvert2, Peter Tashkoff, John Ormond, Colin du Plessis, Shawn Tan, Ron Scott, Aaron Keown, Nick Kearney, Lyn Murphy, David Olsen, Frances Denz, Dave Moore, Mike Bridge, Lech Beltowski, Beryl Good, Ashok Kumar, Dave Tattersfield, William Wong, John Thompson, Kevin Campbell, Mark Davies, Michael Bailey, Carl Freimann, Chris Albers, Vince Ashworth, Shane Atkinson, Ray Bassett, Hardev Brar, Mike Collins, Alan Davidson, Andrew Falloon, John Fraser | |
Māori | Angeline Greensill, Derek Fox, Naida Glavish, Iritana Tāwhiwhirangi, Hector Matthews, Te Orohi Paul, Amokura Panoho, Grant Hawke, Bronwyn Yates, Josie Peita, Richard Orzecki, Mereana Pitman, Te Awanuiarangi Black, Georgina Haremate-Crawford | |
Progressive | Matt Robson, Josie Pagani, Paula Gillon, Philip Clearwater, Vivienne Shepherd, Trevor Barnard, Brenda Hill, Craig Hutchinson, Justin Robson, Ngov Ly, Sukerna Amirapu, Somnath Sarkar Bagchi, Sukhdev Singh Bains, Sokunthea Cheam, Seyed Kazemi Yazdi, Debbie Lucas, Claire Main, Philippa Main, John Maurice, Jacqueline McAlpine, Elizabeth Patchett, Talatala Po'e, Pavitra Roy, Elspeth Sandys, David Somerset, Ralph Taylor | |
United Future | Judy Turner, Denise Krum, Graeme Reeves, Aaron Solomon, Murray Smith, Neville Wilson, Francis Owen, Janet Tuck, Karuna Muthu, Robin Loomes, Gregory Graydon, Damian Light, Vanessa Roberts, Aaron Galey-Young, Ian McInnes, Kelleigh Sheffield-Cranstoun, Brian Ward, Vaughan Smith, James Stowers, Bryan Mockridge, Arthur Solomon, Jennifer Hurn, Manogi Head, Diane Brown, Quentin Todd, Rochelle White, John Langford, Philip Johnson, Kenneth Smith | |
Bill and Ben | Jamie Linehan (Bill), Benjamin Boyce (Ben) | |
Kiwi | Larry Baldock, Gordon Copeland, Simon Kan, Frank Naea, Simonne Dyer, Bernie Ogilvy, Anthony Christiansen, Antony Buntin, Vapnierka Kupenga, Leighton Baker, Camilia Chin, Kevin Stitt, Robyn Jackson, Josephine van Kempen, Marjorie Mulholland, Joel Sison, Grace Haden, Joseph Rebello, Robin Westley, Rebekah Clement, Alistair Belcher, Amjad Khan, Lindsay Cameron, Philip Wescombe, Christian Dawson | |
Legalise Cannabis | Michael Appleby, Michael Britnell, Paula Lambert, Kevin O'Connell, Julian Crawford, Irinka Britnell, Steven Wilkinson, Judy Daniels, Vincent McLeod, Daniel Bruce, Paul McMullan, Jeffrey Lye, Philip Pophristoff, Jason Baker-Sherman, Judith Matangi, Neville Yates, Elanor Stedman, Peter Green, Mark Bradford, Frederick MacDonald | |
Pacific | Taito Phillip Field, Milo Siilata, Matapakia Ngaroi, Aiolupotea Roache, Darren Jones, Galumalemana Hunkin, Fia Turner-Tupou, Tevaga Leavasa, Vui Muliagatele Vitale, Maifea Tiumalumatua Fetu, Lupe Tofilau Eti-Vaofanua, Craig Jones, Fiasili Ah Tong, Timothy Manu | |
Family Party | Richard Lewis, Paul Adams, Li Tao Xu, George Ngatai, Poutoa Papali'i, Samuel Dennis, Michael Kidd, Melanie Taylor, Karl Adams, Louise Cleary, Paul Tankard, Yih Woh Chong, Elias Kanaris, Jerry Filipaina | |
Alliance | Kay Murray, Andrew McKenzie, Victor Billot, Paul Piesse, Richard Wallis, Sarah Campbell, Robert van Ruyssevelt, Jim Flynn, Sarita Divis, Amy Tubman, Richard Mitchell, Jack Yan, Thomas Dowie, Thomas O'Neill, Kelly Buchanan, Jennifer Olsen, Greg Kleis, Matthew Stephen, Marvin Hubbard, Norman MacRitchie, Sandra Ethell, Justin Wilson, Quentin Findlay, Valerie Quinn, Sarah Martin, Peta Knibb, Warren Brewer, Denis O'Connor, Eric Gamble, Samuel Murray | |
Democrats | Stephnie de Ruyter, John Pemberton, David Wilson, Katherine Ransom, Carolyn McKenzie, David Tranter, Heather Smith, Hessel Van Wieren, Barry Pulford, Dawn McIntosh, Iain Parker, Nicholas McIlraith, Edgar Goodhue, John McCaskey, John Ring, Leslie Port, Bruce Stirling, Ross Weddell, Kelly Pemberton, David Espin, Ross Hayward, John Steemson, Karl Hewlett, Edward Fox, Malcolm Keoghan, John Kilbride, Harry Alchin-Smith, Alida Steemson, Roger White, Gary Gribben, Olive McRae | |
Libertarianz | Bernard Darnton, Richard McGrath, Susan Ryder, Mitchell Lees, Colin Cross, Peter Cresswell, Peter Linton, Philip Howison, Nikolas Haden, Timothy Wikiriwhi, Michael Webber, Elahrairah Zamora, Helen Hughes, Michael Murphy, Peter Osborne, Sean Fitzpatrick, Scott Wilson, Luke Howison, Benjamin Morgan, Shane Pleasance, Robert Palmer, Shirley Riddle, Bruce Whitehead, Terence Verhoeven, Kenneth Riddle, Alfred Stevens, Euan McPetrie, Christopher Robertson, Peter Kermode, Lawrence Couper, Donald Rowberry, Willem Verhoeven, Mark Hubbard, Sean Kimpton, Julian Darby, Richard Goode | |
Workers Party | Donald Franks, Daphna Whitmore, Nicholas Kelly, Paul Hopkinson, Byron Clark, Jasmine Freemantle, Rebecca Broad, Timothy Bowron, Jennifer Isle, Heleyni Pratley, Joel Cosgrove, Marika Pratley, Joshua Glue, Nicolas Scullin | |
RAM | Oliver Woods, Grant Brookes, Roger Fowler, Elliott Blade, Michelle Ducat, Martin Kaipo, Cordelia Black, Stephen Cooper, Daphne Lawless, Grant Rogers, Donald Archer, Patrick O'Dea, Bronwen Beechey, Robyn Hughes, Benjamin Doherty, Rafe Copeland, Michael Lai, Curwen Rolinson, Peter Hughes, David Colyer, Kyle Webster, Samuel Richardson, Thomas Pearce, Leonard Parker, Jonathan Williams, Peter de Wall | |
RONZ | Kerry Bevin, Jack Gielen, David Llewell, Brett Docherty, Justin Harnish, David Macartney |
- Notes
- Party list members resigned during the parliamentary term.
- Originally unsuccessful party list members declared elected to parliament when elected list MPs resigned.
Dates
New Zealand elections traditionally occur after September in the third year following the last election, and snap elections occur rarely; the only three elections out of sync in the period of 1948 to 2008 took place in 1951, 1984 and 2002—and the last two came only a few months early. Convention in New Zealand expects Parliaments to run for a full three years unless the government loses the confidence of the House, although this has not happened since 1911.
The Constitution Act 1986 defines the term of Parliament as "three years from the day fixed for the return of the writs issued for the last preceding general election of members of the House of Representatives, and no longer". Since the writs for the 2005 election were returned on 6 October 2005,[5]
the ensuing 48th New Zealand Parliament expired on 6 October 2008, making 15 November the final possible date for the 2008 general election.
On Friday 12 September 2008, Prime Minister Helen Clark announced that the general election would take place on 8 November 2008. This set the full election timetable as:
- Dissolution of parliament – Friday, 3 October 2008.
Writ day – Wednesday, 8 October.- Nominations day – Tuesday, 14 October.
- Election day – Saturday, 8 November.
- Official results declared and writs returned by Saturday, 22 November.
- The 49th Parliament must convene no later than Saturday 3 January 2009.[6]
Political parties
Contesting parties
Nineteen registered political parties contested the party vote:[7]
party | leader(s) | elections contested by party | seats won in 2005 | seats won in 2008 | |
parties that won seats at the 2005 general election | |||||
ACT | Rodney Hide | 1996– | 2 | 5 | |
Green Party | Jeanette Fitzsimons & Russel Norman | 1990; 1999– | 6 | 9 | |
Labour Party | Helen Clark | 1919– | 50 | 43 | |
Māori Party | Tariana Turia & Pita Sharples | 2005– | 4 | 5 | |
National Party | John Key | 1938– | 48 | 58 | |
New Zealand First | Winston Peters | 1993– | 7 | 0 | |
Progressive Party | Jim Anderton | 2002– | 1 | 1 | |
United Future | Peter Dunne | 1996– | 3 | 1 | |
parties that did not win seats at the 2005 election | |||||
Aotearoa Legalise Cannabis Party | Michael Appleby | 1996– | 0 | 0 | |
| Alliance | Andrew McKenzie & Kay Murray | 1993– | 0 | 0 | |
Democrats for Social Credit | Stephnie de Ruyter | 1954–1990 (As Social Credit until 1985); 2005– | 0 | 0 | |
Libertarianz | Bernard Darnton | 1996– | 0 | 0 | |
The Republic of New Zealand Party | Kerry Bevin | 2005– | 0 | 0 | |
parties that have not previously contested a general election in New Zealand | |||||
| Bill and Ben | Jamie Linehan & Ben Boyce | 2008 | – | 0 | |
The Family Party | Richard Lewis | 2008 | – | 0 | |
Kiwi Party | Larry Baldock | 2008 | – | 0 | |
New Zealand Pacific Party | Taito Phillip Field | 2008 | – | 0 | |
Residents Action Movement | Oliver Woods | 2008 | – | 0 | |
Workers Party | Daphna Whitmore | 2008 | – | 0 | |
Non-contesting parties
The following parties either disappeared during the previous parliament's term (2005 to 2008), or did not contest the 2008 elections for other reasons.
party | leader(s) | elections contested by party | ||
registered political parties that did not submit a list | ||||
Direct Democracy | Kelvyn Alp | 2005– | ||
New World Order Party | Nathan Couper | – | ||
parties dissolved or deregistered since 2005 election | ||||
99 MP Party | Margaret Robertson | 2005 | ||
Christian Heritage | Ewen McQueen | 1990–2005 | ||
Destiny New Zealand | Richard Lewis | 2005 | ||
New Zealand Family Rights Protection Party | Susi Pa'o Williams | 2005 | ||
OneNZ | Alan McCulloch | 1999–2005 | ||
Retiring MPs
In the months preceding the election 13 Members of Parliament announced that they would not seek re-election to the House of Representatives in 2008, namely:
- from Labour, 9 members:
Tim Barnett (Christchurch Central)
David Benson-Pope (Dunedin South)
Mark Gosche (Maungakiekie)[8]
Marian Hobbs (Wellington Central)
Steve Maharey (Palmerston North)
Jill Pettis (list MP)
Dover Samuels (list MP)
Paul Swain (Rimutaka)
Margaret Wilson (list MP)
- from National, 4 members:
Mark Blumsky (list MP)
Bob Clarkson (Tauranga)
Katherine Rich (list MP)
Clem Simich (list MP)
Several list MPs elected in 2005 resigned before the end of the term; for a full list, see 48th New Zealand Parliament#Changes during term.
MPs who lost their seats
New Zealand First
New Zealand First received 4.07% of the party vote – below the threshold of 5% – and failed to win an electorate seat. The party's seven MPs lost their seats:
Winston Peters Leader, and second in Tauranga by 11,742 votes
Peter Brown 2nd on List and Deputy Leader
Ron Mark (list MP; 3rd in Rimutaka)
Doug Woolerton (list MP)
Barbara Stewart (list MP)
Pita Paraone (list MP)
Dail Jones (list MP at number 14)
United Future Party
Judy Turner (list MP)
Labour Party
Damien O'Connor (MP for West Coast-Tasman)
Dave Hereora (list MP)
Harry Duynhoven (MP for New Plymouth)
Judith Tizard (MP for Auckland Central)
Lesley Soper (list MP)
Louisa Wall (list MP)
Mahara Okeroa (MP for Te Tai Tonga)
Mark Burton (MP for Taupo)
Martin Gallagher MP for Hamilton West)
Russell Fairbrother (list MP; MP for Napier from 2002 to 2005)
Independents
Gordon Copeland (list MP)
Taito Phillip Field (MP for Mangere)
Voter enrolment and turnout
The rolls listed almost 3 million people registered to vote in the election, a record number representing 95.3% of the estimated eligible voting population.[9]
In contrast, voter turnout of 79.5% of enrolled voters came in lower than in most previous elections, the second-lowest since 1978 (when a large number of outdated and duplicate enrolments deflated the figure) and third-lowest since 1902.[10][11]
Political scientist Stephen Levine from Victoria University speculated that the low turnout may have resulted from the National Party's large lead over Labour in opinion polls running up to the election.[12]
Māori Party co-leader Pita Sharples expressed concern that only 55% of those on the Maori roll had voted.[13]
Issues
Electoral Finance Act
The Electoral Finance Act 2007 passed by the Labour government had a "chilling effect" on political activity in 2008, according to the Electoral Commission.[14]
Some parties attempted to make this an election issue.
Economic conditions
On 5 August 2008, the Treasury announced that the New Zealand economy had entered a recession.[15]
Economic downturn has led to high-profile job losses, such as the closure of factories in Foxton,[16]
in west Dunedin[17]
and in southern Hawke's Bay.[18]
At the same time, inflation hit an eighteen-year high,[19]
with an upwards tug on the prices of basics such as food and petrol, the latter crossing the two-dollar-per-litre mark in late May.[20]
At the Labour Party's campaign launch on 12 October 2008, Helen Clark became the latest world leader to guarantee bank deposits, unveiling a plan worth $150 billion whereby all retail deposits would be unconditionally covered.[21] The plan would be voluntary to join; within two days, reports appeared stating that all of New Zealand's major trading banks had signed up.[22] Also signed up to the plan was the National Party, with deputy leader and finance spokesperson Bill English saying that there was "still time to change the...scheme if banks find it hard to borrow overseas".[23]
Taxation
On 6 October, two days before the National Party's scheduled release of details of the tax-cut plan it had over and above the governing coalition's three-stage series of tax cuts revealed in the 2008 Budget,[24]
the Government disclosed its full fiscal situation; it showed that it expected to take $3.1 billion less tax in 2009, forcing the government to borrow $5.9 billion in 2009, rising to $7.3 billion by 2013. This implied higher costs for KiwiSaver, Working For Families and the 20 hours subsidised early-childhood plan; and higher numbers of people forced onto benefits by any prospective economic downturn. Over the next fiscal year, Dr Cullen expected GDP to rise by just 0.1%, with median house prices dropping by an estimated 10–15%.[25][26]
John Key responded to the news by describing the numbers as "a bit worse than we had anticipated", and stated "I'm confident we can deliver a programme of tax cuts."[27]
The same day Helen Clark reiterated her opinion on tax cuts beyond the government's proposal, saying "now is not the time to go out and recklessly borrow to offer tax cuts",[28]
an opinion she had first voiced in early August[29]
when the National Party used its annual conference to promise to speed up the implementation of the tax cuts, and to borrow several billion dollars to fund infrastructure projects such as a $1.5 billion broadband plan and a new prison in its first term.[30]
On 9 October, National released its policy, promising people on the average wage or higher around $47 a week extra in the hand, funded through a combination of cutting contributions to KiwiSaver, eliminating a tax credit for science and development, and changing Working For Families entitlements.[31]
Trust
On calling the 2008 election, Prime Minister Helen Clark declared that it would be "about trust", labelling the National Party's recent commitments to preserve Labour Party programmes such as KiwiSaver and Kiwibank as "insincere".[32]
Members of the Labour Party accused John Key of lying about his shareholding in Tranz Rail, by not disclosing nearly half of the shares he and his family trusts owned in the company, even though this presented a clear conflict of interest with Key's role as his party's spokesperson on transport, at a time when he asked several questions in the House about the government's plans regarding rail infrastructure.[33]
New Zealand First leader Winston Peters faced an attack on his party's credibility, first over allegations that his party did not declare a $100,000 donation from millionaire ex-patriate property developer Owen Glenn to cover Winston Peters' legal costs in a challenge to the result in the seat of Tauranga. This was referred to a House of Representatives Privileges Committee. On 22 September, the committee determined that Peters had "provided misleading information" and recommended he be censured;[34] this was done by the House of Representatives in a 62–56 vote two days later.[35] The second allegation revolved around the party's failure to declare the use of a secret trust to funnel large donations into New Zealand First's bank account, even though no donations over $10,000 to New Zealand First has been declared, as the law requires. This case was referred to the Serious Fraud Office for further investigation; on 11 October, New Zealand First was cleared of charges that Peters called a "waste of time"[36] and on 24 October, New Zealand First was cleared of wrongdoing by the Electoral Commission, which was investigating donations that the party failed to declare.[37]
Electorates
Boundary changes
The Representation Commission altered many of the boundaries of New Zealand's parliamentary electorates following the 2006 census; the large growth in population between censuses lead to significant boundary changes, particularly in Auckland, the area around Christchurch and the central North Island. In May 2007, the Representation Commission announced the boundary changes[38]
to take effect for the next general election, with the boundaries finalised in September 2007.
The Commission announced the formation of a new electorate in Greater Auckland, bringing the number of geographical constituencies to 70. The new seat, originally dubbed "Howick" (after the Auckland suburb), would have included parts of the existing Pakuranga, Manukau East and Clevedon electorates. After Pakuranga electors made strong objections to the proposed changes (which would have seen the inclusion of the population centres Panmure, Point England and Glen Innes into the electorate) the Commission largely reverted proposed changes to the boundaries of the Pakuranga electorate. The Commission opted to alleviate population pressures by moving the Auckland City suburb of Otahuhu into Manukau East. The revised new seat received the name "Botany" to reflect its focus on the growing population-centres of Botany Downs–Dannemora. On paper, Botany counts as a safe National seat.
Even though the number of South Island electorates remains fixed, the decline in the population of electorates south of Christchurch has resulted in the boundaries of electorates from Invercargill north to Rakaia shifting northwards. The seats of Aoraki, Otago, Rakaia and Banks Peninsula all gravitated towards Christchurch. In the process:
Aoraki received the new name of Rangitata
Otago received the new name of Waitaki
Rakaia received the new name of Selwyn
Banks Peninsula received the new name of Port Hills
Other seats in the lower South Island increased dramatically in size.
Situation after 2005
In 2005 four MPs won seats with majorities of under a thousand: Labour's Darren Hughes beat National candidate Nathan Guy in Ōtaki by 382 votes (1.00%), and in Hamilton West, Martin Gallagher of the Labour Party won an 825-vote majority (2.46%) over National's Tim Macindoe. Both these seats saw a rematch in 2008, with the National Party candidates emerging victorious in each.
The swing to National in the central North Island saw two Bay of Plenty seats produce close results: in Rotorua, the sitting Labour MP Steve Chadwick prevailed by just 662 votes (2.17%) over National's Gil Stehbens, and in Tauranga, property developer Bob Clarkson defeated New Zealand First's leader and seven-term MP for Tauranga Winston Peters by 730 votes (2.02%). Rotorua fell to National's Todd McClay in 2008, while Simon Bridges held Tauranga for National by a wide margin, preventing Peters from returning to Parliament.
Besides the three Labour-held narrow-margin seats mentioned above (Otaki, Hamilton West and Rotorua), National had prospects of gaining Taupō, where boundary changes have added the National-leaning town of Cambridge and with it nearly 20,000 different voters – putting sitting MP Mark Burton's 2005 majority of just 1,285 votes (4.43%) at risk. Similarly, the seat of West Coast-Tasman gave Labour's Damien O'Connor a majority of 2,154 (6.77%). National reversed all of these majorities in 2008 and captured all three seats.
Part of National's core vote comes from provincial centres. In 1990, when Labour lost power, it lost every seat between the southern fringe of the Auckland urban area and Porirua except Palmerston North; in 2005, National again won several provincial seats off Labour:
- East Coast
- Tukituki
- Napier
- Whanganui
- Hamilton East
- Otago
- Aoraki
National also won Tauranga off New Zealand First leader Winston Peters in 2005 and the lion's share of the ACT and United parties' core votes[citation needed] (and in the process gained Northcote off Labour).
The newly-drawn seat of Botany on Auckland's eastern fringe presented an electoral problem for the Labour Party – on 4 July 2008 a crowd of mostly Asian marchers numbered in the thousands[39] protested against Labour's record on crime and sentencing and a perceived upswing in anti-Asian crime. Because of the large Asian population in the new seat, such trends may have given National candidate and victor Pansy Wong a possible advantage. Boundary changes have also shaken up the electoral landscape of the South Island.[38] Three new seats – Selwyn, Waitaki and Rangitata, drawn respectively out of Aoraki, Otago and Rakaia, three National-held seats in 2005, damaged Labour's chances outside of Christchurch and Dunedin.[citation needed]
On Labour's other flank, the three Māori seats that it held last time against a strong Māori Party challenge were in danger of falling as they did in 1996 when New Zealand First broke Labour's sixty-year stranglehold. Nanaia Mahuta again faced Angeline Greensill for the new Hauraki-Waikato seat, and narrowly held it. Māori Affairs Minister Parekura Horomia also held on by a small margin against veteran broadcaster Derek Fox in Ikaroa-Rāwhiti. Incumbent Mahara Okeroa, however, was defeated by Rahui Katene in Te Tai Tonga, giving the Māori Party an additional seat.
The seats of Tauranga and Epsom provided particular resonances: Winston Peters failed to retake the marginal Tauranga (and Ron Mark failed to win the Rimutaka seat), meaning New Zealand First's chances of returning to the House depended on winning 5% of the party vote, which they did not accomplish. Similarly, the electoral fortunes of the ACT Party depended very largely on Rodney Hide retaining Epsom, which he did.
Amongst other parties very aware of the 5% barrier, United Future appeared more secure in the light of Peter Dunne's grip on Ōhariu, which he maintained, though by a narrower margin than previously; and the Progressive Party retained a very strong hold via Jim Anderton's "safe seat" of Wigram.
The Greens never appeared in danger of slipping below the 5% threshold, although lacking an obvious winnable electorate seat (co-leader Jeanette Fitzsimons had won Coromandel in 1999, but the electorate returned to National in 2002).
Seats that changed hands
National won nine electorate seats from Labour:
Auckland Central: Nikki Kaye defeated sitting Labour MP Judith Tizard, the first time National has won this seat.
Hamilton West: won by Tim Macindoe who ousted sitting Labour MP Martin Gallagher, a reversal of the 2005 election when Gallagher narrowly defeated Macindoe.
Maungakiekie: Sam Lotu-Iiga achieved a majority of 1,876 over Carol Beaumont after incumbent Mark Gosche retired. Beaumont entered Parliament as a Labour list member.
New Plymouth: the most marginal electorate, where Jonathan Young won by 314 votes to oust Harry Duynhoven.
Otaki: the most marginal 2005 seat fell to Nathan Guy, who defeated incumbent Minister Darren Hughes by 1,422 votes. Hughes remained in Parliament through the Labour list.
Rotorua: fell to Todd McClay who defeated sitting Minister Steve Chadwick by 4,855 votes. Chadwick returned to Parliament through the party list.
Taupo: won by Louise Upston, who defeated Mark Burton by nearly 6,000 votes, to reverse a 1,198 majority in 2005.
Waitakere: Paula Bennett defeated Lynne Pillay by just over 600 votes, Pillay returned to Parliament as a List MP. This Waitakere seat differs from that previously held by National's Brian Neeson.[citation needed]
West Coast-Tasman: Chris Auchinvole defeated Cabinet Minister Damien O'Connor.
The Māori Party also won a seat from Labour.
Te Tai Tonga: Rahui Katene won the seat from Mahara Okeroa.
New seats won by incumbent MPs
- National's Pansy Wong became the first Member for the new Botany seat. She had become the first Asian list MP in 1996, and in 2008 became the first Asian electorate MP.
- National's Paul Hutchison, sitting MP for Port Waikato, returned to Parliament as Member for Hunua which covers most of his former electorate and parts of the former Clevedon electorate.
- United Future's Peter Dunne, sitting MP for Ohariu-Belmont, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Ōhariu.
- National's Judith Collins, sitting MP for Clevedon, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Papakura.
- Labour's Ruth Dyson, sitting MP for Banks Peninsula, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Port Hills.
- National's Jo Goodhew, sitting MP for Aoraki, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Rangitata.
- National's Lindsay Tisch, sitting MP for Piako, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Waikato, covering most of Piako and rural areas north of Hamilton West.
- National's Jacqui Dean, sitting MP for Otago, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Waitaki which takes in most of Dean's former Otago electorate, and Queenstown and Arrowtown.
- Labour's Nanaia Mahuta, sitting MP for the Maori electorate of Tainui, returned to Parliament as the new Member for Hauraki-Waikato.
New MPs in vacated seats
A number of seats elected new MPs following the retirement of their sitting Members:
Brendon Burns held for Labour Christchurch Central by just over 800 votes, previously held by retiring MP Tim Barnett.
Clare Curran held for Labour Dunedin South vacated by David Benson-Pope who did not achieve party reselection.
William Sio held for Labour the seat of Mangere, defeating Taito Phillip Field. Field won the seat in the 2005 general election, but left the party after being indicted on fraud charges and contested this election as leader of New Zealand Pacific Party.
Iain Lees-Galloway held for Labour the seat of Palmerston North following the retirement of sitting MP Steve Maharey.
Christopher Hipkins held for Labour the seat of Rimutaka following the retirement of sitting MP Paul Swain.
Amy Adams won for National the new seat of Selwyn, taking in part of the former Rakaia electorate. Sitting Rakaia MP Brian Connell retired from politics.
Simon Bridges held for National the seat of Tauranga following the retirement of sitting MP Bob Clarkson.
Grant Robertson held for Labour the seat of Wellington Central following the retirement of sitting MP Marian Hobbs.
Opinion polling
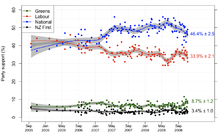
Poll results for all political parties that exceeded the 5% mixed-member proportional (MMP) representation threshold between the 2005 and 2008 elections.
Having come first in the party vote at the 2005 election by just two percentage points, Labour held a slender lead in aggregate polling through the first half of 2006; a two-point lead in the first half of the year turned into a two-point deficit by May. Polling for a preferred Prime Minister showed Helen Clark nearly twice as popular as then National Party leader Don Brash.
Things changed in early 2007, with new National leader John Key improving on Brash's preferred Prime Minister rating by ten points, and overtaking Clark as preferred Prime Minister in May; at the same time National jumped out to a sizeable lead over Labour ranging from between eight and eighteen points, spending most of 2007 and 2008 with support from around fifty percent of the electorate. Labour's popularity slumped, hitting its lowest point in the winter of 2008, before beginning a slow climb into the high thirties in August and September.
Leading up to the election, polls indicated a range of possible outcomes on election day; some suggested Labour could form a coalition government, while others predicted National in control. Of the "minor" parties, only the Green Party consistently polled over the five-percent threshold, and United Future and the Progressive Party frequently failed to register a mention. Both ACT's and the Māori Party's popularity since 2005 remained steady at around two percent, while New Zealand First failed to poll over the threshold after December 2006. The polls gave varied results for preferred Prime Minister, with some giving Clark a slight lead, and others giving Key a sturdy margin.
Coalition preferences during the campaign
The coalition preferences of various parties played a role during the campaign, due to the likelihood that no party would get an absolute majority of seats in the House. ACT emerged as the first "minor" party to announce that it would support a prospective National-led government.[40]United Future also announced that it would side with National in late October, after supporting the Labour government for six years.[41]
The Progressive Party, led by Jim Anderton, had served as a steady coalition partner to Labour and the electorate probably expected it to remain so. The Green Party, which abstained from opposing the Labour-led government in supply and confidence votes through the life of the 48th Parliament (2005 to 2008), said on 20 October that the only party of the two main parties it could form a coalition with was Labour.[42] In the light of New Zealand First's run-in with the Serious Fraud Office, John Key ruled out that party as a government support partner on 31 August 2008, saying "the sheer weight of allegations and the actions of Mr Peters in the last few months means that I have lost that confidence in him".[43]
At that time, Peters' future seemed under a cloud; after his party being cleared of charges of serious fraud, National restated its position, saying that the result of the case has not altered it.[44]
Based on polls commissioned by the Māori news show Marae,[45] the Māori Party appeared likely to win most of the Māori seats and stood a chance of holding the balance of power. The party's MP for Te Tai Tokerau, Hone Harawira, stated at the end of September that the party could work with both Labour and National.[46] On 28 September, National announced a commitment to abolish the Māori seats in time for the 2014 election.[47]
The Māori Party has benefited greatly from the Māori seats, and its co-leader Tariana Turia was unimpressed: "They think again that they can deny us the right to participate. If they want a relationship with the Māori Party then very clearly they're starting off on the wrong foot".[47]Marae polls released on 12 October showed 62 percent of voters polled in the two northernmost Māori electorates were resistant to the idea of a National–Māori government; co-leader Pita Sharples responded to the poll results by saying his party would be "stupid" to ignore the poll figures.[48]
Candidates
See:
- Candidates in the New Zealand general election, 2008 by electorate
- Party lists in the New Zealand general election, 2008
See also
- Elections in New Zealand
- Electoral system of New Zealand
- 2008 in New Zealand
Notes
^ "Key announces shape of new National-led government". National Business Review. NZPA. 16 November 2008. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
^ "Results of the 2008 General Election". Electoral Commission. 29 January 2013. Retrieved 17 April 2015.
^
Colin James (political commentator) on TV 1 election coverage.
^ http://www.electionresults.govt.nz/electionresults_2008/electoratestatus.html
^
Electoral Commission: Post-election deadlines – Election '05 Source Archived 2 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine.
^ "Key promises 'issues' election". Stuff.co.nz. 12 September 2008. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
^ "Registered Political Parties – overview and Register". Elections New Zealand. 29 July 2008. Archived from the original on 14 October 2008. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
^ Dominion Post 30 May 2008 page A4
^
Enrolment records set for 2008 General Election[permanent dead link], press release, Electoral Enrolment Centre, 12 November 2008.
^
Turnout statistics reflect the percentage of those enrolled to vote. "New Zealand general election, 2008 – Official Results". Elections New Zealand. Archived from the original on 30 June 2012. Retrieved 23 November 2008.
^
General elections 1853–2005 – dates & turnout Archived 17 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine., Electoral Compendium 2005 Archived 5 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine.. Electoral Commission, Wellington, 2005.
^ "Low voter turnout for 2008 election". Radio New Zealand. Radio NZ. 12 November 2008. Archived from the original on 25 July 2009. Retrieved 12 November 2008.
^ "Low Maori voter turnout shows lack of trust - Sharples". The New Zealand Herald. 12 November 2008. Retrieved 30 October 2011.
^ "Electoral Commission blasts EFA – again". The New Zealand Herald. NZPA. 2 October 2008. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
^
"NZ in recession – Treasury". Stuff. New Zealand. 5 August 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
"Tears flow at Feltex Foxton". scoop.co.nz. 1 August 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
"138 jobs axed in latest meatworks closure". The New Zealand Herald. 29 May 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
"Oringi meatworks closure". scoop.co.nz. 13 May 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
"Inflation Hits 18 year high". nzity.co.nz. 13 May 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
"Petrol price up again – 95 passes $2 mark". Stuff. New Zealand. 30 May 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
"Govt deposit liability 'huge but risk low'". Stuff. New Zealand. 12 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^
"Banks sign up for Govt's $150b guarantee". Stuff. New Zealand. 13 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
[dead link]
^
"Change deposit guarantee scheme if banks can't borrow – National". Radio New Zealand. 14 October 2008. Archived from the original on 12 February 2012. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^
"Budget 2008 Minister's Statement". scoop.co.nz. 22 May 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^
"Cullen: Pre-election Economic and Fiscal Update 0". scoop.co.nz. 6 October 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^
Oliver, Paula (6 October 2008). "No More Safety In Numbers For Cullen". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^ Oliver, Paula (6 October 2008). "Cullen rains on Key's parade". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^
"is there still money for tax cuts?". TVNZ. 6 October 2008. Archived from the original on 7 October 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^
"PM describes Nats' plan as 'Nuts'". 3 News. 3 August 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
Rushworth, Anna (3 August 2008). "Faster tax cuts, vows National". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
^
Gay, Edward (9 October 2008). "Key gives tax cuts, reduces KiwiSaver". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^
Young, Audrey (13 September 2008). "Poll all about trust, says Clark". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 25 September 2008.
^ "Committee recommends censuring Peters". Stuff. New Zealand. 22 September 2008. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^ "Parliament votes to censure Peters". Newstalk ZB. 22 September 2008. Archived from the original on 25 July 2009. Retrieved 7 October 2008.
^ "Peters cleared but PM keeps his portfolio". Stuff. New Zealand. 11 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
[dead link]
^ "Peters buoyed by donations ruling".
^ ab The New Zealand Herald (3 May 2007). "Auckland to get an extra seat in Parliament". The New Zealand Herald.
Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "elect_com" defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
^
"Clean, green but not safe". Eastern Courier. 5 July 2008. Archived from the original on 23 February 2013.
^ "Be The Difference – Party Vote ACT". ACT New Zealand. 12 October 2008. Archived from the original on 14 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^
Oliver, Paula (27 October 2008). "Dunne cites Greens as reason for backing Key". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
^ "Greens rule out coalition with National". Radio New Zealand. 20 October 2008. Archived from the original on 21 October 2008. Retrieved 24 October 2008.
^
"Nats won't shift position on Peters – Key". National Business Review. 31 August 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^ "Peters won't get portfolios back, despite SFO finding". Radio New Zealand. 12 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
[dead link]
^
"Marae – election 08". TVNZ. 12 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^
"Māori Party could work with Nats or Labour – Harawira". TVNZ. 21 September 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^ ab
Tahana, Yvonne (29 September 2008). "National to dump Maori seats in 2014". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
^
"Maori voters push for deal with Labour". Stuff. New Zealand. 13 October 2008. Retrieved 14 October 2008.
[dead link]
Further reading
- Jack Vowles, "The 2008 General Election in New Zealand". 2009. Electoral Studies 28(3): 507–510 (note: paywalled, see summary)
Roberts, Nigel S.; Levine, Stephen, eds. (2010). Key to Victory: The New Zealand General Election of 2008. Wellington: Victoria University Press. ISBN 9780864736130.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2008 New Zealand election. |
Official site for enrolments and for the Chief Electoral Office








