Russian legislative election, 2016
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 450 seats to the State Duma 226 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 47.88% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 The upper map shows the winning party vote in the territorial election commissions, the lower map shows the party of the winner and his vote in the single mandate constituencies. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of the Russian Federation |
|---|
 |
|
Presidency
|
Executive
|
Legislature
|
|
Elections
|
Federalism
|
Foreign relations
|
Related topics
|
|
Legislative elections were held in Russia on 18 September 2016, having been brought forward from 4 December.[2] At stake were the 450 seats in the State Duma of the 7th convocation, the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Russia. Prior to the election United Russia had been the ruling party since winning the 2011 elections with 49.32% of the vote, and taking 238 seats (53%) of the seats in the State Duma.
Prior to the election, observers expected that turnout would be low and called the election campaign the dullest in recent memory.[3]
109,820,679 voters were registered in the Russian Federation (including Crimea[nb 1]) on 1 January 2016. Taking into account people registered outside the Russian Federation and the voters in Baikonur, the total number of eligible voters for 1 January 2016 was 111,724,534.[5] The vote had a record low turnout of 47.88%,[6] with just 28% of Muscovites casting their votes before 6pm.[7]
Contents
1 Background
2 Electoral system
3 Chronology
4 Conduct
5 Participating parties
5.1 Parties that participated in the election
5.2 Parties that did not participate in the election
5.3 Single-member constituencies
6 Opinion polls
7 Exit polls
8 Results
8.1 By region
8.2 By constituency
9 Notes
10 References
11 External links
Background
Although the elections had been planned for 4 December 2016, deputies discussed the issue of rescheduling to an earlier date since the spring of 2015, with the second and third Sundays of September or October 2016 as possible alternatives. On 1 July 2015 the Constitutional Court of Russia accepted the possibility of conducting early elections to the Duma in 2016 under certain conditions. According to the Court, the constitution does not require the election date to be exactly five years after the previous elections and the election date can be shifted if the following conditions are met:[8]
- Shifting of the election date does not disrupt reasonable periodicity of elections.
- Limiting of the real terms of the Duma deputies is insignificant (less than a few months).
- Shifting of the election dates is announced in advance, so to give all the parties enough time to prepare for the elections.
On 19 June 2015 the State Duma approved the first reading of a bill to bring the election to the State Duma forward from 4 December 2016 to the third Sunday of September 2016. The corresponding bill was adopted by the State Duma on the second and third (and final) reading with 339 deputies in favour and 102 against, with no abstentions. The document was put together by the speaker of the Duma, Sergei Naryshkin, and the three leaders of the Duma factions, Vladimir Vasilyev (United Russia), Vladimir Zhirinovsky (LDPR), and Sergei Mironov (A Just Russia). The initiative to transfer the date of elections had not been supported by the deputies of the Communist Party, who called it an unconstitutional decision. Earlier, a similar opinion was expressed by the leader of the Communist Party, Gennady Zyuganov. The September elections were not satisfactory to the Communists in part because the debate fell in August, "when one will be in the garden, the latter on the beach, others with their children" said Zyuganov. The Russian government supported the bill.
On 17 June 2016 President Vladimir Putin signed a decree on the appointment of the State Duma elections on 18 September 2016.[9] From that day parties had the right to start the nomination process for deputies to hold congresses and transmit documents of candidates to the Central Election Commission of the Russian Federation (CEC) for registration.[10]
For the first time since the controversial and unilateral 2014 Russian annexation of Crimea (from Ukraine), Crimean voters could vote in a Russian general election.[3] Ukraine strongly condemned the vote.[11] Various countries (among them the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and France) did not recognize the legitimacy of the election in Crimea.[12][13][14] According to Russia correspondent for Al Jazeera English Rory Challands, (on election day) "Despite many Crimeans voting in Russian elections for 1st time, there's little excitement. Main sentiments so far are apathy and cynicism."[15] Scuffles between police and Ukrainian nationalists were reported near polling stations for Russian citizens in (the Ukrainian cities) Kiev and Odessa.[3][16]
In Syria, 4,751 Russian citizens (most of them taking part in the Russian military intervention in Syria) voted.[17]
Electoral system

Single-member constituency map adopted in 2015.
The State Duma is elected on a single election day for a term of five years, with parallel voting that was used between 1993 and 2003.
Out of 450 seats, 225 are elected by proportional representation from party lists with a 5% electoral threshold, the whole country forming a single constituency. Each political party should adopt a party list which should be divided into a federal part and regional groups. The federal part should have from 1 to 10 candidates, with the rest of the party list candidates comprising the regional groups. There should be at least 35 regional groups. Total number of candidates in a party list should be between 200 and 400.
Seats are allocated using Hare quota and largest remainder method.
The other 225 seats are elected in single-member constituencies using the first-past-the-post system.[18]
Chronology

A supporter of United Russia handing out leaflets in the street
On June 17, President Vladimir Putin set the date of the election as 18 September 2016. On June 20 the Central Election Commission approved the calendar of the election campaign.[19]
- From June 18 to July 13 — Period for nomination of candidates (parties in the federal list and single-mandate constituencies, self-nominated in single member constituencies).
- From July 4 to August 3 — Period of registration of federal lists of candidates to the Central Election Commission and of the registration of candidates in single-member constituencies in the district election commissions.
- August 12 — Draw that decided allocation of parties on the federal-list ballot was held.[20]
- August 16 and 18 — Draw that decided distribution of free TV time (August 16) and free space for parties or candidates in newspapers (August 18) was held.[21]
- From August 20 to September 16 — Election campaign.
- From 3 August to 6 September — Territorial election commissions issue absentee ballots.
- From 7 to 17 September — Voters can get absentee ballots through election commissions at polling station.
- September 17 — Day of Election silence.
- September 18 — Election day.
Conduct
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe published its full report of the election on 23rd December 2016. It noted many problems with the election, such as the lack of "clear political alternatives [with the main four parliamentary parties, limiting] voters' choice", over-regulation of the registration of political parties, lack of proper conduct during counting of votes, voters not folding their ballots on 70% of occasions and lack of transparency of campaign finance.[22]
Participating parties
The Central Election Commission determined that 14 political parties could submit lists of candidates without collecting signatures.[23] Whilst other parties were required to present at least 200,000 signatures (with a maximum of 7,000 signatures per region).[18]
Parties that participated in the election
Fourteen parties were registered to participate in the election. These are the same fourteen parties that did not have to collect signatures in order to participate. None of the parties tasked with collecting signatures were registered on the ballot due to various violations or failure to submit documents.
| № on ballot | Party | Abb. | Party leader | № 1 in party list | Convention date[24] | Ideology | Contesting on party list? [25] | Contesting on SMC? [25] | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rodina | Rodina | Aleksey Zhuravlyov | Aleksey Zhuravlyov | 2 July 2016 | National conservatism / Ultranationalism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 8[26] | |
| 2 | Communists of Russia | CoR | Maxim Suraykin | Maxim Suraykin | 1 July 2016 | Communism / Marxism–Leninism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 3[27] | |
| 3 | Russian Party of Pensioners for Justice | RPPJ | Vladimir Burakov | Vladimir Burakov | 9 July 2016 | Social conservatism | ✓ | ✘ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 12[28] | |
| 4 | United Russia | UR | Dmitry Medvedev | Dmitry Medvedev | 26–27 June 2016 | Statism / Centrism / National conservatism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 12[29] | |
| 5 | Russian Ecological Party "The Greens" | Greens | Anatoly Panfilov | Oleg Mitvol | 6 July 2016 | Environmentalism / Centrism / Green politics | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on July 29[30] | |
| 6 | Civic Platform | CPl | Rifat Shaykhutdinov | Rifat Shaykhutdinov | 2 July 2016 | Conservatism / Economic Liberalism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on July 27[31] | |
| 7 | Liberal Democratic Party of Russia | LDPR | Vladimir Zhirinovsky | Vladimir Zhirinovsky | 28 June 2016 | Russian nationalism / Pan-Slavism / Euroscepticism / Anticommunism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on July 18[32] | |
| 8 | People's Freedom Party | PARNAS | Mikhail Kasyanov | Mikhail Kasyanov | 2 July 2016 | Conservative liberalism / Liberal democracy / Pro-Europeanism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 3[33] | |
| 9 | Party of Growth | PoG | Boris Titov | Boris Titov | 4 July 2016 | Liberal conservatism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 1[34] | |
| 10 | Civilian Power | CPo | Kirill Bykanin | Kirill Bykanin | 8 July 2016 | Liberalism / Green politics | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 3[35] | |
| 11 | Yabloko | Yabloko | Emilia Slabunova | Grigory Yavlinsky | 1–3 July 2016 | Social liberalism / Pro-Europeanism / Social democracy | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 5[36] | |
| 12 | Communist Party of the Russian Federation | CPRF | Gennady Zyuganov | Gennady Zyuganov | 25 June 2016 | Communism / Left-wing nationalism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on August 1[37] | |
| 13 | Patriots of Russia | PoR | Gennady Semigin | Gennady Semigin | 1 July 2016 | Democratic socialism / Left-wing nationalism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on July 27[38] | |
| 14 | A Just Russia | JR | Sergey Mironov | Sergey Mironov | 27 June 2016 | Social democracy / Democratic socialism | ✓ | ✓ | CEC registered the list of candidates on July 22[39] | |
Parties that did not participate in the election
| Party | Abb. | Party leader | № 1 in party list | Convention date[24] | Ideology | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Alliance of Greens and Social Democrats | AGSD | Alexander Zakondyrin | Alexander Zakondyrin | 2 July 2016 | Grassroots democracy | Barred from the election because the party leadership did not notify the CEC about holding a pre-election convention[40] | |
Great Fatherland Party | GFP | Nikolai Starikov | Nikolai Starikov | 28 June 2016 | Centrism / National conservatism | CEC refused to register the list of candidates[29] | |
Native Party | NP | Alexander Samokhin | — | 24 June 2016 | Party failed to submit the necessary signatures and as such will not be participating in the election[41] | ||
Party of Good Deeds | PGD | Andrey Kirillov | — | 2 July 2016 | Party did not submit documents to the CEC[42] | ||
Party of the Parents of Future | PPF | Marina Voronova | — | — | Party failed to submit the necessary signatures and as such will not be participating in the election[43] | ||
Party of Rural Revival | PRR | Vasily Vershinin | — | 6 July 2016 | Agrarianism | Announced that it would not be taking part in the election.[44] However, nominated several candidates in single-member districts | |
Party of Social Reforms | PSR | Stanislav Polishchuk | — | 26 June 2016 | Barred from the election due to critical deficiencies in the documents filed with the CEC[45] | ||
People Against Corruption | PAC | Grigory Anisimov | — | 22 June 2016 | Party did not submit documents to the CEC[42] | ||
Revival of Agrarian Russia | RAR | Vasily Krylov | — | 5 July 2016 | Agrarianism | CEC refused to certify the list of candidates[46] | |
Union of Labor | UL | Alexander Shershukov | Svetlana Antropova | 21 June 2016 | CEC refused to register the list of candidates[29] | ||
Volya | Volya | Svetlana Peunova | Marina Gerasimova | 25 June and 2 July 2016 | Left-wing nationalism / Democratic socialism / Narodniks | Party failed to submit the necessary signatures and as such will not be participating in the election[47] | |
Single-member constituencies
In 225 single-member constituencies, candidates could be nominated by a party, or be self-nominated.
Opinion polls

Opinion polling for ruling party (WCIOM)

Opinion polling for opposition parties (WCIOM)
Exit polls
| Date | Poll source | UR | CPRF | LDPR | JR | PARNAS | Yabloko | CPl | Rodina | PoR | Greens | PoG[nb 2] | CoR | RPPJ | CPo | Spoilt vote | Lead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 September 2016 | WCIOM | 44.5% | 14.9% | 15.3% | 8.1% | 1.2% | 3.5% | 0.3% | 2.3% | 0.8% | 0.8% | 1.8% | 2.6% | 2% | 0.2% | 1.7% | 29.2% over LDPR |
| 18 September 2016 | FOM | 48.4% | 16.3% | 14.2% | 7.6% | 1% | 3.2% | 0.2% | 1.8% | 0.6% | 0.8% | 1.5% | 1.5% | 1.9% | 0.1% | ? | 32.1% over CPRF |
Results
United Russia won a supermajority of seats, which will allow them to change the Constitution without the votes of other parties. Turnout was reported as low. Throughout the day there were reports of voting fraud including video purporting to show officials stuffing ballot boxes.[48] Additionally, results in many regions demonstrate that United Russia on many poll stations got anomalously close results, for example, 62.2% in more than hundred poll stations in Saratov Oblast. This suggests that the results in these regions likely have been rigged.[49] The government said there was no evidence of any large scale cheating.[50] However, on 22 September the Central Electoral Committee canceled the results in seven constituencies, where the number of used ballots exceeded the number of registered voters, or where the authorities were videotaped stuffing the ballots.[51] According to research by University of Michigan political scientists Kirill Kalinin and Walter R. Mebane, Jr., the election results are fraudulent.[52]

Seat composition before election: JR – 64, CPRF – 92, UR – 238, LDPR – 56
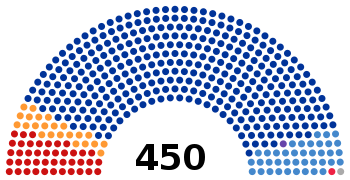
Seat composition after election: UR – 343, CPRF – 42, LDPR – 39, JR – 23, Rodina – 1, CPl – 1, Independent – 1
| Party | Party list | Constituency | Total result | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | ±pp | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | Seats | +/– | |||
| United Russia | 28,527,828 | 55.23 | +5.13 | 140 | 25,162,770 | 50.12 | 203 | 343 | +105 | ||
| Communist Party of the Russian Federation | 7,019,752 | 13.59 | –5.91 | 35 | 6,492,145 | 12.93 | 7 | 42 | −50 | ||
| Liberal Democratic Party of Russia | 6,917,063 | 13.39 | +1.53 | 34 | 5,064,794 | 10.09 | 5 | 39 | −17 | ||
| A Just Russia | 3,275,053 | 6.34 | –7.11 | 16 | 5,017,645 | 10.00 | 7 | 23 | −41 | ||
| Communists of Russia | 1,192,595 | 2.31 | – | 0 | 1,847,824 | 3.68 | – | 0 | New | ||
| Yabloko | 1,051,335 | 2.04 | –1.45 | 0 | 1,323,793 | 2.64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Russian Party of Pensioners for Justice | 910,848 | 1.76 | – | 0 | – | – | – | 0 | New | ||
| Rodina | 792,226 | 1.53 | – | 0 | 1,241,642 | 2.47 | 1 | 1 | New | ||
| Party of Growth | 679,030 | 1.31 | +0.71 | 0 | 1,171,259 | 2.33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| The Greens | 399,429 | 0.77 | – | 0 | 770,076 | 1.53 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| People's Freedom Party | 384,675 | 0.74 | – | 0 | 530,862 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Patriots of Russia | 310,015 | 0.60 | –0.39 | 0 | 704,197 | 1.40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Civic Platform | 115,433 | 0.22 | – | 0 | 364,100 | 0.73 | 1 | 1 | New | ||
| Civilian Power | 73,971 | 0.14 | – | 0 | 79,922 | 0.16 | 0 | 0 | New | ||
| Independent | – | – | – | – | 429,051 | 0.85 | 1 | 1 | +1 | ||
| Invalid/blank votes | 982,596 | – | – | – | 1,767,725 | – | – | – | – | ||
| Total | 52,631,849 | 100 | – | 225 | 51,967,805 | 100 | 225 | 450 | 0 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 110,061,200 | 47.82 | –12.22 | – | 109,636,794 | 47.40 | – | – | – | ||
| Source: Central Election Commission | |||||||||||
By region
The breakdown of the party-list results by region is as follows:[1]
| Region | JR | CPl | CPo | CPRF | CoR | LDPR | PoG | PoR | PARNAS | Rodina | RPPJ | Greens | UR | Yabloko | Turnout | Invalid ballots |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.83% | 0.13% | 0.10% | 13.37% | 2.23% | 12.66% | 0.69% | 0.24% | 0.33% | 1.13% | 1.35% | 0.65% | 59.45% | 0.89% | 53.9% | ||
| 13.78% | 0.15% | 0.15% | 17.25% | 3.66% | 19.82% | 0.84% | 0.30% | 0.60% | 1.15% | 1.76% | 0.71% | 35.19% | 2.03% | 40.7% | ||
| 4.10% | 0.11% | 0.14% | 18.89% | 2.69% | 12.73% | 0.52% | 0.69% | 0.94% | 5.66% | 1.36% | 0.55% | 48.81% | 0.81% | 45.1% | ||
| 4.15% | 0.19% | 0.17% | 16.62% | 2.49% | 29.02% | 0.63% | 0.52% | 0.45% | 1.28% | 2.54% | 0.72% | 37.91% | 0.91% | 42.4% | ||
| 9.17% | 0.17% | 0.13% | 12.78% | 1.97% | 19.73% | 1.21% | 0.45% | 0.83% | 1.62% | 2.99% | 0.86% | 44.48% | 2% | 36.5% | ||
| 17.56% | 0.19% | 0.17% | 14.18% | 3.31% | 13.13% | 0.89% | 0.38% | 0.73% | 1.10% | 1.57% | 0.64% | 42.22% | 0.99% | 36.9% | ||
| 2.42% | 0.16% | 0.14% | 11.98% | 1.65% | 29.73% | 0.79% | 0.59% | 0.70% | 1.94% | 2.70% | 0.99% | 42.64% | 1.03% | 43.1% | ||
| 6.88% | 0.30% | 0.14% | 18.62% | 1.84% | 11.29% | 0.36% | 0.39% | 0.21% | 0.69% | 0.99% | 0.51% | 56.37% | 0.52% | 69.7% | ||
| 7.01% | 0.20% | 0.12% | 14.93% | 1.94% | 13.73% | 0.67% | 0.29% | 0.44% | 1.20% | 1.73% | 0.68% | 54.73% | 0.78% | 62.1% | ||
| 3.48% | 0.19% | 0.10% | 13.29% | 1.83% | 10.80% | 0.54% | 0.32% | 0.38% | 1.43% | 1.26% | 0.44% | 63.91% | 0.76% | 55.1% | ||
| 6.55% | 0.82% | 0.14% | 20.59% | 2.87% | 13.54% | 3.90% | 0.40% | 0.52% | 0.83% | 2.19% | 0.57% | 43.34% | 1.17% | 40.5% | ||
| 1.12% | 0.02% | 0.07% | 0.02% | 0.96% | 0.01% | 0.16% | 0.36% | 0.01% | 0.26% | 0.11% | 0.53% | 96.29% | 0.03% | 94.9% | ||
| 17.48% | 0.2% | 0.15% | 12.02% | 2.43% | 16.73% | 1.23% | 0.48% | 0.94% | 1.80% | 2.34% | 1.07% | 38.19% | 2.14% | 44.4% | ||
| 3.13% | 0.19% | 0.13% | 7.76% | 1.62% | 17.34% | 0.70% | 0.48% | 0.39% | 1.21% | 2.17% | 0.81% | 58.8% | 0.80% | 64.5% | ||
| 10.69% | 0.31% | 0.18% | 13.42% | 1.94% | 11.72% | 0.77% | 0.60% | 0.63% | 1.02% | 2.78% | 1.01% | 50.92% | 1.01% | 59.3% | ||
| 2.06% | 0.20% | 0.09% | 5.60% | 1.26% | 11.14% | 0.41% | 0.26% | 0.54% | 1.39% | 1.07% | 0.69% | 72.80% | 0.68% | 49.1% | ||
| 2.20% | 0.07% | 0.08% | 5.35% | 0.37% | 0.52% | 0.47% | 0.53% | 0.07% | 0.32% | 0.25% | 0.17% | 88.90% | 0.15% | 88.1% | ||
| 9.57% | 0.22% | 0.54% | 5.65% | 0.20% | 1.65% | 2.14% | 2.20% | 0.06% | 3.85% | 0.11% | 0.88% | 72.41% | 0.20% | 81.4% | ||
| 5.19% | 0.30% | 0.13% | 24.08% | 3.09% | 17.01% | 1.25% | 0.87% | 0.48% | 1.46% | 1.95% | 0.89% | 39.77% | 1.43% | 34.6% | ||
| 7.31% | 0.23% | 0.10% | 18.08% | 3.07% | 17.67% | 1.09% | 0.55% | 0.94% | 1.48% | 2.53% | 0.94% | 42.38% | 2.02% | 38.5% | ||
| 2.80% | 0.16% | 0.14% | 17.11% | 3.31% | 21.90% | 0.65% | 0.43% | 0.45% | 0.98% | 1.94% | 0.65% | 45.03% | 0.93% | 39.6% | ||
| 2.09% | 0.01% | 0.01% | 18.90% | 0.11% | 0.15% | 0.24% | 0.11% | 0.01% | 0.06% | 0.02% | 0.54% | 77.71% | 0.04% | 90.1% | ||
| 5.62% | 0.21% | 0.14% | 13.99% | 2.76% | 16.60% | 2.30% | 3.42% | 1.04% | 2.03% | 2.21% | 0.81% | 43.39% | 2.37% | 44.0% | ||
| 3.18% | 0.27% | 0.11% | 11.69% | 1.56% | 4.29% | 0.58% | 2.31% | 0.34% | 0.50% | 1.24% | 0.42% | 70.61% | 1.42% | 57.5% | ||
| 6.21% | 0.17% | 0.13% | 15.95% | 2.40% | 17.38% | 1.33% | 0.60% | 0.86% | 1.87% | 2.41% | 0.91% | 45.75% | 2.21% | 43.1% | ||
| 4.42% | 0.22% | 0.17% | 12.59% | 2.54% | 21.31% | 1.26% | 0.74% | 0.54% | 1.42% | 2.37% | 0.98% | 46.70% | 1.40% | 39.5% | ||
| 1.07% | 0.10% | 0.05% | 7.97% | 6.59% | 0.64% | 0.20% | 0.65% | 0.40% | 0.20% | 0.11% | 0.10% | 81.67% | 0.40% | 93.3% | ||
| 10.09% | 0.30% | 0.13% | 13.05% | 2.56% | 17.57% | 1.66% | 0.90% | 0.82% | 1.42% | 2.32% | 0.95% | 37.30% | 7.80% | 39.6% | ||
| 4.51% | 0.10% | 0.09% | 7.21% | 0.60% | 7.72% | 0.15% | 0.49% | 0.16% | 0.23% | 0.35% | 0.17% | 77.33% | 0.44% | 86.7% | ||
| 4.52% | 0.23% | 0.17% | 16.46% | 3.31% | 25.01% | 1.11% | 0.42% | 1.13% | 1.60% | 2.99% | 1.22% | 37.31% | 1.85% | 36.9% | ||
| 7.17% | 0.17% | 0.14% | 20.90% | 3.49% | 19.52% | 0.86% | 0.76% | 0.70% | 1.32% | 2.09% | 1.03% | 38.06% | 1.44% | 39.4% | ||
| 5.57% | 0.22% | 0.15% | 9.69% | 2.15% | 22.31% | 1.03% | 0.59% | 0.62% | 2.25% | 2.17% | 0.77% | 47.61% | 1.13% | 39.2% | ||
| 9.46% | 0.23% | 0.16% | 13.58% | 2.64% | 24.94% | 1.40% | 0.36% | 0.56% | 1.43% | 2.38% | 0.74% | 37.96% | 1.63% | 41.9% | ||
| 8.82% | 0.25% | 0.22% | 12.49% | 3.67% | 22.59% | 1.23% | 0.69% | 0.85% | 1.86% | 3.51% | 1.12% | 37.85% | 1.76% | 40.7% | ||
| 8.05% | 0.15% | 0.10% | 21.40% | 3.17% | 18.85% | 1.32% | 0.30% | 0.81% | 2.73% | 2.32% | 0.74% | 36.56% | 1.77% | 39.4% | ||
| 3.69% | 0.19% | 0.14% | 12.63% | 1.98% | 13.76% | 1.21% | 0.42% | 0.54% | 1.55% | 1.62% | 0.61% | 59.30% | 0.97% | 51.2% | ||
| 4.86% | 0.26% | 0.16% | 14.41% | 3.06% | 20.26% | 1.02% | 5.13% | 0.77% | 1.84% | 2.20% | 1.15% | 40.45% | 1.57% | 36.6% | ||
| 13.79% | 0.14% | 0.11% | 14.56% | 3.03% | 18.83% | 0.66% | 0.42% | 0.51% | 1.40% | 1.93% | 0.60% | 41.51% | 0.96% | 41.8% | ||
| 4.55% | 0.21% | 0.13% | 12.83% | 3.55% | 15.66% | 0.74% | 2.61% | 0.55% | 1.24% | 1.62% | 0.92% | 51.70% | 1.28% | 47.0% | ||
| 9.61% | 0.23% | 0.14% | 10.37% | 2.22% | 13.30% | 2.46% | 0.37% | 0.95% | 1.81% | 2.13% | 0.90% | 50.04% | 2.57% | 44.1% | ||
| 5.96% | 0.15% | 0.11% | 13.68% | 1.99% | 12.33% | 0.69% | 0.45% | 0.51% | 1.80% | 2.50% | 0.49% | 56.19% | 1.20% | 52.6% | ||
| 7.72% | 0.35% | 0.10% | 14.84% | 2.74% | 19.15% | 1.22% | 0.48% | 0.64% | 1.26% | 2.51% | 0.87% | 44.69% | 1.08% | 40.5% | ||
| 4.60% | 0.21% | 0.10% | 27.28% | 4.11% | 10.44% | 0.55% | 0.24% | 0.42% | 0.96% | 1.23% | 0.60% | 46.70% | 0.86% | 53.3% | ||
| 2.49% | 0.06% | 0.05% | 5.16% | 0.60% | 5.19% | 0.18% | 0.20% | 0.15% | 0.29% | 0.33% | 0.14% | 84.36% | 0.31% | 83.0% | ||
| 6.54% | 0.32% | 0.25% | 13.90% | 1.97% | 13.09% | 3.55% | 0.60% | 2.62% | 3.52% | 2.93% | 1.77% | 37.76% | 9.53% | 35.2% | ||
| 5.02% | 0.25% | 0.17% | 15.24% | 2.04% | 14.89% | 1.90% | 0.62% | 1.19% | 2.57% | 2.56% | 1.34% | 45.99% | 3.45% | 37.9% | ||
| 8.72% | 1.13% | 0.17% | 11.13% | 2.73% | 19.97% | 1.38% | 0.41% | 1.00% | 1.79% | 3.26% | 1.09% | 41.98% | 2.28% | 39.7% | ||
| 4.41% | 0.21% | 0.20% | 18.45% | 2.87% | 21.80% | 1.02% | 0.51% | 0.77% | 2.22% | 2.24% | 1.08% | 41.11% | 1.23% | 44.8% | ||
| 5.11% | 0.14% | 0.12% | 12.83% | 2.26% | 12.36% | 0.94% | 0.40% | 0.68% | 1.70% | 1.69% | 0.52% | 58.15% | 1.30% | 44.4% | ||
| 1.86% | 0.05% | 0.04% | 22.18% | 0.74% | 1.75% | 0.17% | 3.92% | 0.10% | 0.98% | 0.25% | 0.22% | 67.09% | 0.15% | 85.6% | ||
| 12.60% | 0.25% | 0.14% | 15.67% | 2.58% | 16.18% | 1.78% | 0.42% | 0.75% | 1.34% | 2.33% | 0.81% | 40.05% | 2.81% | 39.8% | ||
| 5.61% | 0.26% | 0.13% | 19.55% | 3.48% | 19.55% | 0.96% | 0.37% | 1.04% | 3.13% | 1.82% | 0.84% | 38.26% | 2.30% | 34.9% | ||
| 6.24% | 0.24% | 0.16% | 25.21% | 4.55% | 15.61% | 1.98% | 0.31% | 0.74% | 1.27% | 1.72% | 0.64% | 36.32% | 1.91% | 38.7% | ||
| 5.39% | 0.21% | 0.13% | 18.38% | 3.08% | 22.66% | 1.02% | 0.62% | 0.60% | 1.04% | 1.68% | 0.55% | 40.85% | 1.35% | 41.6% | ||
| 5.63% | 0.24% | 0.12% | 17.86% | 3.74% | 15.33% | 0.94% | 0.38% | 0.64% | 1.13% | 1.73% | 0.75% | 47.93% | 1.10% | 53.5% | ||
| 4.44% | 0.12% | 0.08% | 12.48% | 2.12% | 10.02% | 0.58% | 0.24% | 0.47% | 0.89% | 1.37% | 0.47% | 64.26% | 1.03% | 60.6% | ||
| 9.02% | 0.21% | 0.16% | 14.24% | 3.36% | 15.75% | 1.74% | 0.35% | 0.86% | 1.45% | 2.24% | 0.69% | 42.65% | 3.07% | 35.1% | ||
| 5.16% | 0.21% | 0.17% | 17.95% | 3.38% | 19.66% | 1.51% | 0.45% | 0.86% | 1.87% | 3.80% | 0.82% | 38.99% | 1.79% | 37.3% | ||
| 7.27% | 0.19% | 0.18% | 17.41% | 2.59% | 14.23% | 1.18% | 0.71% | 0.53% | 1.47% | 2.17% | 0.81% | 45.15% | 4.14% | 42.1% | ||
| 4.34% | 0.20% | 0.12% | 13.60% | 2.29% | 12.49% | 0.82% | 0.34% | 0.57% | 1.53% | 1.58% | 0.58% | 58.79% | 1.18% | 48.2% | ||
| 5.00% | 0.18% | 0.10% | 13.99% | 2.58% | 14.99% | 0.82% | 0.30% | 0.73% | 1.49% | 1.85% | 0.72% | 54.52% | 1.34% | 43.3% | ||
| 6.90% | 0.28% | 0.31% | 11.31% | 1.23% | 11.36% | 8.52% | 0.44% | 2.18% | 2.62% | 2.19% | 1.53% | 39.71% | 9.08% | 32.5% | ||
| 15.20% | 0.82% | 0.16% | 14.35% | 3.14% | 10.70% | 0.73% | 0.30% | 0.49% | 1.56% | 2.34% | 0.82% | 46.42% | 1.16% | 48.1% | ||
| 3.40% | 0.21% | 0.14% | 15.44% | 3.25% | 20.03% | 1.07% | 0.59% | 0.72% | 1.72% | 3.00% | 0.90% | 45.44% | 1.74% | 37.1% | ||
| 4.47% | 0.51% | 0.16% | 15.94% | 2.75% | 14.27% | 1.45% | 0.36% | 0.91% | 1.33% | 1.44% | 0.86% | 50.77% | 1.99% | 52.8% | ||
| 4.22% | 0.14% | 0.18% | 10.36% | 2.06% | 9.36% | 0.59% | 0.53% | 0.36% | 1.03% | 0.76% | 0.49% | 68.17% | 0.89% | 64.4% | ||
| 5.09% | 0.12% | 0.07% | 12.07% | 1.90% | 15.36% | 3.58% | 0.30% | 0.56% | 2.29% | 0.98% | 0.78% | 53.78% | 0.65% | 47.0% | ||
| 4.35% | 0.20% | 0.11% | 15.82% | 2.23% | 19.42% | 0.86% | 0.59% | 0.64% | 1.38% | 2.10% | 0.72% | 48.13% | 1.33% | 40.3% | ||
| 4.34% | 0.18% | 0.15% | 13.19% | 2.67% | 15.52% | 1.02% | 0.42% | 0.52% | 1.29% | 1.72% | 0.85% | 54.26% | 0.99% | 42.0% | ||
| 13.20% | 0.35% | 0.16% | 11.88% | 2.61% | 16.54% | 1.47% | 0.50% | 0.97% | 1.57% | 3.03% | 1.25% | 40.53% | 2.90% | 41.4% | ||
| 3.89% | 0.11% | 0.09% | 10.77% | 1.76% | 7.76% | 0.42% | 0.21% | 0.39% | 7.21% | 0.94% | 0.38% | 63.51% | 0.87% | 49.2% | ||
| 2.26% | 0.12% | 0.11% | 4.07% | 3.02% | 2.25% | 0.23% | 0.20% | 0.27% | 0.41% | 0.49% | 0.20% | 85.27% | 0.55% | 78.7% | ||
| 7.33% | 0.20% | 0.17% | 12.58% | 3.52% | 20.46% | 1.84% | 0.50% | 1.10% | 1.45% | 1.91% | 1.55% | 40.67% | 3.71% | 33.8% | ||
| 4.47% | 0.17% | 0.13% | 14.41% | 2.61% | 14.28% | 0.98% | 0.32% | 0.77% | 1.79% | 2.60% | 0.99% | 53.02% | 1.76% | 45.6% | ||
| 4.35% | 0.10% | 0.09% | 4.17% | 1.15% | 3.12% | 0.23% | 0.24% | 0.47% | 0.25% | 0.94% | 0.26% | 82.61% | 0.93% | 89.7% | ||
| 9.61% | 0.17% | 0.14% | 15.23% | 2.18% | 16.35% | 1.07% | 0.41% | 0.79% | 1.94% | 2.26% | 0.76% | 45.00% | 1.92% | 41.6% | ||
| 11.45% | 0.14% | 0.11% | 12.27% | 0.50% | 14.12% | 0.25% | 0.24% | 0.20% | 0.35% | 0.53% | 0.23% | 58.35% | 0.39% | 81.1% | ||
| 8.91% | 0.31% | 0.13% | 13.93% | 2.24% | 12.28% | 3.18% | 0.67% | 0.61% | 1.15% | 1.82% | 0.62% | 50.52% | 1.19% | 44.4% | ||
| 3.34% | 0.21% | 0.12% | 19.16% | 3.24% | 15.99% | 1.81% | 0.46% | 0.61% | 1.13% | 1.89% | 0.54% | 48.46% | 1.23% | 52.3% | ||
| 7.61% | 0.39% | 0.15% | 13.03% | 3.37% | 17.96% | 1.25% | 0.42% | 0.84% | 1.94% | 3.04% | 0.99% | 45.20% | 1.77% | 38.4% | ||
| 5.61% | 0.16% | 0.11% | 14.94% | 2.53% | 16.17% | 0.88% | 0.79% | 0.73% | 1.27% | 1.82% | 0.73% | 50.64% | 1.76% | 42.1% | ||
| 10.54% | 0.23% | 0.15% | 13.87% | 2.76% | 21.40% | 1.45% | 0.40% | 0.97% | 1.40% | 4.03% | 1.00% | 37.21% | 2.43% | 40.8% | ||
| 7.07% | 0.12% | 0.10% | 15.59% | 1.98% | 9.25% | 0.70% | 0.54% | 0.53% | 1.48% | 1.28% | 0.56% | 58.67% | 0.97% | 53.7% | ||
| 4.74% | 0.28% | 0.27% | 6.86% | 1.15% | 14.02% | 0.65% | 0.46% | 0.43% | 0.73% | 0.90% | 0.49% | 67.14% | 0.67% | 74.3% | ||
| 10.27% | 0.28% | 0.11% | 16.04% | 2.19% | 17.36% | 1.43% | 0.59% | 1.26% | 2.50% | 2.51% | 1.46% | 38.43% | 3.77% | 37.8% | ||
| 4.17% | 0.35% | 0.16% | 15.93% | 3.38% | 26.40% | 0.66% | 0.81% | 0.50% | 1.19% | 2.13% | 0.78% | 39.87% | 0.82% | 38.9% | ||
| Total | 6.23% | 0.22% | 0.14% | 13.34% | 2.27% | 13.14% | 1.29% | 0.59% | 0.73% | 1.51% | 1.73% | 0.76% | 54.19% | 1.99% | 47.8% |
 Turnout (red) and United Russia vote (blue) |  KPRF (red) vs LDPR (blue), percentage difference based on total number of registered voters |
By constituency
Notes
^ Recognized by most members of the UN as part of Ukraine.[4]
^ In opinion polls often found under the old name of "Right Cause"
^ Recognized by most members of the UN as part of Ukraine[53][54][55][56]
^ Recognized by most members of the UN as part of Ukraine[53]
References
^ ab "Выборы депутатов Госдумы VII созыва | РИА Новости – события в России и мире: темы дня, фото, видео, инфографика, радио". Ria.ru. Retrieved 2016-12-15..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "State Duma passes first reading of bill to postpone the elections". Vedomosti. 19 June 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
^ abc Russia votes in parliamentary election with firm Putin grip, BBC News (18 September 2016)
^ UKRAINE REPORTS RUSSIAN MILITARY ACTIVITY ON CRIMEA BORDER, Newsweek (8 August 2016)
Gutterman, Steve. "Putin signs Crimea treaty, will not seize other Ukraine regions". Reuters.com. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
Ukraine crisis timeline, BBC News
UN General Assembly adopts resolution affirming Ukraine's territorial integrity, China Central Television (28 March 2014)
^ "Сведения об общей численности избирателей, участников референдума Российской Федерации по состоянию на 1 января 2016 года – Центральная избирательная комиссия Российской Федерации". Cikrf.ru. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ Shaun Walker. "Russia stays loyal to Kremlin in election with record low turnout | World news". The Guardian. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Vladimir Putin's party wins again". The Economist. 2016-09-19. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "On 1 July 2015, Constitutional Court of Russia announces ruiling on interpretation of part 1 of article 96 and parts 1, 2, and 4 of article 99 of the Russian Constitution". Constitutional Court of Russia. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Владимир Путин назначил выборы в Госдуму на 18 сентября". Kommersant.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016 – via Kommersant.
^ "Владимир Путин объявил выборы в Госдуму". Kommersant.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016 – via Kommersant.
^ Shaun Walker. "Russia votes in election unlikely to loosen Putin's grip on power | World news". The Guardian. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "U.S. Says Russian Duma Elections In Crimea Are Illegal". Rferl.mobi. 2016-09-17. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Париж не признает законность голосования жителей Крыма на выборах в Госдуму". Retrieved 2016-09-19.
^ "Canada will not recognize elections in Crimea: Canada becomes another country not to recognize the Russian elections in annexed Crimea". Uatoday.tv. 2016-09-20. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Twitter". Mobile.twitter.com. 2016-09-18. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Protesters At Russian Embassy In Kyiv On Election Day". Rferl.mobi. 2016-09-18. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Russland: Zahl der Soldaten in Syrien enthüllt – SPIEGEL ONLINE". Spiegel.de. 2016-09-23. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ ab "Федеральный закон "О выборах депутатов Государственной Думы Федерального Собрания Российской Федерации" от 22.02.2014 N 20-ФЗ (действующая редакция, 2016) / КонсультантПлюс". Consultant.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "Центральная избирательная комиссия Российской Федерации". Cikrf.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "ЦИК РФ ПРОВЕДЕТ ЖЕРЕБЬЕВКУ ПОРЯДКА НАИМЕНОВАНИЙ ПАРТИЙ В БЮЛЛЕТЕНЯХ 12 АВГУСТА". Mskagency.ru. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "Жеребьёвка эфирного времени в СМИ для депутатов пройдёт в ЦИК 16 и 18 августа". Pnp.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ Petersen, Jan et al. (23 December 2016). OSCE/ODIHR Election Observation Mission – Final Report (Report). Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. Retrieved 5 July 2017.CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link) CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al. (link)
^ "Information on political parties allowed to participate in the election of deputies of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation without the collection of voter signatures (in accordance with Article 44 of the Federal Law of 22 February 2014 "On elections of deputies of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation")" (doc). Central Election Commission of Russia (cikrf.ru). 2014-10-28. Retrieved 2015-12-31.
^ ab "Парад партийных съездов". Ng.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ ab "ЦИК заверил списки: 20 партий продолжат участие в думской кампании". Ria.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал федеральный список "Родины" на выборах в Госдуму". Retrieved 2016-08-08.
^ "ЦИК РФ зарегистрировал федеральный список кандидатов в депутаты Госдумы от "Коммунистов России"" (in Russian). Retrieved 2016-08-03.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал список Российской партии пенсионеров на выборах". Retrieved 2016-08-12.
^ abc "ЦИК зарегистрировал список кандидатов из 14 партий в Госдуме". Retrieved 2016-08-12.
^ [1][dead link]
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал федеральный список "Гражданской платформы"". Ria.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "ЦИК РФ зарегистрировал список ЛДПР для участия в выборах в Госдуму". Tass.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "Центризбирком зарегистрировал федеральный список кандидатов в депутаты Госдумы от ПАРНАС" (in Russian). Retrieved 2016-08-03.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал федеральный список "Партии роста" на выборах в Госдуму". Retrieved 2016-08-02.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал федеральный список "Гражданской силы" на выборах". Retrieved 2016-08-03.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал федеральный список "Яблока" на выборах". Retrieved 2016-08-05.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал список КПРФ на выборах в Госдуму". ТВ Центр – Официальный сайт телекомпании (in Russian). Retrieved 2016-08-02.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировала федеральный список "Патриотов России"". Ria.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "ЦИК зарегистрировал список кандидатов "Справедливой России" на выборах в ГД". Ria.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "Памфилова заявила о неправомерности съезда партии "Альянс зеленых"". Gr-sily.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ "ЦИК не зарегистрировал на выборах в Госдуму список "Родной партии"". Retrieved 2016-08-10.
^ ab "ЦИК: Списки кандидатов в Госдуму сдали 22 партии". Vedomosti.ru. 2016-07-14. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ ""Партия родителей будущего" не собрала подписи для выборов в Госдуму". www.tv2.tomsk.ru. Retrieved 2016-08-04.
^ "Непарламентские партии рассказали о сборе подписей для участия в выборах". Retrieved 2016-08-04.
^ "ЦИК отказался заверять списки "Партии социальных реформ" на выборах в ГД". Ria.ru. Retrieved 18 September 2016.
^ [2][dead link]
^ "ЦИК не зарегистрировал список партии "Воли" на выборах". Retrieved 2016-08-05.
^ "Reports of voting fraud in Russia poll". Bbc.co.uk. 2016-09-18. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ Zelensky, Mikhail (22 September 2016). "Загадочные 62%. На родине Володина нашлась самая подозрительная цифра выборов". Slon.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 22 September 2016.
^ "Pro-Putin party wins Russian parliamentary election". Reuters. 2016-09-18. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
^ Sharkov, Damien (22 September 2016). "Russia Cancels Election Results After Ballot Stuffing". The Newsweek. Retrieved 23 September 2016.
^ "When the Russians fake their election results, they may be giving us the statistical finger". Washington Post. Retrieved 2017-01-11.
^ ab Sharkov, Damien. "Ukraine Reports Russian Military Activity on Crimea Border". Europe.newsweek.com. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ Gutterman, Steve. "Putin signs Crimea treaty, will not seize other Ukraine regions". Reuters.com. Retrieved 26 March 2014.
^ "Ukraine crisis: Timeline – BBC News". Bbc.co.uk. 2014-11-13. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
^ "UN General Assembly adopts resolution affirming Ukraine's territorial integrity – CCTV News – CCTV.com English". English.cntv.cn. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Russian legislative election, 2016. |
- Central Elections Commission of Russia
- WCIOM
- FOM
- 2016 State Duma Elections
Full info on Ura.ru





