Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | Rosalind Elsie Franklin (1920-07-25)25 July 1920 Notting Hill, London, England, UK |
| Died | 16 April 1958(1958-04-16) (aged 37) Chelsea, London, England, UK |
| Cause of death | Ovarian cancer |
| Resting place | Willesden United Synagogue Cemetery 51°32′41″N 0°14′24″W / 51.5447°N 0.2399°W / 51.5447; -0.2399 |
| Nationality | English |
| Education | St Paul's Girls' School |
| Alma mater | University of Cambridge (PhD) |
| Known for |
|
| Scientific career | |
| Fields |
|
| Institutions |
|
| Thesis | The physical chemistry of solid organic colloids with special reference to coal (1945) |
| Doctoral students | John Finch and Kenneth Holmes |
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 1920 – 16 April 1958)[1] was an English chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, coal, and graphite.[2] Although her works on coal and viruses were appreciated in her lifetime, her contributions to the discovery of the structure of DNA were largely recognised posthumously.
Born to a prominent British Jewish family, Franklin was educated at a private day school at Norland Place in West London, Lindores School for Young Ladies in Sussex, and St Paul's Girls' School, London. Then she studied the Natural Sciences Tripos at Newnham College, Cambridge, from which she graduated in 1941. Earning a research fellowship, she joined the University of Cambridge physical chemistry laboratory under Ronald George Wreyford Norrish, who disappointed her for his lack of enthusiasm.[3] The British Coal Utilisation Research Association (BCURA) offered her a research position in 1942, and started her work on coals. This helped her earn a Ph.D. in 1945.[4] She went to Paris in 1947 as a chercheur (post-doctoral researcher) under Jacques Mering at the Laboratoire Central des Services Chimiques de l'Etat, where she became an accomplished X-ray crystallographer. She became a research associate at King's College London in 1951 and worked on X-ray diffraction studies, which would eventually facilitate the double helix theory of the DNA.[5] In 1953, after two years, owing to disagreement with her director John Randall and more so with her colleague Maurice Wilkins, she was compelled to move to Birkbeck College.[5] At Birkbeck, John Desmond Bernal, chair of the physics department, offered her a separate research team. She died in 1958 at the age of 37 of ovarian cancer.
Franklin is best known for her work on the X-ray diffraction images of DNA, particularly Photo 51, while at King's College London, which led to the discovery of the DNA double helix for which James Watson, Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1962. Watson suggested that Franklin would have ideally been awarded a Nobel Prize in Chemistry, along with Wilkins, but, although there was not yet a rule against posthumous awards,[6] the Nobel Committee generally does not make posthumous nominations.[7][8]
After finishing her work on DNA, Franklin led pioneering work at Birkbeck on the molecular structures of viruses.[9] Her team member Aaron Klug continued her research, winning the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1982.
Contents
1 Education and early life
1.1 Cambridge and World War II
2 Career and research
2.1 Paris
2.2 King's College London
2.3 DNA structure
2.4 Birkbeck College
3 Personal life
3.1 Illness and death
4 Controversies after death
4.1 Allegations of sexism
4.2 Contribution to the model of DNA
4.3 Recognition of her contribution to the model of DNA
4.4 Nobel Prize
5 Awards and honours
5.1 Posthumous recognition
5.2 Cultural references
6 Publications
7 See also
8 References
8.1 Sources
9 Further reading
10 External links
Education and early life
Franklin was born on 25 July 1920 in 50 Chepstow Villas,[10] Notting Hill, London, into an affluent and influential British Jewish family.[11][12] Her father was Ellis Arthur Franklin (1894–1964), a politically liberal London merchant banker who taught at the city's Working Men's College, and her mother was Muriel Frances Waley (1894–1976). Rosalind was the elder daughter and the second child in the family of five children. David (born 1919) was the eldest brother; Colin (born 1923), Roland (born 1926), and Jenifer (born 1929) were her younger siblings.[13] Her father's uncle was Herbert Samuel (later Viscount Samuel), who was the Home Secretary in 1916 and the first practising Jew to serve in the British Cabinet.[14] Her aunt, Helen Caroline Franklin, known in the family as Mamie, was married to Norman de Mattos Bentwich, who was the Attorney General in the British Mandate of Palestine.[15] Helen Caroline Franklin was active in trade union organisation and the women's suffrage movement, and was later a member of the London County Council.[16][17] Her uncle, Hugh Franklin, was another prominent figure in the suffrage movement, although his actions therein embarrassed the Franklin family. Rosalind's middle name, "Elsie", was in memory of Hugh's first wife, who died in the 1918 flu pandemic.[13] Her family was actively involved with the Working Men's College, where her father taught the subjects of electricity, magnetism, and the history of the Great War in the evenings, later becoming the vice-principal.[18][19]
Franklin's parents helped settle Jewish refugees from Europe who had escaped the Nazis, particularly those from the Kindertransport.[20] They took in two Jewish children to their home, and one of them, a nine-year-old Austrian, Evi Eisenstädter, shared Jenifer's room.[21] (Evi's father Hans Mathias Eisenstädter had been imprisoned in Buchenwald, and after liberation, the family adopted the surname "Ellis".)[22][23]
From early childhood, Franklin showed exceptional scholastic abilities. At the age of six, she joined her brother Roland at Norland Place School, a private day school in West London. At that time, her aunt Mamie (Helen Bentwich), described her to her husband: "Rosalind is alarmingly clever – she spends all her time doing arithmetic for pleasure, and invariably gets her sums right."[24] She also developed an early interest in cricket and hockey. At the age of nine, she entered a boarding-school, Lindores School for Young Ladies in Sussex.[25] The school was near the seaside, and the family wanted a good environment for her delicate health. She was 11 when she went to St Paul's Girls' School, West London, one of the few girls' schools in London that taught physics and chemistry.[25][26][27] At St Paul's she excelled in science, Latin,[28] and sports.[29] She also learned German, and became fluent in French, a language she would later find useful. She topped her classes, and won annual awards. Her only educational weakness was in music, for which the school music director, the composer Gustav Holst, once called upon her mother to inquire whether she might have suffered from hearing problem or tonsillitis.[30] With six distinctions, she passed her matriculation in 1938, winning a scholarship for university, the School Leaving Exhibition of £30 a year for three years, and £5 from her grandfather.[31] Her father asked her to give the scholarship to a deserving refugee student.[25]
Cambridge and World War II
Franklin went to Newnham College, Cambridge in 1938 and studied chemistry within the Natural Sciences Tripos. There she met the spectroscopist Bill Price, who worked with her as a laboratory demonstrator and who later became one of her senior colleagues at King's College London.[32] In 1941, she was awarded second-class honours from her final exams. The distinction was accepted as a bachelor's degree in qualifications for employment. Cambridge began awarding titular B.A. and M.A. degrees to women from 1947, and the previous women graduates retroactively received these.[33] In her last year at Cambridge, she met a French refugee Adrienne Weill, a former student of Marie Curie, who had a huge influence on her life and career and helped her to improve her spoken French.[34]
Franklin was awarded a research fellowship at Newnham College, with which she joined the physical chemistry laboratory of the University of Cambridge to work under Ronald George Wreyford Norrish, who later won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. In her one year of work there, she did not have much success.[35] As described by his biographer, Norrish was "obstinate and almost perverse in argument, overbearing and sensitive to criticism".[36] He could not decide for her what to work upon, and at that time was succumbing to heavy drinking. Franklin wrote that he made her despise him completely.[37] Resigning from Norrish's Lab, she fulfilled the requirements of the National Service Acts by working as an assistant research officer at the British Coal Utilisation Research Association (BCURA) in 1942.[9] The BCURA was located on the Coombe Springs Estate near Kingston upon Thames near the southwestern boundary of London. Norrish acted as advisor to the military at BCURA. John G. Bennett was the director. Marcello Pirani and Victor Goldschmidt, both refugees from the Nazis, were consultants and lectured at BCURA while Franklin worked there.[2] During her BCURA research, she stayed at Adrienne Weill's boarding house in Cambridge until her cousin Irene Franklin asked to join her in a vacated house of her uncle in Putney. With Irene, she volunteered as an Air Raid Warden and regularly made patrols to see the welfare of people during air raids.[38]
She studied the porosity of coal using helium to determine its density.[39] Through this, she discovered the relationship between the fine constrictions in the pores of coals and the permeability of the porous space. By concluding that substances were expelled in order of molecular size as temperature increased, she helped classify coals and accurately predict their performance for fuel purposes and for production of wartime devices such as gas masks.[40] This work was the basis of her Ph.D. thesis The physical chemistry of solid organic colloids with special reference to coal for which the University of Cambridge awarded her a Ph.D. in 1945.[4] It was also the basis of several papers.[2]
Career and research
Franklin spent her career working in London and Paris.
Paris
With World War II ending in 1945, Franklin asked Adrienne Weill for help and to let her know of job openings for "a physical chemist who knows very little physical chemistry, but quite a lot about the holes in coal". At a conference in the autumn of 1946, Weill introduced her to Marcel Mathieu, a director of the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS), the network of institutes that comprise the major part of the scientific research laboratories supported by the French government. This led to her appointment with Jacques Mering at the Laboratoire Central des Services Chimiques de l'État in Paris. She joined the labo (as referred to by the staff) of Mering on 14 February 1947 as one of the fifteen chercheurs (researchers).[41][42]
Mering was an X-ray crystallographer who applied X-ray diffraction to the study of rayon and other amorphous substances, in contrast to the thousands of regular crystals that had been studied by this method for many years.[2] He taught her the practical aspects of applying X-ray crystallography to amorphous substances. This presented new challenges in the conduct of experiments and the interpretation of results. Franklin applied them to further problems related to coal, in particular the changes to the arrangement of atoms when it is converted to graphite.[2] She published several further papers on this work which has become part of the mainstream of the physics and chemistry of coal. This work was covered in a 1993 monograph,[43] and in the regularly-published textbook Chemistry and Physics of Carbon.[44] Mering continued the study of carbon in various forms, using X-ray diffraction and other methods.[45]
King's College London
Double helix 
|
In 1950, Franklin was granted a three-year Turner & Newall Fellowship to work at King's College London. In January 1951, she started working as a research associate in the Medical Research Council's (MRC) Biophysics Unit, directed by John Randall.[46] She was originally appointed to work on X-ray diffraction of proteins and lipids in solution, but Randall redirected her work to DNA fibres because of new developments in the field, and she was to be the only experienced experimental diffraction researcher at King's at the time.[47][48] Randall made this reassignment, even before she started working at King's, because of the following pioneering work by Maurice Wilkins and Raymond Gosling – a Ph.D. student assigned to help her.[49]
Even using crude equipment, Wilkins and Gosling had obtained an outstanding diffraction picture of DNA which sparked further interest in this molecule. They had been carrying out X-ray diffraction analysis of DNA in the unit since May 1950, but Randall had not informed them that he had asked Franklin to take over both the DNA diffraction work and guidance of Gosling's thesis.[50] Randall's lack of communication about this reassignment significantly contributed to the well documented friction that developed between Wilkins and Franklin.[51]
Franklin, working with Gosling,[52] started to apply her expertise in X-ray diffraction techniques to the structure of DNA. She used a new fine-focus X-ray tube and microcamera ordered by Wilkins, but which she refined, adjusted and focused carefully. Drawing upon her physical chemistry background, she also skillfully manipulated the critical hydration of her specimens.[53] When Wilkins inquired about this improved technique, she replied in terms which offended Wilkins as Franklin had "an air of cool superiority".[54]
Franklin presented her data at a lecture in November 1951, in King's College London. In her lecture notes, Franklin wrote the following[55]:
.mw-parser-output .templatequote{overflow:hidden;margin:1em 0;padding:0 40px}.mw-parser-output .templatequote .templatequotecite{line-height:1.5em;text-align:left;padding-left:1.6em;margin-top:0}
"The results suggest a helical structure (which must be very closely packed) containing 2, 3 or 4 co‐axial nucleic acid chains per helical unit, and having the phosphate groups near the outside."
Franklin's habit of intensely looking people in the eye while being concise, impatient and direct unnerved many of her colleagues. In stark contrast, Wilkins was very shy, and slowly calculating in speech while he avoided looking anyone directly in the eye.[56] In spite of the intense atmosphere, Franklin and Gosling discovered that there were two forms of DNA: at high humidity (when wet), the DNA fibre became long and thin; when it was dried it became short and fat.[57][58]
Franklin named these two forms "B" and "A" respectively. (The biological functions of A-DNA were only discovered 60 years later.[59]) Because of the intense personality conflict developing between Franklin and Wilkins, Randall[60] divided the work on DNA. Franklin chose the data rich "A" form while Wilkins selected the "B" form[60][61] because, according to his self-written biography, Wilkins' preliminary pictures had hinted it might be helical. The X-ray diffraction pictures, including the landmark Photo 51, taken by Franklin at this time have been called by John Desmond Bernal as "amongst the most beautiful X-ray photographs of any substance ever taken".[57]
By the end of 1951 it was generally accepted at King's that the B form of DNA was a helix, but after she had recorded an asymmetrical image in May 1952, Franklin became unconvinced that the A form of DNA was a helix.[62] In July 1952, as a practical joke on Wilkins (who frequently expressed his view that both forms of DNA were helical), Franklin and Gosling produced a funeral notice regretting the 'death' of helical crystalline DNA (A-DNA).[63] During 1952, they worked at applying the Patterson function to the X-ray pictures of DNA they had produced.[64] This was a long and labour-intensive approach but would yield significant insight into the structure of the molecule.[65][66]
By January 1953, Franklin had reconciled her conflicting data, concluding that both DNA forms had two helices, and had started to write a series of three draft manuscripts, two of which included a double helical DNA backbone (see below). Her two A-DNA manuscripts reached Acta Crystallographica in Copenhagen on 6 March 1953, one day before Crick and Watson had completed their model on B-DNA. She must have mailed them while the Cambridge team was building their model, and certainly had written them before she knew of their work.[67] On 8 July 1953 she modified one of these "in proof" Acta articles, "in light of recent work" by the King's and Cambridge research teams.[68]
The third draft paper was on the B form of DNA, dated 17 March 1953, which was discovered years later amongst her papers,[69] by Franklin's Birkbeck colleague, Aaron Klug. He then published an evaluation of the draft's close correlation with the third of the original trio of 25 April 1953 Nature DNA articles.[70] Klug designed this paper to complement the first article he had written defending Franklin's significant contribution to DNA structure.[71] He had written this first article in response to the incomplete picture of Franklin's work depicted in Watson's 1968 memoir, The Double Helix.
As vividly described in The Double Helix, on 30 January 1953, Watson travelled to King's carrying a preprint of Linus Pauling's incorrect proposal for DNA structure. Since Wilkins was not in his office, Watson went to Franklin's lab with his urgent message that they should all collaborate before Pauling discovered his error. The unimpressed Franklin became angry when Watson suggested she did not know how to interpret her own data. Watson hastily retreated, backing into Wilkins who had been attracted by the commotion. Wilkins commiserated with his harried friend and then showed Watson Franklin's DNA X-ray image.[72] Watson, in turn, showed Wilkins a prepublication manuscript by Pauling and Corey, which contained a DNA structure remarkably like their first incorrect model.[73]
DNA structure
In February 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick of the Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge University had started to build a molecular model of the B form of DNA using data similar to that available to both teams at King's. Much of their data was derived directly from research done at King's by Wilkins and Franklin. Franklin's research was completed by February 1953, ahead of her move to Birkbeck, and her data was critical.[74] Model building had been applied successfully in the elucidation of the structure of the alpha helix by Linus Pauling in 1951,[61][75] but Franklin was opposed to prematurely building theoretical models, until sufficient data were obtained to properly guide the model building. She took the view that building a model was to be undertaken only after enough of the structure was known.[62][76]
Ever cautious, she wanted to eliminate misleading possibilities. Photographs of her Birkbeck work table show that she routinely used small molecular models, although certainly not ones on the grand scale successfully used at Cambridge for DNA. In the middle of February 1953, Crick's thesis advisor, Max Perutz, gave Crick a copy of a report written for a Medical Research Council biophysics committee visit to King's in December 1952, containing many of Franklin's crystallographic calculations.[77]
Since Franklin had decided to transfer to Birkbeck College and Randall had insisted that all DNA work must stay at King's, Wilkins was given copies of Franklin's diffraction photographs by Gosling. By 28 February 1953, Watson and Crick felt they had solved the problem enough for Crick to proclaim (in the local pub) that they had "found the secret of life".[78] However, they knew they must complete their model before they could be certain.[79]
Watson and Crick finished building their model on 7 March 1953, one day before they received a letter from Wilkins stating that Franklin was finally leaving and they could put "all hands to the pump".[80] This was also one day after Franklin's two A-DNA papers had reached Acta Crystallographica. Wilkins came to see the model the following week, according to Franklin's biographer Brenda Maddox on 12 March, and allegedly informed Gosling on his return to King's.[81]
It is uncertain how long it took for Gosling to inform Franklin at Birkbeck, but her original 17 March B-DNA manuscript does not reflect any knowledge of the Cambridge model. Franklin did modify this draft later before publishing it as the third in the trio of 25 April 1953 Nature articles. On 18 March,[82] in response to receiving a copy of their preliminary manuscript, Wilkins penned the following: "I think you're a couple of old rogues, but you may well have something".[83]
Crick and Watson then published their model in Nature on 25 April 1953 in an article describing the double-helical structure of DNA with only a footnote acknowledging "having been stimulated by a general knowledge of" Franklin and Wilkins' "unpublished" contribution.[84] Actually, although it was the bare minimum, they had just enough specific knowledge of Franklin and Gosling's data upon which to base their model. As a result of a deal struck by the two laboratory directors, articles by Wilkins and Franklin, which included their X-ray diffraction data, were modified and then published second and third in the same issue of Nature, seemingly only in support of the Crick and Watson theoretical paper which proposed a model for the B form of DNA.[85][86]
Weeks later, on 10 April, Franklin wrote to Crick for permission to see their model.[87] Franklin retained her scepticism for premature model building even after seeing the Watson–Crick model, and remained unimpressed. She is reported to have commented, "It's very pretty, but how are they going to prove it?" As an experimental scientist, Franklin seems to have been interested in producing far greater evidence before publishing-as-proven a proposed model. As such, her response to the Watson–Crick model was in keeping with her cautious approach to science.[88] Most of the scientific community hesitated several years before accepting the double helix proposal. At first mainly geneticists embraced the model because of its obvious genetic implications.[89][90][91]
Birkbeck College
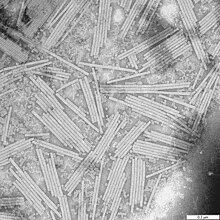
An electron micrograph of tobacco mosaic virus
Franklin left King's College London in mid-March 1953 for Birkbeck College, in a move that had been planned for some time and that she described (in a letter to Adrienne Weill in Paris) as "moving from a palace to the slums ... but pleasanter all the same."[92] She was recruited by physics department chair John Desmond Bernal,[93] a crystallographer who was a communist, known for promoting women crystallographers. Her new laboratories were housed in 21 Torrington Square, one of a pair of dilapidated and cramped Georgian houses containing several different departments; Franklin frequently took Bernal to task over the careless attitudes of some of the other laboratory staff, notably after workers in the pharmacy department flooded her first-floor laboratory with water on one occasion.[94]
Despite the parting words of Bernal to stop her interest in nucleic acids, she helped Gosling to finish his thesis, although she was no longer his official supervisor. Together they published the first evidence of double helix in the A form of DNA in the 25 July issue of Nature.[95] At the end of 1954, Bernal secured funding for Franklin from the Agricultural Research Council (ARC), which enabled her to work as a senior scientist supervising her own research group.[96][97] John Finch, a physics student from King's College London, subsequently joined Franklin's group, followed by Kenneth Holmes, a Cambridge graduate, in July 1955. Despite the ARC funding, Franklin wrote to Bernal that the existing facilities remained highly unsuited for conducting research "...my desk and lab are on the fourth floor, my X-ray tube in the basement, and I am responsible for the work of four people distributed over the basement, first and second floors on two different staircases."[98]
Franklin continued to explore another major nucleic acid, RNA, a molecule equally central to life as DNA. She again used X-ray crystallography to study the structure of the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), an RNA virus. Her meeting with Aaron Klug in early 1954 led to a longstanding and successful collaboration. Klug had just then earned his PhD from Trinity College, Cambridge, and joined Birkbeck in late 1953. In 1955 Franklin published her first major works on TMV in Nature, in which she described that all TMV virus particles were of the same length.[99] This was in direct contradiction to the ideas of the eminent virologist Norman Pirie, though her observation ultimately proved correct.[100]
Franklin assigned the study of the complete structure of TMV to her PhD student Holmes. They soon discovered (published in 1956) that the covering of TMV was protein molecules arranged in helices.[101] Her colleague Klug worked on spherical viruses with his student John Finch, with Franklin coordinating and overseeing the work.[102] As a team, from 1956 they started publishing seminal works on TMV,[103] cucumber virus 4 and turnip yellow mosaic virus.[104]
Franklin also had a research assistant, James Watt, subsidised by the National Coal Board and was now the leader of the ARC group at Birkbeck.[105] The Birkbeck team members continued working on RNA viruses affecting several plants, including potato, turnip, tomato and pea.[106] In 1955 the team was joined by an American post-doctoral student Donald Caspar. He worked on the precise location of RNA molecules in TMV. In 1956 he and Franklin published individual but complementary papers in the 10 March issue of Nature, in which they showed that the RNA in TMV is wound along the inner surface of the hollow virus.[107][108] Caspar was not an enthusiastic writer, and Franklin had to write the entire manuscript for him.[109]
In 1957 her research grant from ARC expired, and was given a one-year extension ending in March 1958. She applied for a new grant from the United States Public Health Service of the National Institutes of Health, which approved £10,000 for three years, the largest fund ever received at Birkbeck.[110][111] In her grant application, Franklin mentioned her new interest in animal virus research. The previous year, Franklin had visited the University of California, Berkeley, where colleagues had suggested her group research the polio virus.[112] She obtained Bernal's consent in July 1957, though serious concerns were raised after she disclosed her intentions to research live, instead of killed, polio virus at Birkbeck. Eventually, Bernal arranged for the virus to be safely stored at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine during the group's research. With her group, Franklin then commenced deciphering the structure of the polio virus while it was in a crystalline state. She attempted to mount the virus crystals in capillary tubes for X-ray studies, but was forced to end her work due to her rapidly failing health.[113]
Expo 58, the first major international fair after World War II, was to be held in Brussels in 1958.[114][115] Franklin was invited to make a five-foot high model of TMV, which she started in 1957. Her materials included table tennis balls and plastic bicycle handlebar grips.[116] The Brussels world's fair, with an exhibit of her virus model at the International Science Pavilion, opened on 17 April, one day after she died.[117]
After Franklin's death, Klug succeeded her as group leader, and he, Finch and Holmes continued researching the structure of the polio virus. They eventually succeeded in obtaining extremely detailed X-ray images of the virus. In June 1959, Klug and Finch published the group's findings, revealing the polio virus to have icosahedral symmetry, and in the same paper suggested the possibility for all spherical viruses to possess the same symmetry, as it permitted the greatest possible number (60) of identical structural units.[118] The team moved to the Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge in 1962,[119] and the old Torrington Square laboratories were demolished four years later, in May 1966.[120]
Personal life
Franklin was best described as an agnostic.[121] Her lack of religious faith apparently did not stem from anyone's influence, rather from her own line of thinking. She developed her scepticism as a young child. Her mother recalled that she refused to believe in the existence of God, and remarked, "Well, anyhow, how do you know He isn't She?"[122] She later made her position clear, now based on her scientific experience, and wrote to her father in 1940:
[S]cience and everyday life cannot and should not be separated. Science, for me, gives a partial explanation of life ... I do not accept your definition of faith i.e. belief in life after death ... Your faith rests on the future of yourself and others as individuals, mine in the future and fate of our successors. It seems to me that yours is the more selfish ...[123] [as to] the question of a creator. A creator of what? ... I see no reason to believe that a creator of protoplasm or primeval matter, if such there be, has any reason to be interested in our insignificant race in a tiny corner of the universe.[124]
However, she did not abandon Jewish traditions. As the only Jewish student at Lindores School, she had Hebrew lessons on her own while her friends went to church.[125] She joined the Jewish Society while in her first term at Newnham College, Cambridge, out of respect of her grandfather's request.[126] She confided to her sister that she was "always consciously a Jew".[124]
Franklin loved travelling abroad, particularly trekking. She first "qualified" at Christmas 1929 for a vacation at Menton, France, where her grandfather went to escape English winter.[127] Her family frequently spent vacations in Wales or Cornwall. A trip to France in 1938 gave her a lasting love for France and its language. She considered the French lifestyle at that time as "vastly superior to that of English".[128] In contrast, she described English people as having "vacant stupid faces and childlike complacency".[129] Her family was almost stuck in Norway in 1939, as World War II was declared on their way home.[130] In another instance, she trekked the French Alps with Jean Kerslake in 1946, which almost cost her her life. She slipped off on a slope, and was barely rescued.[131] But she wrote to her mother, "I am quite sure I could wander happily in France forever. I love the people, the country and the food."[132]
She made several professional trips to US, and was particularly jovial among her American friends and constantly displayed her sense of humour. William Ginoza of the University of California, Los Angeles later recalled that she was the opposite of Watson's description of her, and as Maddox comments, Americans enjoyed her "sunny side".[133]
In his book The Double Helix, Watson provides his first-person account of the search for and discovery of DNA. He paints a sympathetic but sometimes critical portrait of Franklin. He praises her intellect and scientific acumen, but portrays her as difficult to work with and careless with her appearance. After introducing her in the book as “Rosalind,” he writes that he and his male colleagues usually referred to her as "Rosy", the name people at King's College London used behind her back.[134] She did not want to be called by that name because she had a great-aunt Rosy. In the family, she was called "Ros".[135] To others, she was simply "Rosalind". She made it clear to an American visiting friend Dorothea Raacke, while sitting with her at Crick's table in The Eagle pub in Cambridge: Raacke asked her how she was to be called and she replied "I'm afraid it will have to be Rosalind", adding "Most definitely not Rosy."[136]
She often expressed her political views. She initially blamed Winston Churchill for inciting the war, but later admired him for his speeches. She actively supported Professor John Ryle as an independent candidate for parliament in 1940, but he was unsuccessful.[137]
She did not seem to have an intimate relationship with anyone, and always kept her deepest personal feelings to herself. After her younger days, she avoided close friendship with the opposite sex. Once her cousins visited them, she paid Roland to accompany them.[128] In her later years, Evi Ellis, who had shared her bedroom when a child refugee and who was then married to Ernst Wohlgemuth[23] and had moved to Notting Hill from Chicago, tried matchmaking her with Ralph Miliband but failed. Franklin once told Evi that her flatmate asked her for a drink, but she did not get the intention.[138] She was quite infatuated by her French mentor Mering, who had a wife and a mistress.[132] Mering also admitted that he was captivated by her "intelligence and beauty".[139] According to Sayre, she did confess her feeling for Mering when she was undergoing surgery, but her family denied this. But Mering wept when he visited her later,[137] and destroyed all her letters.[140]
Her closest personal affair was probably with her once post-doctoral student Donald Caspar. In 1956, she visited him at his home in Colorado after her tour to University of California, Berkeley, and she was known to remark later that Caspar was one "she might have loved, might have married". In her letter to Sayre, she described him as "an ideal match".[141]
Illness and death
In mid-1956, while on a work-related trip to the United States, Franklin first began to suspect a health problem. While in New York she found difficulty in zipping her skirt; her stomach had bulged. Back in London she consulted Mair Livingstone, who asked her, "You're not pregnant?" to which she retorted, "I wish I were." Her case was marked "URGENT".[142] An operation on 4 September of the same year revealed two tumours in her abdomen.[143] After this period and other periods of hospitalization, Franklin spent time convalescing with various friends and family members. These included Anne Sayre, Francis Crick, his wife Odile, with whom Franklin had formed a strong friendship,[136] and finally with the Roland and Nina Franklin family where Rosalind's nieces and nephews bolstered her spirits.
Franklin chose not to stay with her parents because her mother's uncontrollable grief and crying upset her too much. Even while undergoing cancer treatment, Franklin continued to work, and her group continued to produce results – seven papers in 1956 and six more in 1957.[144] At the end of 1957, Franklin again fell ill and she was admitted to the Royal Marsden Hospital. On 2 December, she made her will. She named her three brothers as executors and made her colleague Aaron Klug the principal beneficiary, who would receive £3,000 and her Austin car. Her other friends Mair Livingstone would get £2,000, Anne Piper £1,000, and her nurse Miss Griffith £250. The remainder of the estate was to be used for charities.[145]
She returned to work in January 1958, and she was given a promotion to Research Associate in Biophysics on 25 February.[146] She fell ill again on 30 March, and she died on 16 April 1958, in Chelsea, London,[147][148] of bronchopneumonia, secondary carcinomatosis, and ovarian cancer. Exposure to X-ray radiation is sometimes considered to be a possible factor in her illness.[149]
Other members of her family have died of cancer, and the incidence of gynaecological cancer is known to be disproportionately high among Ashkenazi Jews.[150] Her death certificate states: A Research Scientist, Spinster, Daughter of Ellis Arthur Franklin, a Banker.[151] She was interred on 17 April 1958 in the family plot at Willesden United Synagogue Cemetery at Beaconsfield Road in London Borough of Brent. The inscription on her tombstone reads:[152][153]
IN MEMORY OF
ROSALIND ELSIE FRANKLIN
מ' רחל בת ר' יהודה [Rochel/Rachel daughter of Yehuda, her Hebrew name]
DEARLY LOVED ELDER DAUGHTER OF
ELLIS AND MURIEL FRANKLIN
25TH JULY 1920 – 16TH APRIL 1958
SCIENTIST
HER RESEARCH AND DISCOVERIES ON
VIRUSES REMAIN OF LASTING BENEFIT
TO MANKIND
ת נ צ ב ה [Hebrew initials for "her soul shall be bound in the bundle of life"]
Controversies after death
Various controversies surrounding Rosalind Franklin came to light following her death.
Allegations of sexism
Anne Sayre, Franklin's friend and one of her biographers, stated in her book Rosalind Franklin and DNA, "In 1951 ... King's College London as an institution, was not distinguished for the welcome that it offered to women ... Rosalind ... was unused to purdah [a religious and social institution of female seclusion] ... there was one other woman scientist on the laboratory staff".[154] Andrzej Stasiak states "Sayre's book became widely cited in feminist circles for exposing rampant sexism in science."[155] Farooq Hussain states "there were seven women in the biophysics department ... Jean Hanson became an FRS, Dame Honor B. Fell, Director of Strangeways Laboratory, supervised the biologists".[156] Maddox states, "Randall ... did have many women on his staff ... they found him ... sympathetic and helpful."[157]
Sayre states "that while the male staff at King's lunched in a large, comfortable, rather clubby dining room" the female staff of all ranks "lunched in the student's hall or away from the premises".[158][159] Elkin states that most of the MRC group typically ate lunch together (including Franklin) in the mixed dining room discussed below.[56] And Maddox states, of Randall, "He liked to see his flock, men and women, come together for morning coffee, and at lunch in the joint dining room, where he ate with them nearly every day."[157] Francis Crick also commented that "her colleagues treated men and women scientists alike."[160]
Sayre also discusses at length Franklin's struggle in pursuing science, particularly her father's concern about women in academic professions.[161] This account had been taken to accuse Ellis Franklin of sexism against his daughter. A good deal of information explicitly claims that he strongly opposed her entering Newnham College.[162][163][164][165] Franklin's Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) biography goes further by stating that he refused to pay her fees, and that an aunt stepped in for her.[166] Her sister Jenifer Glynn claimed that these stories are myths, and that her parents fully supported Franklin's entire career.[167]
Sexism is said to pervade the memoir of one peer, James Watson, in his book The Double Helix published 10 years after Franklin's death and after Watson had returned from Cambridge to Harvard.[168] His Cambridge colleague, Peter Pauling, wrote in a letter, "Morris [sic] Wilkins is supposed to be doing this work; Miss Franklin is evidently a fool."[169] Crick acknowledges later, "I'm afraid we always used to adopt – let's say, a patronizing attitude towards her."[170]
Glynn accuses Sayre of making her sister a feminist heroine,[171] and Watson's The Double Helix as the root of what she calls "Rosalind Industry". She conjectures that these alleged sexism stories would "have embarrassed her [Rosalind Franklin] almost as much as Watson's account would have upset her",[167] and declared that "she was never a feminist."[172] Klug and Crick also concurred that she was definitely not a feminist.[173]
Franklin's letter to her parents in January 1939 is often taken as reflecting her own prejudiced attitude and that she was "not immune to the sexism rampant in these circles." In it she remarked one lecturer as "very good, though female."[174] But as Maddox explains, it was more of circumstantial comment rather than a gender bias. It was more of an admiration because at the time woman teachers of science were a rarity. She in fact laughed at men who were embarrassed by the appointment of the first female professor Dorothy Garrod.[175]
Contribution to the model of DNA
Rosalind Franklin's first important contributions to the model popularised by Crick and Watson was her lecture at the seminar in November 1951, where she presented to those present, among them Watson, the two forms of the molecule, type A and type B, her position being that the phosphate units are located in the external part of the molecule. She also specified the amount of water to be found in the molecule in accordance with other parts of it, data that have considerable importance in terms of the stability of the molecule. Franklin was the first to discover and formulate these facts, which in fact constituted the basis for all later attempts to build a model of the molecule. However, Watson, at the time ignorant of the chemistry, failed to comprehend the crucial information, and this led to construction of a wrong model.[176]
The other contribution included an X-ray photograph of B-DNA (called Photo 51),[177] that was briefly shown to Watson by Wilkins in January 1953,[178][179] and a report written for an MRC biophysics committee visit to King's in December 1952 which was shown by Perutz at the Cavendish Laboratory to both Crick and Watson. This MRC report contained data from the King's group, including some of Franklin's and Gosling's work, and was given to Crick – who was working on his thesis on haemoglobin structure – by his thesis supervisor Perutz, a member of the visiting committee.[180][181]
Sayre's biography of Franklin contains a story[182] alleging that the photograph 51 in question was shown to Watson by Wilkins without Franklin's permission,[155][183][184] and that this constituted a case of bad science ethics.[185] Others dispute this story, asserting that Wilkins had been given photograph 51 by Franklin's Ph.D. student Gosling because she was leaving King's to work at Birkbeck, and there was allegedly nothing untoward in this transfer of data to Wilkins[186][187] because Director Randall had insisted that all DNA work belonged exclusively to King's and had instructed Franklin in a letter to even stop working on it and submit her data.[188] Also, it was implied by Horace Freeland Judson, that Maurice Wilkins had taken the photograph out of Franklin's drawer, but this is also said to be incorrect.[189]
Likewise, Perutz saw "no harm" in showing an MRC report containing the conclusions of Franklin and Gosling's X-ray data analysis to Crick, since it had not been marked as confidential, although "The report was not expected to reach outside eyes".[190] Indeed, after the publication of Watson's The Double Helix exposed Perutz's act, he received so many letters questioning his judgment that he felt the need to both answer them all[191] and to post a general statement in Science excusing himself on the basis of being "inexperienced and casual in administrative matters".[192]
Perutz also claimed that the MRC information was already made available to the Cambridge team when Watson had attended Franklin's seminar in November 1951. A preliminary version of much of the important material contained in the 1952 December MRC report had been presented by Franklin in a talk she had given in November 1951, which Watson had attended but not understood.[67][193]
The Perutz letter was as said one of three letters, published with letters by Wilkins and Watson, which discussed their various contributions. Watson clarified the importance of the data obtained from the MRC report as he had not recorded these data while attending Franklin's lecture in 1951. The upshot of all this was that when Crick and Watson started to build their model in February 1953 they were working with critical parameters that had been determined by Franklin in 1951, and which she and Gosling had significantly refined in 1952, as well as with published data and other very similar data to those available at King's. It was generally believed that Franklin was never aware that her work had been used during construction of the model,[194] but Gosling asserted in his 2013 interview that, "Yes. Oh, she did know about that."[195]
Recognition of her contribution to the model of DNA
Upon the completion of their model, Crick and Watson had invited Wilkins to be a co-author of their paper describing the structure.[196] Wilkins turned down this offer, as he had taken no part in building the model.[197] He later expressed regret that greater discussion of co-authorship had not taken place as this might have helped to clarify the contribution the work at King's had made to the discovery.[198] There is no doubt that Franklin's experimental data were used by Crick and Watson to build their model of DNA in 1953. Some, including Maddox, have explained this citation omission by suggesting that it may be a question of circumstance, because it would have been very difficult to cite the unpublished work from the MRC report they had seen.[81]
Indeed, a clear timely acknowledgment would have been awkward, given the unorthodox manner in which data were transferred from King's to Cambridge. However, methods were available. Watson and Crick could have cited the MRC report as a personal communication or else cited the Acta articles in press, or most easily, the third Nature paper that they knew was in press. One of the most important accomplishments of Maddox's widely acclaimed biography is that Maddox made a well-received case for inadequate acknowledgement. "Such acknowledgement as they gave her was very muted and always coupled with the name of Wilkins".[199]
Fifteen years after the fact, the first clear recitation of Franklin's contribution appeared as it permeated Watson's account, The Double Helix, although it was buried under descriptions of Watson's (often quite negative) regard towards Franklin during the period of their work on DNA. This attitude is epitomized in the confrontation between Watson and Franklin over a preprint of Pauling's mistaken DNA manuscript.[200] Watson's words impelled Sayre to write her rebuttal, in which the entire chapter nine, "Winner Take All" has the structure of a legal brief dissecting and analyzing the topic of acknowledgement.[201]
Sayre's early analysis was often ignored because of perceived feminist overtones in her book. Watson and Crick did not cite the X-ray diffraction work of Wilkins and Franklin in their original paper, though they admit having "been stimulated by a knowledge of the general nature of the unpublished experimental results and ideas of Dr. M. H. F. Wilkins, Dr. R. E. Franklin and their co-workers at King's College London".[84] In fact, Watson and Crick cited no experimental data at all in support of their model. Franklin and Gosling's publication of the DNA X-ray image, in the same issue of Nature, served as the principal evidence:
Thus our general ideas are not inconsistent with the model proposed by Watson and Crick in the preceding communication.[202]
Nobel Prize
Franklin was never nominated for a Nobel Prize.[203][204] Her work was a crucial part in the discovery of DNA's structure, which along with subsequent related work led to Francis Crick, James Watson, and Maurice Wilkins being awarded a Nobel Prize in 1962.[205] She had died in 1958, and during her lifetime the DNA structure was not considered to be fully proven. It took Wilkins and his colleagues about seven years to collect enough data to prove and refine the proposed DNA structure. Moreover, its biological significance, as proposed by Watson and Crick, was not established. General acceptance for the DNA double helix and its function did not start until late in the 1950s, leading to Nobel nominations in 1960, 1961, and 1962 for Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, and in 1962 for Nobel Prize in Chemistry.[206] The first breakthrough was from Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958, who experimentally showed the DNA replication of a bacterium Escherichia coli.[207] Now known as Meselson–Stahl experiment, DNA was found to replicate into two double-stranded helices, with each helix having one of the original DNA strands. This DNA replication was firmly established by 1961 after further demonstration in other species,[208] and of the stepwise chemical reaction.[209][210] According to the 1961 Crick–Monod letter, this experimental proof, along with Wilkins having initiated the DNA diffraction work, were the reasons why Crick felt that Wilkins should be included in the DNA Nobel Prize.[211]
In 1962 the Nobel Prize was subsequently awarded to Crick, Watson, and Wilkins.[9][212][213] Nobel rules prohibit posthumous nominations or splitting of Prizes more than three ways.[214][215] The award was for their body of work on nucleic acids and not exclusively for the discovery of the structure of DNA.[216] By the time of the award Wilkins had been working on the structure of DNA for more than 10 years, and had done much to confirm the Watson–Crick model.[217] Crick had been working on the genetic code at Cambridge and Watson had worked on RNA for some years.[218] Watson has suggested that ideally Wilkins and Franklin would have been awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry.[7]
Aaron Klug, Franklin's colleague and principal beneficiary in her will, was the sole winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982, "for his development of crystallographic electron microscopy and his structural elucidation of biologically important nucleic acid-protein complexes."[219] This work was exactly what Franklin had started and which she introduced to Klug, and it is highly plausible that, were she alive, she would have shared the Nobel Prize.[220]
Awards and honours
Posthumous recognition
- 1982, Iota Sigma Pi designated Franklin a National Honorary Member.[221]

Mural inscription on King's College London's Franklin-Wilkins Building, co-named in honour of Rosalind Franklin's work

Blue plaque on 107 Drayton Gardens, London SW10
- 1992, English Heritage placed a blue plaque commemorating Franklin on the building in Drayton Gardens, London, where she lived until her death.[222][223]
- 1993, King's College London renamed the Orchard Residence at their Hampstead Campus as Rosalind Franklin Hall.[224]
- 1993, King's College London placed a blue plaque on its outside wall bearing the inscription: "R. E. Franklin, R. G. Gosling, A. R. Stokes, M. H. F. Wilkins, H. R. Wilson – King's College London – DNA – X-ray diffraction studies – 1953."[225]
- 1995, Newnham College, Cambridge opened a graduate residence named Rosalind Franklin Building[226] and put a bust of her in its garden.[227][228]
- 1997, Birkbeck, University of London School of Crystallography opened the Rosalind Franklin Laboratory.[229]
- 1997, the asteroid discovered in 1997 was named 9241 Rosfranklin.
- 1998, National Portrait Gallery in London added Rosalind Franklin's portrait next to those of Francis Crick, James Watson and Maurice Wilkins.[230]
- 1999, the Institute of Physics at Portland Place, London, renamed its theatre as Franklin Lecture Theatre.[231]
- 2000, King's College London opened the Franklin–Wilkins Building in honour of Franklin's and Wilkins's work at the college.[232]
- 2001, the American National Cancer Institute established the Rosalind E. Franklin Award for women in cancer research.[233]
- 2002, the University of Groningen, supported by the European Union, launched the Rosalind Franklin Fellowship to encourage women researchers to become full university professors.[234][235]
- 2003, the Royal Society established the Rosalind Franklin Award (officially the Royal Society Rosalind Franklin Award and Lecture) for an outstanding contribution to any area of natural science, engineering or technology.[236] The award consists of a silver-coated medal and a grant of £30,000.[237]
- 2003, the Royal Society of Chemistry declared King's College London as "National Historic Chemical Landmark" and placed a plaque on the wall near the entrance of the building, with the inscription: "Near this site Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, Raymond Gosling, Alexander Stokes and Herbert Wilson performed experiments that led to the discovery of the structure of DNA. This work revolutionised our understanding of the chemistry behind life itself."[238]

Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science at Illinois
- 2004, Finch University of Health Sciences/The Chicago Medical School, located in North Chicago, Illinois, USA changed its name to the Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science.[239] It also adopted a new motto "Life in Discovery", and Photo 51 as its logo.[240]
- 2004, the Gruber Foundation started the Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award for two female geneticists from all over the world. It carries an annual fund of $25,000, each award is for three years, and selection is made by a joint committee appointed by the Genetics Society of America and the American Society of Human Genetics.[241]
- 2004, the Advanced Photon Source (APS) and the APS Users Organization (APSUO) started the APSUO Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award for young scientists who made contributions through the APS.[242]
- 2005, the DNA sculpture (donated by James Watson) outside Clare College, Cambridge's Memorial Court incorporates the words "The double helix model was supported by the work of Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins."[243]
- 2006, the Rosalind Franklin Society was established in New York by Mary Ann Liebert.[244][245] The Society aims to recognise, foster, and advance the important contributions of women in the life sciences and affiliated disciplines.[246]
- 2008, Columbia University awarded an honorary Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize to Franklin, "for her seminal contributions to the discovery of the structure of DNA".[247]
- 2008, the Institute of Physics established a biennual award the Rosalind Franklin Medal and Prize.[248]
St Paul's Girls School established the Rosalind Franklin Technology Centre.[25]
- 2012, the bioinformatics education software platform Rosalind is named in honour of Franklin.[249]
- 2012, The Rosalind Franklin Building is opened at Nottingham Trent University.[250]
- 2013, Google honoured Rosalind Franklin with a doodle, showing her gazing at a double helix structure of DNA with an X-ray of Photo 51 beyond it.[251][252]
- 2013, a plaque was placed on the wall of The Eagle pub in Cambridge commemorating Franklin's contribution to the discovery of the structure of DNA, on the sixtieth anniversary of Crick and Watson's announcement in the pub.[253][254]
- 2014, the Rosalind Franklin Award for Leadership in Industrial Biotechnology was established by Biotechnology Industry Organization in collaboration with the Rosalind Franklin Society, for an outstanding woman in the field of industrial biotechnology and bioprocessing.[255]
- 2014, the Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science unveiled a bronze statue of Franklin, created by Julie Rotblatt-Amrany, near its front entrance.[256]
- 2014, the Rosalind Franklin STEM Elementary was opened in Pasco, Washington, the first science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) elementary school in the district.[257][258]
- 2014, the University of Wolverhampton opened its new laboratory building named the Rosalind Franklin Science Building.[259][260]
- 2015, Newnham College Boat Club, Cambridge, launched a new racing VIII, naming it the Rosalind Franklin[261]
- 2015, the Rosalind Franklin Appathon was launched by University College London as a national app competition for women in STEMM (science, technology, engineering, maths and medicine).[262]
- 2015, a high performance computing and cloud facility in London was named Rosalind.[263]
- 2016, the British Humanist Association added the Rosalind Franklin Lecture to its annual lecture series, aimed to explore and celebrate the contribution of women towards the promotion and advancement of humanism.[264]
- 2016, the Rosalind Franklin Prize and Tech Day was held on 23 February in London, organised by University College London, i-sense, UCL Enterprise, the London Centre for Nanotechnology and the UCL Athena Swan Charter.[265]
- 2017, DSM opened the Rosalind Franklin Biotechnology Center in Delft, the Netherlands.[266]
- 2017, the Historic England listed the tomb of Franklin under the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990 as a "special architectural or historic interest". Official description states that "the tomb commemorates the life and achievements of Rosalind Franklin, a scientist of exceptional distinction, whose pioneering work helped lay the foundations of molecular biology; Franklin’s X-ray observation of DNA contributed to the discovery of its helical structure."[267]
- 2019, the European Space Agency (ESA) named their ExoMars rover Rosalind Franklin.[268]
Cultural references
Franklin's part in the discovery of the nature of DNA was shown in the 1987 TV Movie Life Story, starring Tim Pigott-Smith as Crick, Alan Howard as Wilkins, Jeff Goldblum as Watson, and Juliet Stevenson as Franklin. This movie portrayed Franklin as somewhat stern, but also alleged that Watson and Crick did use a lot of her work to do theirs.[269][270]
A 56-minute documentary of the life and scientific contributions of Franklin, DNA – Secret of Photo 51, was broadcast in 2003 on PBS Nova.[271] Narrated by Barbara Flynn, the program features interviews with Wilkins, Gosling, Klug, Maddox,[272] including Franklin's friends Vittorio Luzzati, Caspar, Anne Piper, and Sue Richley.[273] The UK version produced by BBC is titled Rosalind Franklin: DNA's Dark Lady.[274]
The first episode of another PBS documentary serial, DNA, was aired on 4 January 2004.[275] The episode titled The Secret of Life centres much around the contributions of Franklin. Narrated by Jeff Goldblum, it features Watson, Wilkins, Gosling and Peter Pauling (son of Linus Pauling).[276]
A play titled Rosalind: A Question of Life was written by Deborah Gearing to mark the work of Franklin, and was first performed on 1 November 2005 at the Birmingham Repertory Theatre,[277] and published by Oberon Books in 2006.[278]
Another play, Photograph 51 by Anna Ziegler, published in 2011,[279] has been produced at several places in the US,[280] and in late 2015 was put on at the Noel Coward Theatre, London, with Nicole Kidman playing Franklin.[281] Ziegler's version of the 1951–53 'race' for the structure of DNA sometimes emphasizes the pivotal role of Franklin's research and her personality. Although sometimes altering history for dramatic effect, the play nevertheless illuminates many of the key issues of how science was and is conducted.[282]
False Assumptions by Lawrence Aronovitch is a play about the life of Marie Curie in which Franklin is portrayed as frustrated and angry at the lack of recognition for her scientific contributions.[283]
Publications
Library resources about Rosalind Franklin |
|
By Rosalind Franklin |
|---|
|
Rosalind Franklin's most notable publications are listed below. The last two were published posthumously.
.mw-parser-output .refbegin{font-size:90%;margin-bottom:0.5em}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul{list-style-type:none;margin-left:0}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>ul>li,.mw-parser-output .refbegin-hanging-indents>dl>dd{margin-left:0;padding-left:3.2em;text-indent:-3.2em;list-style:none}.mw-parser-output .refbegin-100{font-size:100%}
D. H. Bangham & Rosalind E.Franklin (1946), "Thermal expansion of coals and carbonised coals" (PDF), Transactions of the Faraday Society, 48: 289–295, doi:10.1039/TF946420B289, retrieved 14 January 2011 from The Rosalind Franklin Papers, in "Profiles in Science", at National Library of Medicine.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
R. E. Franklin (1949), "A study of the fine structure of carbonaceous solids by measurements of true and apparent densities: Part 1. Coals" (PDF), Transactions of the Faraday Society, 45 (3): 274–286, doi:10.1039/TF9494500274, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of Medicine above. Citation count 88
R. E. Franklin (1949), "A study of the fine structure of carbonaceous solids by measurements of true and apparent densities: Part 2. Carbonized coals" (PDF), Transactions of the Faraday Society, 45 (7): 668–682, doi:10.1039/TF9494500668, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of Medicine above. Citation count 49
R. E. Franklin (1949), "Note sur la structure colloïdale des houilles carboniseés", Bulletin de la société chimique de France, 16 (1–2): D53–D54 Citation count 0
R. E. Franklin (1950), "On the structure of carbon" (PDF), Journal de Chimie Physique et de Physico-Chimie Biologique, 47 (5–6): 573–575, Bibcode:1950JCP....47..573F, doi:10.1051/jcp/1950470573, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of Medicine above. Citation count 16. Note: this journal ceased publication in 1999
R. E. Franklin (1950), "A rapid approximate method for correcting the low-angle scattering measurements for the influence of the finite height of the X-ray beam", Acta Crystallographica, 3 (2): 158–159, doi:10.1107/S0365110X50000343 Citation count 15
R. E. Franklin (1950), "The interpretation of diffuse X-ray diagrams of carbon", Acta Crystallographica, 3 (2): 107–121, doi:10.1107/S0365110X50000264 Citation count 245. (In this article, Franklin cites Moffitt)
R. E. Franklin (1950), "Influence of the bonding electrons on the scattering of X-rays by carbon", Nature, 165 (4185): 71–72, Bibcode:1950Natur.165...71F, doi:10.1038/165071a0, PMID 15403103 citation count 11
R. E. Franklin (1951), "Les carbones graphitisables et non-graphitisables", Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des sciences, Presented by G. Rimbaud, session of 3rd January, 1951, 232 (3): 232–234 Citation count 7
R. E. Franklin (1951), "The structure of graphitic carbons" (PDF), Acta Crystallographica, 4 (3): 253–261, doi:10.1107/S0365110X51000842 Citation count 398
G. E. Bacon & R.E. Franklin (1951), "The alpha dimension of graphite", Acta Crystallographica, 4 (6): 561–562, doi:10.1107/s0365110x51001793 Citation count 8
R. E. Franklin (1951), "Crystallite growth in graphitizing and non-graphitizing carbons", Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 209 (1097): 196–218, Bibcode:1951RSPSA.209..196F, doi:10.1098/rspa.1951.0197 Citation count 513. Downloadable free from doi site, or alternatively from The Rosalind Franklin Papers collection at National Library of Medicine
R. E. Franklin (1953), "Graphitizing and non-graphitizing carbons, their formation, structure and properties", Angewandte Chemie, 65 (13): 353–353, doi:10.1002/ange.19530651311 Citation count 0
R. E. Franklin (1953), "The role of water in the structure of graphitic acid", Journal de Chimie Physique et de Physico-Chimie Biologique, 50: C26
R. E. Franklin (1953), "Graphitizing and nongraphihastizing carbon compounds. Formation, structure and characteristics", Brenstoff-Chemie, 34: 359–361
R. E. Franklin & R. G. Gosling (25 April 1953), "Molecular Configuration in Sodium Thymonucleate" (PDF), Nature, 171 (4356): 740–741, Bibcode:1953Natur.171..740F, doi:10.1038/171740a0, PMID 13054694, retrieved 15 January 2011 Reprint also available at Resonance Classics
Franklin, R. E.; Gosling, R. G. (1953). "The structure of sodium thymonucleate fibres. I. The influence of water content". Acta Crystallographica. 6 (8): 673–677. doi:10.1107/S0365110X53001939.
Franklin, R. E.; Gosling, R. G. (1953). "The structure of sodium thymonucleate fibres. II. The cylindrically symmetrical Patterson function". Acta Crystallographica. 6 (8): 678–685. doi:10.1107/S0365110X53001940.
R.E. Franklin & M. Mering (1954), "La structure de l'acide graphitique", Acta Crystallographica, 7 (10): 661–661, doi:10.1107/s0365110x54002137
Rosalind Franklin & K. C. Holmes. (1956), "The Helical Arrangement of the Protein Sub-Units in Tobacco Mosaic Virus" (PDF), Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 21: 405–406, doi:10.1016/0006-3002(56)90043-9, PMID 13363941, retrieved 14 January 2011 Article access per National Library of Medicine above
Rosalind E. Franklina & A. Klug (1956), "The nature of the helical groove on the tobacco mosaic virus particle X-ray diffraction studies", Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 19 (3): 403–416, doi:10.1016/0006-3002(56)90463-2, PMID 13315300
Klug, Aaron, J. T. Finch, and Rosalind Franklin (1957), "The Structure of Turnip Yellow Mosaic Virus: X-Ray Diffraction Studies" (PDF), Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 25 (2): 242–252, doi:10.1016/0006-3002(57)90465-1, PMID 13471561, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of Medicine aboveCS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
Franklin, Rosalind, Aaron Klug, J. T. Finch, and K. C. Holmes (1958), "On the Structure of Some Ribonucleoprotein Particles" (PDF), Discussions of the Faraday Society, 25: 197–198, doi:10.1039/DF9582500197, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of MedicineCS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
Klug, Aaron & Rosalind Franklin (1958), "Order-Disorder Transitions in Structures Containing Helical Molecules" (PDF), Discussions of the Faraday Society, 25: 104–110, doi:10.1039/DF9582500104, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of Medicine
Klug, Aaron, Rosalind Franklin, and S. P. F. Humphreys-Owen (1959), "The Crystal Structure of Tipula Iridescent Virus as Determined by Bragg Reflection of Visible Light" (PDF), Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 32 (1): 203–219, doi:10.1016/0006-3002(59)90570-0, PMID 13628733, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of MedicineCS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
Franklin, Rosalind, Donald L. D. Caspar, and Aaron Klug (1959), "Chapter XL: The Structure of Viruses as Determined by X-Ray Diffraction", Plant Pathology: Problems and Progress, 1908–1958 (PDF), University of Wisconsin Press, pp. 447–461, retrieved 14 January 2011 Per National Library of MedicineCS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list (link)
See also
- Timeline of women in science
Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin, astronomer who discovered the most elemental composition of stars
References
^ "The Rosalind Franklin Papers, Biographical Information". profiles.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
^ abcde "The Rosalind Franklin Papers, The Holes in Coal: Research at BCURA and in Paris, 1942–1951". profiles.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
^ Glynn, p. 60.
^ ab Franklin, Rosalind (1946). The physical chemistry of solid organic colloids, with special reference to the structure of coal and related materials. lib.cam.ac.uk (PhD thesis). University of Cambridge. OCLC 879396430.
EThOS uk.bl.ethos.599181.
^ ab Maddox, Brenda, "The double helix and the ‘wronged heroine’", Nature, Vol. 421, 23 January 2003.
^ Greenwood, Veronique. "First Posthumous Nobel Awarded". Discover Magazine. Discover Magazine. Retrieved 20 October 2018.
^ ab "The Discovery of the Molecular Structure of DNA – The Double Helix". Official Website of the Nobel Prizes. Retrieved 4 February 2014.
^ "Nobel Prize Facts". Official Website of the Nobel Prizes. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
^ abc "James Watson, Francis Crick, Maurice Wilkins, and Rosalind Franklin". Science History Institute. Retrieved 20 March 2018.
^ "Name of Firm: A. Keyser & Co" (PDF). The Gazette. 22 February 1922. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "Rosalind Franklin". London Remembers. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ GRO Register of Births: SEP 1920 1a 250 KENSINGTON – Rosalind E. Franklin, mmn = Waley
^ ab Glynn, p. 1.
^ Maddox, p. 7.
^ Segev p.
^ Sayre, A. (1975). Rosalind Franklin and DNA. New York: Norton. p. 31. ISBN 0-393-07493-5.
^ Maddox, p. 40.
^ Maddox, p. 20.
^ Sayre, p. 35.
^ Polcovar, p. 20.
^ Simkin, John (1997). "Rosalind Franklin". Spartacus Educational. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "Hans (John) Mathias Eisenstadter Ellis". Geni. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ ab "Evi Ellis". Ancestry.com. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ Maddox, p. 15.
^ abcd Berger, Doreen (3 December 2014). "A Biography of The Dark Lady Of Notting Hill". United Synagogue Women. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
^ Glynn, p. 25.
^ Sayre, p. 41.
^ Maddox, p. 30.
^ Maddox, p. 26.
^ Glynn, p. 28.
^ Glynn, p. 30.
^ Dixon, R. N.; D. M. Agar; R. E. Burge (1997). "William Charles Price. 1 April 1909−−10 March 1993". Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society. 43: 438. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1997.0023. JSTOR 770344.
^ Fact sheet: Women at Cambridge: A Chronology, [1]. Archived 14 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine
^ Polcovar, p. 31.
^ Rosalind Franklin, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory's Dolan DNA Learning Center, ID 1649, [2].
^ Dainton, Sir Frederick Sydney (1981). "Ronald George Wreyford Norrish, 9 November 1897 – 7 June 1978". Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society. 27: 379–424. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1981.0016. JSTOR 769878.
^ Maddox, p. 72.
^ Polcovar, p. 37.
^ Harris, P.J.F. (March 2001). "Rosalind Franklin's work on coal, carbon, and graphite" (PDF). Interdisciplinary Science Reviews. 26 (3): 204–210. doi:10.1179/030801801679467.
^ "The Rosalind Franklin Papers: The Holes in Coal: Research at BCURA and in Paris, 1942–1951". Profiles.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2013-07-25.
^ "Rosalind Franklin". Timetoast. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
^ "Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958)". DNA Learning Center, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
^ D. W. van Krevelen, Coal, Third Edition: Typology – Physics – Chemistry – Constitution, Elsevier, New York, 1993.
^ Chemistry and Physics of Carbon, vol 1–, 1968–, Elsevier, New York.
^ G. Terriere, A. Oberlin, J. Mering, Oxidation of graphite in liquid medium – observations by means of microscopy and electron diffraction, Carbon, 5, 431--, 1967.
^ Maddox, p. 124.
^ Maddox, p. 114.
^ Wilkins, Wilkins, M., The Third Man of the Double Helix, an autobiography (2003) Oxford University Press, Oxford. pp. 143–144.
^ Wilkins, p. 121.
^ Maddox, pp. 149–150, Elkin, p 45. Elkin, L.O. Rosalind Franklin and the Double Helix. Physics Today, March 2003(available free on-line, see references). Olby, R. The Path to the Double Helix (London: Macmillan, 1974).
^ Sayre, Olby, Maddox, Elkin, Wilkins.
^ Maddox, p. 129.
^ Elkin, p. 43.
^ Wilkins, p. 155.
^ Sayre, Anne (2000). Rosalind Franklin and DNA. W. W. Norton. ISBN 0-393-32044-8.
^ ab Elkin p. 45.
^ ab Maddox, p. 153.
^ Wilkins, p. 154.
^ Wood, Bayden R. (2016). "The importance of hydration and DNA conformation in interpreting infrared spectra of cells and tissues". Chemical Society Reviews. 45: 1980–98. doi:10.1039/C5CS00511F. PMID 26403652.
^ ab Maddox, p. 155.
^ ab Wilkins, p. 158.
^ ab Wilkins, p. 176.
^ Wilkins, p. 182.
^ Maddox, p. 168.
^ Maddox, p. 169.
^ Wilkins, pp. 232–233.
^ ab Maddox, p. 199.
^ Franklin and Gosling (1953). Acta Crystallographica, 6, 673–677.
^ "Wellcome Library Encore – [The Papers of Rosalind Franklin] [archive material]". search.wellcomelibrary.org. Retrieved 11 October 2016.
^ Klug, A. "Rosalind Franklin and the Double Helix", Nature 248 (26 April 1974): 787–788.
^ Klug, A. Rosalind Franklin and the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, Nature 219 (24 August 1968): 808–810 & 843.
^ Hubbard, Ruth (2013). "Science, Power, Gender: How DNA Became the Book of Life". Women, Science, and Technology (3rd ed.). Hoboken: Taylor and Francis. p. 269. ISBN 1-135-05542-4.
^ Yockey, pp. 9–10.
^ Crick's 31 December 1961 letter to Jacque Monod cited above.
^ Maddox, p. 147.
^ Maddox, p. 161.
^ Hubbard, Ruth (1990). The Politics of Women's Biology. Rutgers State University. p. 60. ISBN 0-8135-1490-8.
^ "The Double Helix", p. 115.
^ "The Double Helix", p. 60.
^ "All hands to the pump" letter is preserved in the Crick archives at the University of California, San Diego, and was posted as part of their Web collection. It is also quoted by both Maddox, p 204, and Olby.
^ ab Maddox, p. 207.
^ In contrast to his other letters to Crick, Wilkins dated this one.
^ "Old rogues" letter is preserved in the Crick archives at the University of California at San Diego, and was posted as part of their web collection. It is also quoted by both Maddox, p. 208, and Olby.
^ ab Watson, J. D., F. H. Crick (April 1953). "Molecular structure of nucleic acids; a structure for deoxyribose nucleic acid" (PDF). Nature. 171 (4356): 737–738. Bibcode:1953Natur.171..737W. doi:10.1038/171737a0. PMID 13054692.CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link) Watson and Crick's article was immediately followed by the two King's College London submissions: Wilkins, M. H., A. R. Stokes, H. R. Wilson (April 1953). "Molecular structure of deoxypentose nucleic acids" (PDF). Nature. 171 (4356): 738–740. Bibcode:1953Natur.171..738W. doi:10.1038/171738a0. PMID 13054693.CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link) then by: Franklin, R. E., R. G. Gosling (April 1953). "Molecular configuration in sodium thymonucleate" (PDF). Nature. 171 (4356): 740–741. Bibcode:1953Natur.171..740F. doi:10.1038/171740a0. PMID 13054694.CS1 maint: Uses authors parameter (link)
^ Franklin and Gosling (1953).
^ Maddox, p. 210.
^ 10 April 1953 Franklin postcard to Crick asking permission to view model. The original is in the Crick archives at the University of California, San Diego.
^ Holt, J. (2002).
^ Rich, Alexander (2003). "The double helix: a tale of two puckers". Nature Structural Biology. 10 (4): 247–249. doi:10.1038/nsb0403-247. PMID 12660721.
^ Scher, Stanley (2004). "Was Watson and Crick's model truly self-evident?". Nature. 427 (6975): 584–584. Bibcode:2004Natur.427..584S. doi:10.1038/427584c. PMID 14961092.
^ Arnott, Struther (2006). "Historical article: DNA polymorphism and the early history of the double helix". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 31 (6): 349–354. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2006.04.004. PMID 16678428.
^ Maddox, p. 205.
^ Maddox, p. 229.
^ Brown, Andrew, J. D. Bernal, the sage of science (2005), Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 353–355.
^ Franklin, RE; Gosling, RG (1953). "Evidence for 2-chain helix in crystalline structure of sodium deoxyribonucleate". Nature. 172 (4369): 156–157. Bibcode:1953Natur.172..156F. doi:10.1038/172156a0. PMID 13072614.
^ Maddox, p. 235.
^ Brown, pp. 356–357.
^ Brown, pp. 356–357.
^ Franklin, RE. (1955). "Structure of Tobacco Mosaic Virus". Nature. 175 (4452): 379–381. Bibcode:1955Natur.175..379F. doi:10.1038/175379a0. PMID 14356181.
^ Maddox, p. 252.
^ Franklin and Holmes, 1956.
^ Maddox, p. 254.
^ Franklin, Rosalind E.; Klug, A. (1956). "The nature of the helical groove on the tobacco mosaic virus particle X-ray diffraction studies". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 19 (3): 403–416. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(56)90463-2. PMID 13315300.
^ Franklin et al., 1958.
^ Maddox, p. 256.
^ Maddox, p. 262.
^ Franklin, RE (1956). "Structure of Tobacco Mosaic Virus: Location of the Ribonucleic Acid in the Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particle". Nature. 177 (4516): 928–930. Bibcode:1956Natur.177..928F. doi:10.1038/177928b0.
^ Casper, D. L. D. (1956). "Structure of Tobacco Mosaic Virus: Radial Density Distribution in the Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particle". Nature. 177 (4516): 928–928. Bibcode:1956Natur.177..928C. doi:10.1038/177928a0.
^ Maddox, p. 269.
^ Maddox, p. 296.
^ Glynn, p. 145.
^ Brown, pp. 358–359.
^ Brown, p. 359.
^ "Expo 58". Retrieved 21 January 2015.
^ Devos, Rika (2011). "Expo 58: the catalyst for Belgium's Welfare State Government complex?" (PDF). Planning Perspectives. 26 (4): 649–659. doi:10.1080/02665433.2011.599934.
^ "Behind the picture: Rosalind Franklin and the polio model". Medical Research Council. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
^ Maddox, Brenda. "Mother of DNA". New Humanist. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
^ Brown, pp. 360–361.
^ Glynn, p. 153.
^ Brown, p. 466.
^ "Rosalind Franklin". NNDB. Soylent Communications. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
^ Glynn, p. 12.
^ Glynn, p. 62.
^ ab Maddox, p. 61.
^ Glynn, p. 19.
^ Glynn, p. 44.
^ Glynn, p. 16.
^ ab Polcovar, p. 33.
^ Polcovar, p. 59.
^ Glynn, p. 33.
^ Glynn, p. 79.
^ ab Polcovar, p. 41.
^ Maddox, p. 277.
^ Watson, p. 16.
^ Glynn, p. 157.
^ ab Maddox, p. 288.
^ ab Glynn, p. 52.
^ Maddox, p. 261.
^ Polcovar, p. 51.
^ Maddox, p. 287.
^ Maddox, p. 283.
^ Maddox, p. 284.
^ Maddox, p. 285.
^ Maddox, p. 292.
^ Maddox, p. 301.
^ Maddox, p. 302.
^ GRO Register of Deaths: JUN 1958 5c 257 CHELSEA – Rosalind E. Franklin, age 37.
^ Maddox, pp. 305–307.
^ "Defending Franklin's Legacy". Secret of Photo 51. NOVA. Retrieved 10 November 2010.Along with genetic predisposition; opinion of CSU's Lynne Osman Elkin; see also March 2003 Physics Today
^ Maddox, p.320.
^ Murray, Ruby J. (2011). "Historical Profile: Rosalind Franklin". Dumbo Feather. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ "Rosalind Franklin tomb". Himetop. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ Friedman, Meyer; Friedland, Gerald W. Medicine's 10 Greatest Discoveries. Universities Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-81-7371-226-5.
^ Sayre, p. 96.
^ ab Stasiak, Andrzej (March 2001). "Rosalind Franklin". EMBO Reports. 2 (3): 181. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kve037. PMC 1083834.
^ Hussain, Farooq (20 November 1975). Did Rosalind Franklin deserve DNA Nobel prize?. New Scientist. 68. Reed Business Information. p. 470. Retrieved 10 January 2011.
^ ab Maddox, p. 135.
^ Sayre, p. 97.
^ Bryson, B. (2004), p. 490.
^ Crick, p. 68.
^ Sayre, pp. 42–45.
^ McGrayne, p. 6.
^ "Rosalind Franklin". The Manhattan Project Heritage Preservation Association, Inc. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ Lewis, Jone Johnson. "Rosalind Franklin". About Education. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "Rosalind Franklin". What is Biotechnology. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "Rosalind Franklin". PBS Online. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ ab Glynn, Jenifer (2012). "Remembering my sister Rosalind Franklin". The Lancet. 379 (9821): 1094–1095. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60452-8. PMID 22451966.
^ Harding, Sandra (2006). "Sexist criticism of Watson's memoir". Science and Social Inequality: Feminist and Postcolonial Issues. Urbana: University of Illinois Press. p. 71. ISBN 978-0-252-07304-5. Retrieved 10 January 2011.
^ "Quotes by or related to Rosalind Franklin". Oregon State University Libraries. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
^ McGrayne, p. 318.
^ Glynn, J. (2008). "Rosalind Franklin: 50 years on". Notes and Records of the Royal Society. 62 (2): 253–255. doi:10.1098/rsnr.2007.0052.
^ Glynn, p. 158.
^ Crick, p. 69.
^ Wertheimer, Michael; Clamar, Aphrodite; Siderits, Mary Anne (2007). "The Case of the Purloined Picture: Rosalind Franklin and the Keystone of the Double Helix". In Gavin, Eileen A.; Clamar, Aphrodite; Siderits, Mary Anne. Women of Vision: Their Psychology, Circumstances, and Successes. New York: Springer Science+Business Media. ISBN 978-0-8261-0253-9. Retrieved 10 January 2011 Rosalind's letter quoted
^ Maddox, p. 48.
^ Everson, Ted (2007). The Gene: A Historical Perspective. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. p. 85. ISBN 978-0-313-33449-8.
^ Maddox, pp. 177–178.
^ Maddox, p. 196.
^ Crick (1988), p. 67.
^ Elkin, L.O. (2003), p. 44.
^ Maddox, pp. 198–199.
^ Sayre, p. 151.
^ Minkoff, Eli; Baker, Pamela (2000). Biology Today: An Issues Approach (2 ed.). New York: Garland Publishing. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-8153-2760-8.
^ Creager, Angela (2003). "Crystallizing a Life in Science". American Scientist. Sigma Xi, The Scientific Research Society. Archived from the original on 12 November 2014. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
^ Stasiak, Andrzej (2003). "The First Lady of DNA". EMBO Reports. 4 (1): 14. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor723. PMC 1315822.
^ Maddox, p. 196.
^ Wilkins, p. 198.
^ Maddox, p. 312.
^ Wilkins, p. 257.
^ Maddox, p. 188.
^ Perutz's papers are in the Archive of the J. Craig Venter institute and Science Foundation in Rockville Maryland, which were purchased as part of the Jeremy Norman Archive of Molecular Biology; quoted in Ferry, Georgina, 2007. Max Perutz and the Secret of Life. Published in the UK by Chatto & Windus (
ISBN 0-7011-7695-4), and in the USA by the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
^ Science, 27 June 1969, pp. 207–212, also reprinted in the Norton critical edition of The Double Helix, edited by Gunther Stent.
^ Watson (1969).
^ Maddox, p. 316.
^ Attar, N (2013). "Raymond Goslin: the man who crystallized genes". Genome Biology. 14 (4): 402. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-402. PMC 3663117. PMID 23651528.
^ Wilkins, p. 213.
^ Wilkins, p. 214.
^ Wilkins, p. 226.
^ Maddox, pp. 316–317, and other parts of the epilogue.
^ Watson, J.D. (1968), pp. 95–96.
^ Sayre, A. (1975), pp. 156–167.
^ Franklin, Rosalind E.; Gosling, R. G. (April 25, 1953). "Molecular Configuration in Sodium Thymonucleate" (PDF). Nature. 171 (4356): 740–741. Bibcode:1953Natur.171..740F. doi:10.1038/171740a0. PMID 13054694.
^ "The Discovery of the Molecular Structure of DNA – The Double Helix". Nobelprize.org. 30 September 2003. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
^ Washington, Harriet A. (31 December 2012). "Don't Forget Rosalind Franklin". Ms.
^ Beard, Mary (2001). "Down among the Women (Nobel Laureates)". The Kenyon Review. Harvard University Press. 23 (2): 239–247. JSTOR 4338226.
^ Gann, Alexander; Witkowski, Jan A. (2013). "DNA: Archives reveal Nobel nominations". Nature. 496 (7446): 434. Bibcode:2013Natur.496..434G. doi:10.1038/496434a. PMID 23619686.
^ Meselson, Matthew; Stahl, Franklin W. (1958). "The replication of DNA in Escherichia coli". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 44 (7): 671–682. Bibcode:1958PNAS...44..671M. doi:10.1073/pnas.44.7.671. PMC 528642. PMID 16590258.
^ Nakada, D; Ryan, FJ (1961). "Replication of deoxyribonucleic acid in non-dividing bacteria". Nature. 189 (4762): 398–399. Bibcode:1961Natur.189..398N. doi:10.1038/189398a0. PMID 13727575.
^ Dounce, AL; Sarkar, NK; Kay, ER (1961). "The possible role of DNA-ase I in DNA replication". Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology. 57 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1002/jcp.1030570107. PMID 13724093.
^ Cavalleiri, LF; Rosenberg, BH (1961). "The replication of DNA III. Changes in the number of strands in E. coli DNA during its replication cycle". Biophysical Journal. 1: 337–351. Bibcode:1961BpJ.....1..337C. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(61)86893-8. PMC 1366352. PMID 13691706.
^ Zallen, Doris T. (2003). "Despite Franklin's work, Wilkins earned his Nobel". Nature. 425 (6953): 15. Bibcode:2003Natur.425...15Z. doi:10.1038/425015b. PMID 12955113.(Crick's 31 December 1961 letter to Jacques Monod) However, the data which really helped us to obtain the structure was mainly obtained by Rosalind Franklin
^ Erica Westly (6 October 2008). "No Nobel for You: Top 10 Nobel Snubs". Scientific American.
^ Nobel Prize (1962).
^ "Posthumous Nobel Prizes". NobelPrize.org. Nobel Media. Retrieved 17 August 2017.
^ Hartocollis, Anemona (3 December 2014). "By Selling Prize, a DNA Pioneer Seeks Redemption". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1962". Nobel Media AB. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ Wilkins, p. 240.
^ Wilkins, p. 243.
^ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1982". Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
^ Arnott, S.; Kibble, T.W.B.; Shallice, T. (2006). "Maurice Hugh Frederick Wilkins. 15 December 1916 – 5 October 2004: Elected FRS 1959". Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society. 52: 455–478. doi:10.1098/rsbm.2006.0031. PMID 18551798.
^ "Iota Sigma Pi professional awards recipients". Iotasigmapi.info. 25 July 2000. Archived from the original on 29 August 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
^ "Biography: Rosalind Franklin". The Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "Plaque: Rosalind Franklin". London Remembers. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ "Hampstead Residence". King's College London. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "Plaque: Franklin, Gosling, Stokes, Wilson, Wilkins". London Remembers. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "The Graduate Houses: Rosalind Franklin Building". Newnham College. Archived from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ Rostvik, Camilla. "Rosalind Franklin's Cambridge, Cambridge, UK". BSHS Travel Guide. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ Dugard, Jane (18 March 2003). "A grave injustice". Mail & Guardian Online. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ Sir Aaron Klug opens new Laboratory Archived 25 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine
^ "NPG pictures". Npg.org.uk. 11 June 1946. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
^ "Dielectrophoresis 2014 Venue and accommodation". Dielectrophoresis 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "The future". King's College London. Retrieved 12 May 2015.
^ "Rosalind E. Franklin Award". National Cancer Institute. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
^ "Rosalind Franklin Fellowships at the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Groningen". European Platform of Women Scientists. 6 October 2014. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "€ 6.6 million EU grant for Rosalind Franklin Fellowship". University of Groningen. 2 August 2013.
^ Lambert, F. (2003). "The Royal Society Rosalind Franklin Award". Notes and Records of the Royal Society. 57 (2): 265–266. doi:10.1098/rsnr.2003.0211.
^ "Royal Society Rosalind Franklin Award and Lecture". royalsociety.org. Royal Society.
^ "Plaque: DNA at Kings". London Remembers. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "History". Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Archived from the original on 1 July 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "University Honors Namesake With New Sculpture". Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science. Archived from the original on 15 June 2012. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "2016 Rosalind Franklin Young Investigator Award of The Gruber Foundation". Genetics Society of America. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
^ "APSUO Franklin Award". UChicago Argonne LLC. Retrieved 17 March 2018.
^ "Secret of life revisited". Cambridge News. 9 November 2005. Archived from the original on 6 February 2009. Retrieved 1 November 2010.
^ "The Rosalind Franklin Society, Inc". NYCorporateList. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ Staff (18 December 2013). "Mary Ann Liebert to Receive Award for Stem Cell Education at World Stem Cell Summit in San Diego". Biotech Week. Archived from the original on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 9 July 2016 – via HighBeam Research. (Subscription required (help)).
^ "Mission". Rosalind Franklin Society. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "2008 Horwitz Prize Awarded To Arthur Horwich & Ulrich Hartl For Cellular Protein Folding". Medical News Today. 15 October 2008. Retrieved 10 April 2012.
^ "Rosalind Franklin Medal and Prize". www.iop.org. Institute of Physics, London, UK. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
^ "Researchers Launch Innovative, Hands-on Online Tool for Science Education". Jacobsschool.ucsd.edu. Retrieved 14 January 2016.
^ "Lord Robert Winston opens Rosalind Franklin Building at Nottingham Trent Uni". Nottingham Post. Local World. 16 October 2012. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
^ "Rosalind Franklin, DNA scientist, celebrated by Google doodle", The Guardian, 2013, 25 July.
^ "Rosalind Franklin's 93rd Birthday". Google.
^ Jonny (10 March 2013). "New plaque for Rosalind Franklin". The Cambridge Tour Company. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ Ashwell, Louise (10 March 2013). "New plaque unveiled to commemorate unsung heroine of DNA". Varsity. Varsity Publications Ltd. Retrieved 27 August 2014.
^ Kennedy, Caitlin (11 July 2014). "CA Scientist Receives First BIO Rosalind Franklin Award". Biotechnology Industry Organization.
^ "Rosalind Franklin University unveils bronze statue of its namesake". Daily Herald. 29 May 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
^ "Franklin STEM Elementary". Schoolwires, Inc. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
^ TCAJOBS (14 October 2014). "Building Tri-Cities: Rosalind Franklin STEM Elementary". Tri-Cities Area Journal of Business. Archived from the original on 30 January 2016. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
^ "The Rosalind Franklin Science Building". University of Wolverhampton. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
^ "£25m lab block for the University of Wolverhampton". Express & Star. 17 October 2014. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
^ "Boats – Newnham College Boat Club". Retrieved 5 November 2015.
^ "Launch of the Rosalind Franklin Appathon for Women in STEMM". University College London. 4 November 2015. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
^ Brueckner, Rich (26 December 2015). "HPC Facility in London Named After Dr Rosalind Franklin". insideHPC. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
^ "» Professor Dame Anne Glover to deliver inaugural Rosalind Franklin Lecture on 10 March". British Humanist Association. Retrieved 7 March 2016.
^ "And the winners are ... The Rosalind Franklin Appathon Prize and Tech Day 2016". London Centre for Nanotechnology. 8 March 2016. Retrieved 9 May 2016.
^ "DSM opens biotech center, honors DNA-pioneer Rosalind Franklin". Biofuel Digest. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
^ Historic England (2017). "Tomb of Rosalind Franklin (1444176)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 11 February 2018.
^ "ESA's Mars rover has a name – Rosalind Franklin". European Space Agency. Retrieved 2019-02-07.
^ "Life Story (TV)". Filmaffinity. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Life Story". William Nicholson. Archived from the original on 28 January 2015. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Secret of Photo 51". PBS. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "NOVA: DNA – Secret of Photo 51 (2003)". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Secret of Photo 51 Transcript". PBS. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Rosalind Franklin: DNA's Dark Lady (2003) (TV)". MoviesPictures.ORG. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
^ "Season 1, Episode 1 The Secret of Life". tvguide.com. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Episode 1: The Secret of Life". PBS. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Rosalind: A Question of Life". deborahgearing-playwright.moonfruit.com. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ Gearing, Deborah (2006). Burn, and Rosalind: A Question of Life. London: Oberon Books. ISBN 978-1-84002-659-7.
^ Ziegler, Anna (2011). Photograph 51. New York: Dramatists Play Service. ISBN 978-0-8222-2508-9.
^ Ziegler, Anna (2011). Photograph 51. New York: Dramatists Play Service. ISBN 978-0-8222-2508-9.
^ Porteous, Jacob (24 April 2015). "Nicole Kidman Returns To The West End In Photograph 51". London Theatre Direct. Retrieved 27 October 2015.
^ Grode, Eric (5 November 2010). "The Female Scientist, the Biggest Secret". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
^ "Review of ''False Assumptions''". Productionottawa.com. 27 March 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
Sources
Brown, Andrew (2005). J. D. Bernal: The Sage of Science. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-920565-3.
Bryson, Bill (2004). A Short History of Nearly Everything. London: Black Swan. ISBN 0-552-99704-8.
Crick, F.; Watson, J. (1953), "Molecular structure of nucleic acids" (PDF), Nature, 171 (4356): 737–738, Bibcode:1953Natur.171..737W, doi:10.1038/171737a0, PMID 13054692.
Crick, Francis (1988). What Mad Pursuit: A Personal View of Scientific Discovery. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-09137-7.
- Elkin, L. O., Rosalind Franklin and the Double Helix Physics Today March 2003, pp. 42–48.
Franklin, R. E. (January 1950), "Influence of the bonding electrons on the scattering of X-rays by carbon", Nature, 165 (4185): 71–72, Bibcode:1950Natur.165...71F, doi:10.1038/165071a0, PMID 15403103.
Ferry, Georgina (2007). Max Perutz and the Secret of Life. London: Chatto & Windus. ISBN 0-7011-7695-4.
Franklin, R. E. & Gosling, R. G. (25 April 1953), "Molecular Configuration in Sodium Thymonucleate" (PDF), Nature, 171 (4356): 740–741, Bibcode:1953Natur.171..740F, doi:10.1038/171740a0, PMID 13054694, retrieved 15 January 2011 Reprint also available at Resonance Classics.
Franklin, R. E. (1955), "Structure of tobacco mosaic virus", Nature, 175 (4452): 379–381, Bibcode:1955Natur.175..379F, doi:10.1038/175379a0, PMID 14356181
Franklin, R. E. (1956), "Structure of Tobacco Mosaic Virus: Location of the Ribonucleic Acid in the Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particle", Nature, 177 (4516): 928–30, Bibcode:1956Natur.177..928F, doi:10.1038/177928b0.
Glynn, Jenifer (2012). My Sister Rosalind Franklin. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-969962-9.
- Holt, J. (2002) "Photo Finish: Rosalind Franklin and the great DNA race" The New Yorker October
Judson, Horace Freeland (1996). The Eighth Day of Creation: Makers of the Revolution in Biology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. ISBN 978-0-87969-478-4.
Maddox, Brenda (2003). Rosalind Franklin: The Dark Lady of DNA. London: Harper Collins. ISBN 0-00-655211-0.
McGrayne, Sharon Bertsch (1998). Nobel Prize Women in Science:: Their Lives, Struggles, and Momentous Discoveries (Rev ed.). Washington, D.C.: Joseph Henry Press. ISBN 978-0-309-07270-0.
Robert Cecil, Olby (1994) [1974]. The Path to the Double Helix: The Discovery of DNA (Unabridged, corrected and enlarged Dover ed.). New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-68117-3.
Polcovar, Jane (2006). Rosalind Franklin and the Structure of Life. Greensboro, N.C.: Morgan Reynolds Publishing Inc. ISBN 978-1-59935-022-6.
Sayre, Anne (1987) [1975]. Rosalind Franklin and DNA (Reissued ed.). New York: W.W. Norton and Company. ISBN 0-393-32044-8.
Segev, Tom (2000). One Palestine, Complete Jews and Arabs Under the British Mandate. Henry Holt and Company. ISBN 0-8050-4848-0.
Watson, James D. (1980) [1968], The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, Norton, ISBN 0-393-01245-X
- Watson, J. Letter to Science, 164, p. 1539, 27 (1969).
Wilkins, Maurice (2005). The Third Man of the Double Helix : the autobiography of Maurice Wilkins. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-280667-X.
Yockey, Hubert P. (2004). Information Theory, Evolution, and The Origin of Life. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-80293-2.
Further reading
Brown, Andrew (2007). J.D. Bernal: The Sage of Science. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-920565-5.
Chomet, Seweryn, ed. (1995). D.N.A.: Genesis of a Aiscovery. England: Newman-Hemisphere. ISBN 978-1-56700-138-9.
Crick, Francis (1988). What Mad Pursuit: A Personal View of Scientific Discovery. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-09138-5.
Dickerson, Richard E. (2005). Present at the Flood: How Structural Molecular Biology Came about. Sunderland: Sinauer. ISBN 0-87893-168-6.
Finch, John (2008). A Nobel Fellow on Every Floor: A History of the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology. Cambridge: Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology. ISBN 978-1-84046-940-0.
Gibbons, Michelle G (2012). "Reassessing Discovery: Rosalind Franklin, Scientific Visualization, and the Structure of DNA". Philosophy of Science. 79: 63–80. doi:10.1086/663241.
Hager, Thomas (1995). Force of Nature: The Life of Linus Pauling. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-80909-5.
Horace, Freeland Judson (1996) [1977]. The Eighth Day of Creation: Makers of the Revolution in Biology (Expanded ed.). Plainview, N.Y: CSHL Press. ISBN 0-87969-478-5.
Glynn, Jenifer (1996). "Rosalind Franklin, 1920–1958". In Shils, Edward. Cambridge Women: Twelve Portraits. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 267–282. ISBN 0-521-48287-9.
Klug, Aaron (2004). "R.E. Franklin". In Matthew, H.C.G.; Harrison, Brian. Oxford Dictionary of National Biography: From the Earliest Times to the Year 2000. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-861411-X.
Klug, Aaron (2004). "The discovery of the DNA Double Helix". In Krude, Torsten. DNA: Changing Science and Society. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 5–27. ISBN 0-521-82378-1.
Olby, Robert (1974). "Rosalind Elsie Franklin". In Gillispie, Charles Coulston. Dictionary of Scientific Biography. V.10. New York: Scribner. ISBN 0-684-10121-1.
Olby, Robert (1994). The Path to The Double Helix: The Discovery of DNA (Unabridged, corrected and enlarged Dover ed.). New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-68117-3.
Olby, R. (January 2003). "Quiet debut for the double helix". Nature. 421 (6921): 402–405. Bibcode:2003Natur.421..402O. doi:10.1038/nature01397. PMID 12540907.
Tait, Sylvia A.S.; Tait, James F. (2004). A Quartet of Unlikely Discoveries. London: Athena Press. ISBN 978-1-84401-343-2.
Wilkins, Maurice (2005). The Third Man of the Double Helix: The Autobiography of Maurice Wilkins. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280667-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Rosalind Franklin. |
"The Rosalind Franklin Society".
"Rosalind Franklin (1920–1958)". Contributions of 20th century women to physics. UCLA.
"Rosalind Franklin". The History of Medicine Topographical Database.
- Recordings by Aaron Klug at Web of Stories:
"12. Work at Birkbeck and meeting Rosalind Franklin". Web of Stories.
"13. Work with Rosalind Franklin". Web of Stories.
"17. Rosalind Franklin and the discovery of DNA". Web of Stories.
"18. After Rosalind Franklin's death". Web of Stories.
Franklin, Stephen (24 April 2003). "My aunt, the DNA pioneer". BBC.
Elkin, Lynne Osman (March 2003). "Rosalind Franklin and the double helix". Physics Today. 56: 42–48. Bibcode:2003PhT....56c..42E. doi:10.1063/1.1570771. Archived from the original on 3 February 2016.
Piper, Anne (April 1998). "Light on a dark lady". Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 23 (4): 151–154. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01194-3.
"Franklin, Rosalind Elsie (1920–1958), crystallographer". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/37413.
(Subscription or UK public library membership required.) by Sir Aaron Klug
"Clue to chemistry of heredity found" (PDF). New York Times. 13 June 1953. The first American newspaper coverage of the discovery of the structure of DNA.
Elkin, Lynne. "Rosalind Elsie Franklin 1920–1958". Jewish Women's Encyclopedia.
"Secret of Photo 51". PBS. Website for television program first broadcast in 2003
"The Rosalind Franklin Papers". Profiles in Science. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
"The Papers of Rosalind Franklin". Janus. Documents from the Churchill Archives Centre, Cambridge. Also available at "The Rosalind Franklin papers". Wellcome Library.
"Rosalind Franklin publications". Garfield Library. University of Pennsylvania.
"Rosalind Franklin 1920–1958". Linus Pauling and the race for DNA, a documentary history.
Thomas, T. Dennis (November 2008). "The role of activated charcoal in plant tissue culture" (PDF). Biotechnology Advances. 26 (6): 618–631. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.08.003.
Cobb, Matthew (23 June 2015). "Sexism in science: did Watson and Crick really steal Rosalind Franklin's data?". The Guardian.
