Dorsal fin

Dorsal fin of a shark
A dorsal fin is a fin located on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates such as fishes, cetaceans (whales, dolphins, and porpoises), and the (extinct) ichthyosaur. Most species have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three.
Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of large cetaceans to identify individuals in the field.
The bony or cartilaginous bones that support the base of the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores.
Contents
1 Functions
2 Structure
3 See also
4 Notes
Functions
The main purpose of the dorsal fin is to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin) for propulsion. In anglerfish, the anterior of the dorsal fin is modified into a biological equivalent to a fishing pole and a lure known as illicium or esca. Many catfish can lock the leading ray of the dorsal fin in an extended position to discourage predation or to wedge themselves into a crevice. Some animals have developed dorsal fins with protective functions, such as spines or venom. For example, both the spiny dogfish and the Port Jackson shark have spines in their dorsal fins which are capable of secreting venom.

Most fish, like this Prussian carp, have one dorsal fin
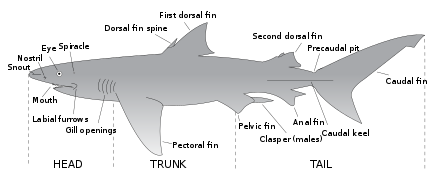
Sharks typically have two dorsal fins
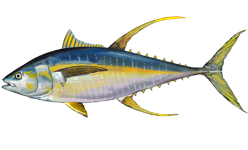
The yellowfin tuna also has two dorsal fins

Haddocks have three dorsal fins
Billfish have prominent dorsal fins. Like tuna, mackerel and other scombroids, billfish streamline themselves by retracting their dorsal fins into a groove in their body when they swim.[1] The shape, size, position and colour of the dorsal fin varies with the type of billfish, and can be a simple way to identify a billfish species. For example, the white marlin has a dorsal fin with a curved front edge and is covered with black spots. The huge dorsal fin, or sail, of the sailfish is kept retracted most of the time. Sailfish raise them if they want to herd a school of small fish, and also after periods of high activity, presumably to cool down.[1][2]

Differences of dorsal fins of orcas between male and female

The dorsal fin of a white shark contains dermal fibers that work "like riggings that stabilize a ship's mast", and stiffen dynamically as the shark swims faster to control roll and yaw.[3]
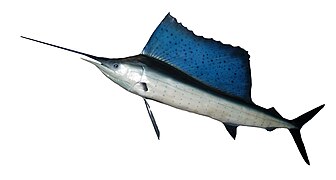
Large retractable dorsal fin of the Indo-Pacific sailfish
Structure
A dorsal fin is classified as a medial, unpaired fin that is located on the midline of the backs of some aquatic vertebrates. In development of the embryo in teleost fish, the dorsal fin arises from sections of the skin that form a caudal fin fold.[4] The larval development and formation of the skeleton that support the median fins in adults result in pterygiophores. The skeletal elements of the pterygiophore includes basals and radials. The basals are located at the base of the dorsal fin, and are closest to the body. The radials extend outward from the body to support the rest of the fin.[4] These elements serve as attachment sites for epaxial muscles.[5] The muscles contract and pull against the basals of the pterygiophores along one side of the body, which helps the fish move through water by providing greater stability.[5] In these types of fish, the fins are made of 2 main components.[5] The first component is the dermal fin rays known as lepidotrichia, and the endoskeletal base with associated muscles for movement is the second.[4]

Dorsal fin of a perch showing the basals and radials of the pterygiophore that support the dorsal fin.

Closeup of the dorsal fin of a common dragonet
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dorsal fins. |
| Look up dorsal in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Fish fin
- Submarine sail
- Vertical stabilizer
Notes
^ ab Aquatic Life of the World pp. 332–333, Marshall Cavendish Corporation, 2000. .mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
ISBN 9780761471707.
^ Dement J Species Spotlight: Atlantic Sailfish (Istiophorus albicans) littoralsociety.org. Retrieved 1 April 2012.
^ Lingham‐Soliar T (2005) "Dorsal fin in the white shark, Carcharodon carcharias: A dynamic stabilizer for fast swimming" Journal of Morphology, 263 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1002/jmor.10207 pdf[permanent dead link]
^ abc Tohru, Suzuki (2003). "Differentiation of chondrocytes and scleroblasts during dorsal fin skeletogenesis in flounder larvae". Development, Growth & Differentiation. 45 (5–6): 435–448. doi:10.1111/j.1440-169X.2003.00711.x.
^ abc Barton, Michael (2007). Bond's Book of Fish (3rd ed.). The Thompson Corporation. pp. 37–39, 60–61.










