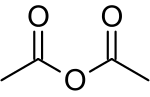
Acetic anhydride
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Preferred IUPAC name Acetic anhydride | |
Systematic IUPAC name Ethanoic anhydride | |
| Other names Ethanoyl ethanoate Acetic acid anhydride Acetyl acetate Acetyl oxide Acetic oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
ChEBI |
|
ChemSpider |
|
ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.241 |
EC Number | 203-564-8 |
PubChem CID |
|
RTECS number | AK1925000 |
UNII |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C4H6O3 |
Molar mass | 102.09 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
Density | 1.082 g cm−3, liquid |
Melting point | −73.1 °C (−99.6 °F; 200.1 K) |
Boiling point | 139.8 °C (283.6 °F; 412.9 K) |
Solubility in water | 2.6 g/100 mL, see text |
Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20 °C)[1] |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -52.8·10−6 cm3/mol |
Refractive index (nD) | 1.3901 |
| Pharmacology | |
Legal status |
|
| Hazards | |
Safety data sheet | ICSC 0209 |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) | Corrosive (C) |
R-phrases (outdated) | R10, R20/22, R34 |
S-phrases (outdated) | (S1/2), S26, S36/37/39, S45 |
NFPA 704 |  2 3 1 |
Flash point | 49 °C (120 °F; 322 K) |
Autoignition temperature | 316 °C (601 °F; 589 K) |
Explosive limits | 2.7–10.3% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LC50 (median concentration) | 1000 ppm (rat, 4 hr)[2] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
PEL (Permissible) | TWA 5 ppm (20 mg/m3)[1] |
REL (Recommended) | C 5 ppm (20 mg/m3)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) | 200 ppm[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related acid anhydrides | Propionic anhydride |
Related compounds | Acetic acid Acetyl chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Infobox references | |
Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.
Contents
1 Structure and properties
2 Production
3 Reactions
3.1 Acetylation of alcohols and amines
3.2 Acetylation of aromatic rings
3.3 Preparation of other acid anhydrides
3.4 Precursor to geminal diacetates
3.5 Hydrolysis
4 Applications
5 Safety
6 References
7 External links
Structure and properties
Acetic anhydride, like most acid anhydrides, is a flexible molecule with a nonplanar structure.[3] The pi system linkage through the central oxygen offers very weak resonance stabilization compared to the dipole-dipole repulsion between the two carbonyl oxygens. The energy barriers to bond rotation between each of the optimal aplanar conformations are quite low.[4]
Like most acid anhydrides, the carbonyl carbon of acetic anhydride has electrophilic character, as the leaving group is carboxylate. The internal asymmetry may contribute to acetic anhydride's potent electrophilicity as the asymmetric geometry makes one side of a carbonyl carbon more reactive than the other, and in doing so tends to consolidate the electropositivity of a carbonyl carbon to one side (see electron density diagram).
Production
Acetic anhydride was first synthesized in 1852 by the French chemist Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (1816-1856) by heating potassium acetate with benzoyl chloride.[5]
Acetic anhydride is produced by carbonylation of methyl acetate:[6]
- CH3CO2CH3 + CO → (CH3CO)2O
The Tennessee Eastman acetic anhydride process involves the conversion of methyl acetate to methyl iodide and an acetate salt. Carbonylation of the methyl iodide in turn affords acetyl iodide, which reacts with acetate salts or acetic acid to give the product. Rhodium chloride in the presence of lithium iodide is employed as catalysts. Because acetic anhydride is not stable in water, the conversion is conducted under anhydrous conditions.
To a decreasing extent, acetic anhydride is also prepared by the reaction of ketene (ethenone) with acetic acid at 45–55 °C and low pressure (0.05–0.2 bar).[7]
- H2C=C=O + CH3COOH → (CH3CO)2O (ΔH = −63 kJ/mol)
The route from acetic acid to acetic anhydride via ketene was developed by Wacker Chemie in 1922,[8] when the demand for acetic anhydride increased due to the production of cellulose acetate.
Due to its low cost, acetic anhydride is usually purchased, not prepared, for use in research laboratories.
Reactions
Acetic anhydride is a versatile reagent for acetylations, the introduction of acetyl groups to organic substrates.[9] In these conversions, acetic anhydride is viewed as a source of CH3CO+.
Acetylation of alcohols and amines
Alcohols and amines are readily acetylated.[10] For example, the reaction of acetic anhydride with ethanol yields ethyl acetate:
- (CH3CO)2O + CH3CH2OH → CH3CO2CH2CH3 + CH3COOH
Often a base such as pyridine is added to function as catalyst. In specialized applications, Lewis acidic scandium salts have also proven effective catalysts.[11]
Acetylation of aromatic rings
Aromatic rings are acetylated by acetic anhydride. Usually acid catalysts are used to accelerate the reaction. Illustrative are the conversions of benzene to acetophenone[12] and ferrocene to acetylferrocene:[13]
- (C5H5)2Fe + (CH3CO)2O → (C5H5)Fe(C5H4COCH3) + CH3CO2H
Preparation of other acid anhydrides
Dicarboxylic acids are converted to the anhydrides upon treatment with acetic anhydride.[14] It is also used for the preparation of mixed anhydrides such as that with nitric acid, acetyl nitrate.
Precursor to geminal diacetates
Aldehydes react with acetic anhydride in the presence of an acidic catalyst to give geminal diacetates.[15] A former industrial route to vinyl acetate involved the intermediate ethylidene diacetate, the geminal diacetate obtained from acetaldehyde and acetic anhydride:[16]
- CH3CHO + (CH3CO)2O → (CH3CO2)2CHCH3
Hydrolysis
Acetic anhydride dissolves in water to approximately 2.6% by weight.[17] Aqueous solutions have limited stability because, like most acid anhydrides, acetic anhydride hydrolyses to give carboxylic acids. In this case, acetic acid is formed:[18]
- (CH3CO)2O + H2O → 2 CH3CO2H
Applications
As indicated by its organic chemistry, Ac2O is mainly used for acetylations leading to commercially significant materials. Its largest application is for the conversion of cellulose to cellulose acetate, which is a component of photographic film and other coated materials, and is used in the manufacture of cigarette filters. Similarly it is used in the production of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid), which is prepared by the acetylation of salicylic acid.[19] It is also used as a wood preservative via autoclave impregnation to make a longer-lasting timber.
In starch industry, acetic anhydride is a common acetylation compound, used for the production of modified starches (E1414, E1420, E1422)
Because of its use for the synthesis of heroin by the diacetylation of morphine, acetic anhydride is listed as a U.S. DEA List II precursor, and restricted in many other countries.[20]
Safety
Acetic anhydride is an irritant and combustible liquid. Because of its reactivity toward water, alcohol foam or carbon dioxide are preferred for fire suppression.[21] The vapour of acetic anhydride is harmful.[22]
References
^ abcd "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0003". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "Acetic anhydride". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
^ Seidel, R. W.; Goddard, R.; Nöthling, N.; Lehmann, C. W. (2016), "Acetic anhydride at 100 K: the first crystal structure determination", Acta Crystallographica Section C, 72 (10): 753–757, doi:10.1107/S2053229616015047.
^ Wu, Guang; Van Alsenoy, C.; Geise, H. J.; Sluyts, E.; Van Der Veken, B. J.; Shishkov, I. F.; Khristenko (2000), "Acetic Anhydride in the Gas Phase, Studied by Electron Diffraction and Infrared Spectroscopy, Supplemented with ab Initio Calculations of Geometries and Force Fields", The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 104 (7): 1576–1587, doi:10.1021/jp993131z.
^ Charles Gerhardt (1852) “Recherches sur les acides organiques anhydres” (Investigations into the anhydrides of organic acids), Comptes rendus … , 34 : 755-758.
^ Zoeller, J. R.; Agreda, V. H.; Cook, S. L.; Lafferty, N. L.; Polichnowski, S. W.; Pond, D. M. (1992), "Eastman Chemical Company Acetic Anhydride Process", Catal. Today, 13 (1): 73–91, doi:10.1016/0920-5861(92)80188-S
^ Arpe, Hans-Jürgen (2007-01-11), Industrielle organische Chemie: Bedeutende vor- und Zwischenprodukte (6th ed.), Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, pp. 200–1, ISBN 3-527-31540-3.
^ Milestones in the history of WACKER, Wacker Chemie AG, retrieved 2009-08-27.
^ "Acid Anhydrides", Understanding Chemistry, retrieved 2006-03-25.
^ Shakhashiri, Bassam Z., "Acetic Acid & Acetic Anhydride", Science is Fun…, Department of Chemistry, University of Wisconsin, archived from the original on 2006-03-03, retrieved 2006-03-25.
^ Macor, John; Sampognaro, Anthony J.; Verhoest, Patrick R.; Mack, Robert A. (2000). "(R)-(+)-2-Hydroxy-1,2,2-Triphenylethyl Acetate". Organic Syntheses. 77: 45. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.077.0045.; Collective Volume, 10, p. 464
^ Roger Adams and C. R. Noller "p-Bromoacetophenone" Org. Synth. 1925, vol. 5, p. 17. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.005.0017
^ Taber, Douglass F., Column chromatography: Preparation of Acetyl Ferrocene, Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Delaware, retrieved 2009-08-27.
^ B. H. Nicolet and J. A. Bender "3-Nitrophthalic Anhydride" Org. Synth. 1927, vol. 7, 74.
doi:10.15227/orgsyn.007.0074
^ R. T. Bertz "Furfuryl Diacetate" Org. Synth. 1953, 33, 39. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.033.0039
^ G. Roscher "Vinyl Esters" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 2007 John Wiley & Sons: New York. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_419
^ Acetic Anhydride: Frequently Asked Questions (PDF), British Petroleum, archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-11, retrieved 2006-05-03.
^ Acetic Anhydride: Material Safety Data Sheet (PDF) (PDF), Celanese, archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-27, retrieved 2006-05-03.
^ Acetic anhydride (PDF), SIDS Initial Assessment Report, Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme, p. 5.
^ UN Intercepts Taliban's Heroin Chemical in Rare Afghan Victory, Bloomberg, retrieved 2008-10-07.
^ "Data Sheets". International Occupational Safety and Health Information Centre. Retrieved 2006-04-13.
^
"NIOSH". Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. Archived from the original on 22 April 2006. Retrieved 2006-04-13.
External links
- ICSC 0209
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards