Energy density
| Energy density | |
|---|---|
| SI unit | J/m3 |
| In SI base units | kg·m−1s−2 |
Derivations from other quantities | U = E/V |
Energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Colloquially it may also be used for energy per unit mass, though the accurate term for this is specific energy. Often only the useful or extractable energy is measured, which is to say that inaccessible energy (such as rest mass energy) is ignored.[1] In cosmological and other general relativistic contexts, however, the energy densities considered are those that correspond to the elements of the stress–energy tensor and therefore do include mass energy as well as energy densities associated with the pressures described in the next paragraph.
Energy per unit volume has the same physical units as pressure, and in many circumstances is a synonym: for example, the energy density of a magnetic field may be expressed as (and behaves as) a physical pressure, and the energy required to compress a compressed gas a little more may be determined by multiplying the difference between the gas pressure and the external pressure by the change in volume. In short, pressure is a measure of the enthalpy per unit volume of a system. A pressure gradient has the potential to perform work on the surroundings by converting enthalpy to work until equilibrium is reached.
Contents
1 Introduction to energy density
1.1 Energy densities of common energy storage materials
2 Energy density in energy storage and in fuel
2.1 Nuclear energy sources
2.1.1 Thermal power of nuclear fission reactors
2.2 Broad implications
2.3 Energy densities ignoring external components
3 Energy density of electric and magnetic fields
4 See also
5 Footnotes
6 Further reading
7 External links
Introduction to energy density
There are many different types of energy stored in materials, and it takes a particular type of reaction to release each type of energy. In order of the typical magnitude of the energy released, these types of reactions are: nuclear, chemical, electrochemical, and electrical.
Nuclear reactions are used by stars and nuclear power plants, both of which derive energy from the binding energy of nuclei. Chemical reactions are used by animals to derive energy from food, and by automobiles to derive energy from gasoline. Liquid hydrocarbons (fuels such as gasoline, diesel and kerozene) are today the most dense way known to economically store and transport chemical energy at a very large scale (1 kg of diesel fuel burns with the oxygen contained in ~15 kg of air). Electrochemical reactions are used by most mobile devices such as laptop computers and mobile phones to release the energy from batteries.
Energy densities of common energy storage materials
The following is a list of the thermal energy densities (that is to say: the amount of heat energy that can be extracted) of commonly used or well-known energy storage materials; it doesn't include uncommon or experimental materials. Note that this list does not consider the mass of reactants commonly available such as the oxygen required for combustion or the energy efficiency in use. An extended version of this table is found at Energy density#Extended Reference Table. Major reference = [2].
The following unit conversions may be helpful when considering the data in the table: 3.6 MJ = 1 kWh ≈ 1.34 HPh.
| Storage material | Energy type | Specific energy (MJ/kg) | Energy density (MJ/L) | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Deuterium (in Fusion reactor) | Nuclear fusion | 87,900,000[3] | 15,822[4] | Experimental |
Uranium (in breeder) | Nuclear fission | 80,620,000[5] | 1,539,842,000 | Electric power plants |
Thorium (in breeder) | Nuclear fission | 79,420,000[5] | 929,214,000 | Experimental |
Plutonium 238 | Nuclear decay | 2,239,000 | 43,277,631 | RTGs |
Tritium | Nuclear decay | 583,529 | 158[6] | Experimental, thermonuclear weapons |
Hydrogen (liquid) | Chemical | 142 | 10 | Rocket engines, Fuel Cells, H2 Storage/Transport |
Hydrogen (compressed at 700 bar) | Chemical | 142 | 9.17 | Fuel Cells, Natural Gas Heating Supplement |
Methane or Liquefied natural gas (compressed) | Chemical | 55.5 | 22.2 | Cooking, home heating, electric power plants |
Diesel | Chemical | 48 | 35.8 | Automotive engines, electric power plants |
LPG (including Propane / Butane) | Chemical | 46.4 | 26 | Cooking, home heating, automotive engines, lighter fluid |
Gasoline (petrol) | Chemical | 46.4[2] | 34.2 | Automotive engines, electric power plants |
Jet fuel (Kerosene) | Chemical | 42.8[7] | 37.4 | Aircraft engines |
Fat (animal/vegetable) | Chemical | 37 | 34 | Human and animal nutrition |
Coal (anthracite or bituminous) | Chemical | ~30 | ~38 | Electric power plants, home heating |
Methanol | Chemical | 19.7 | 15.6 | Fuel engines |
Carbohydrates (including sugars) | Chemical | 17 | 43 | Human and animal nutrition |
Protein | Chemical | 16.8 | ~17 | Human and animal nutrition |
Wood | Chemical | 16.2[8] | 13 | Home heating, cooking |
Gunpowder | Chemical | 4.7–11.3[9] | 5.9-12.9 | Explosives, Ammunition |
TNT | Chemical | 4.184 | 6.92 | Explosives |
Lithium metal battery | Electrochemical | 1.8 | 4.32 | Portable electronic devices |
Lithium-ion battery | Electrochemical | 0.36–0.875[12] | 0.9–2.63 | Automotive motors, portable electronic devices, RC vehicles |
Flywheel | Mechanical | 0.36–0.5 | 5.3 | Power plants, Gyrobusses |
Alkaline battery | Electrochemical | 0.48[13] | 1.3[14] | Portable electronic devices, flashlights |
Nickel-metal hydride battery | Electrochemical | 0.41[15] | 0.504–1.46[15] | Portable electronic devices, flashlights |
Lead-acid battery | Electrochemical | 0.17 | 0.56 | Automotive engine ignition |
Supercapacitor (EDLC) | Electrical (electrostatic) | 0.01–0.036[22] | 0.05–0.06[23] | Electronic circuits |
Electrolytic capacitor | Electrical (electrostatic) | 0.00001–0.0002[24] | 0.00001–0.001[27] | Electronic circuits |
| Storage device | Energy content (Joule) | Energy type | Typical mass (g) | Typical volume (width × height × depth in mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Alkaline AA battery[28] | 9,360 | Electrochemical | 24 | 14.2 × 50 |
Alkaline C battery[28] | 34,416 | Electrochemical | 65 | 26 × 46 |
NiMH AA battery | 9,072 | Electrochemical | 26 | 14.2 × 50 |
NiMH C battery | 19,440 | Electrochemical | 82 | 26 × 46 |
Lithium-ion 18650 battery | 28,800–46,800 | Electrochemical | 44–49[29] | 18 × 65 |
| Potato Chip | 41,900[30] | Chemical | 1.89 | 60 × 40 × 1 |
| Ham and Cheese Sandwich[31] | 1,470,000 | Chemical | 145 | 100 × 100 × 28 |
Energy density in energy storage and in fuel
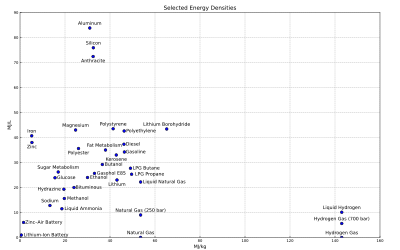
Selected energy densities plot[32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39]
In energy storage applications the energy density relates the mass of an energy store to the volume of the storage facility, e.g. the fuel tank. The higher the energy density of the fuel, the more energy may be stored or transported for the same amount of volume. The energy density of a fuel per unit mass is called the specific energy of that fuel. In general an engine using that fuel will generate less kinetic energy due to inefficiencies and thermodynamic considerations—hence the specific fuel consumption of an engine will always be greater than its rate of production of the kinetic energy of motion.
Nuclear energy sources
The greatest energy source by far is mass itself. This energy, E = mc2, where m = ρV, ρ is the mass per unit volume, V is the volume of the mass itself and c is the speed of light. This energy, however, can be released only by the processes of nuclear fission (0.1%), nuclear fusion (1%), or the annihilation of some or all of the matter in the volume V by matter-antimatter collisions (100%).[citation needed] Nuclear reactions cannot be realized by chemical reactions such as combustion. Although greater matter densities can be achieved, the density of a neutron star would approximate the most dense system capable of matter-antimatter annihilation possible. A black hole, although denser than a neutron star, does not have an equivalent anti-particle form, but would offer the same 100% conversion rate of mass to energy in the form of Hawking radiation. In the case of relatively small black holes (smaller than astronomical objects) the power output would be tremendous.
The highest density sources of energy aside from antimatter are fusion and fission. Fusion includes energy from the sun which will be available for billions of years (in the form of sunlight) but so far (2018), sustained fusion power production continues to be elusive.
Power from fission of uranium and thorium in nuclear power plants will be available for many decades or even centuries because of the plentiful supply of the elements on earth,[40] though the full potential of this source can only be realised through breeder reactors, which are, apart from the BN-600 reactor, not yet used commercially.[41]Coal, gas, and petroleum are the current primary energy sources in the U.S.[42] but have a much lower energy density. Burning local biomass fuels supplies household energy needs (cooking fires, oil lamps, etc.) worldwide.
Thermal power of nuclear fission reactors
The density of thermal energy contained in the core of a light water reactor (PWR or BWR) of typically 1 GWe (1 000 MW electrical corresponding to ~3 000 MW thermal) is in the range of 10 to 100 MW of thermal energy per cubic meter of cooling water depending on the location considered in the system (the core itself (~30 m3), the reactor pressure vessel (~50 m3), or the whole primary circuit (~300 m3)). This represents a considerable density of energy which requires under all circumstances a continuous water flow at high velocity in order to be able to remove the heat from the core, even after an emergency shutdown of the reactor. The incapacity to cool the cores of three boiling water reactors (BWR) at Fukushima in 2011 after the tsunami and the resulting loss of the external electrical power and of the cold source was the cause of the meltdown of the three cores in only a few hours, even though the three reactors were correctly shut down just after the Tōhoku earthquake. This extremely high power density distinguishes nuclear power plants (NPP's) from any thermal power plants (burning coal, fuel or gas) or any chemical plants and explains the large redundancy required to permanently control the neutron reactivity and to remove the residual heat from the core of NPP's.
Broad implications
Energy density differs from energy conversion efficiency (net output per input) or embodied energy (the energy output costs to provide, as harvesting, refining, distributing, and dealing with pollution all use energy). Large scale, intensive energy use impacts and is impacted by climate, waste storage, and environmental consequences.
No single energy storage method boasts the best in specific power, specific energy, and energy density. Peukert's Law describes how the amount of useful energy that can be obtained (for a lead-acid cell) depends on how quickly we pull it out. To maximize both specific energy and energy density, one can compute the specific energy density of a substance by multiplying the two values together, where the higher the number, the better the substance is at storing energy efficiently.
Alternative options are discussed for energy storage to increase energy density and decrease charging time.[43][44][45][46]
Gravimetric and volumetric energy density of some fuels and storage technologies (modified from the Gasoline article):
- Note: Some values may not be precise because of isomers or other irregularities. See Heating value for a comprehensive table of specific energies of important fuels.
- Note: Also it is important to realise that generally the density values for chemical fuels do not include the weight of oxygen required for combustion. This is typically two oxygen atoms per carbon atom, and one per two hydrogen atoms. The atomic weight of carbon and oxygen are similar, while hydrogen is much lighter than oxygen. Figures are presented this way for those fuels where in practice air would only be drawn in locally to the burner. This explains the apparently lower energy density of materials that already include their own oxidiser (such as gunpowder and TNT), where the mass of the oxidiser in effect adds dead weight, and absorbs some of the energy of combustion to dissociate and liberate oxygen to continue the reaction. This also explains some apparent anomalies, such as the energy density of a sandwich appearing to be higher than that of a stick of dynamite.
Energy densities ignoring external components
This table lists energy densities of systems that require external components, such as oxidisers or a heat sink or source. These figures do not take into account the mass and volume of the required components as they are assumed to be freely available and present in the atmosphere. Such systems cannot be compared with self-contained systems. These values may not be computed at the same reference conditions.
| Storage type | Specific energy (MJ/kg) | Energy density (MJ/L) | Specific energy (Wh/kg) | Energy density (Wh/L) | Peak recovery efficiency % | Practical recovery efficiency % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Antimatter | 89,875,517,874 | Depends on the density of the antimatter's form | 24,965,421,631,578 | Depends on the density of the antimatter's form | 100 | |
Plutonium-239 | 83,610,000 (thermal energy) 31,000,000 (electrical energy) | Depends on crystallographic phase | 23,222,915,000 (thermal energy) 8,700,000,000 (electrical energy) | Depends on crystallographic phase | ||
Hydrogen, liquid[47] | 141.86 (HHV) 119.93 (LHV) | 10.044 (HHV) 8.491 (LHV) | 39,405.639,405.6 (HHV) 33,313.9 (LHV) | 2,790.0 (HHV) 2,358.6 (LHV) | ||
Hydrogen, at 690 bar and 15°C[47] | 141.86 (HHV) 119.93 (LHV) | 5.323 (HHV) 4.500 (LHV) | 39,405.639,405.6 (HHV) 33,313.9 (LHV) | 1,478.6 (HHV) 1,250.0 (LHV) | ||
Hydrogen, gas[47] | 141.86 (HHV) 119.93 (LHV) | 0.01188 (HHV) 0.01005 (LHV) | 39,405.639,405.6 (HHV) 33,313.9 (LHV) | 3.3 (HHV) 2.8 (LHV) | ||
Diborane[48] | 78.2 | 21,722.2 | ||||
Beryllium | 67.6 | 125.1 | 18,777.8 | 34,750.0 | ||
Lithium borohydride | 65.2 | 43.4 | 18,111.1 | 12,055.6 | ||
Boron[49] | 58.9 | 137.8 | 16,361.1 | 38,277.8 | ||
Methane (1.013 bar, 15 °C) | 55.6 | 0.0378[a] | 15,444.5 | 10.5 | ||
Natural gas | 53.6[50] | 0.0364[a] | 14,888.9 | 10.1 | ||
LNG (NG at −160 °C) | 53.6[50] | 22.2[a] | 14,888.9 | 6,166.7 | ||
CNG (NG compressed to 250 bar/~3,600 psi) | 53.6[50] | 9[a] | 14,888.9 | 2,500.0 | ||
LPG propane[51] | 49.6 | 25.3[a] | 13,777.8 | 7,027.8 | ||
LPG butane[51] | 49.1 | 27.7[a] | 13,638.9 | 7,694.5 | ||
Gasoline (petrol)[51] | 46.4 | 34.2[a] | 12,888.9 | 9,500.0 | ||
Polypropylene plastic | 46.4[52] | 41.7 | 12,888.9 | 11,583.3 | ||
Polyethylene plastic | 46.3[52] | 42.6 | 12,861.1 | 11,833.3 | ||
Crude oil (according to the definition of ton of oil equivalent) | 46.3 | 37[a][50] | 12,861.1 | 10,277.8 | ||
| Residential heating oil[51] | 46.2 | 37.3[a] | 12,833.3 | 10,361.1 | ||
Diesel fuel[51] | 45.6 | 38.6[a] | 12,666.7 | 10,722.2 | ||
100LL Avgas | 44.0[53] | 31.59 | 12,222.2 | 8,775.0 | ||
Gasohol E10 (10% ethanol 90% gasoline by volume) | 43.54 | 33.18[a] | 12,094.5 | 9,216.7 | ||
Lithium | 43.1 | 23.0 | 11,972.2 | 6,388.9 | ||
Jet A aviation fuel[54]/kerosene | 42.8 | 33[a] | 11,888.9 | 9,166.7 | ||
Biodiesel oil (vegetable oil) | 42.20 | 33[a] | 11,722.2 | 9,166.7 | ||
DMF (2,5-dimethylfuran)[clarification needed] | 42[55] | 37.8 | 11,666.7 | 10,500.0 | ||
Polystyrene plastic | 41.4[52] | 43.5 | 11,500.0 | 12,083.3 | ||
Body fat metabolism | 38 | 35[a] | 10,555.6 | 9,722.2 | 22[56] | |
Butanol | 36.6 | 29.2 | 10,166.7 | 8,111.1 | ||
| Gasohol E85 (85% ethanol 15% gasoline by volume) | 33.1 | 25.65[citation needed] | 9,194.5 | 7,125.0 | ||
Graphite | 32.7 | 72.9 | 9,083.3 | 20,250.0 | ||
Coal, anthracite[57] | 26–33 | 34–43 | 7,222.2–9,166.7 | 9,444.5–11,944.5 | 36 | |
Silicon[58][citation needed] | 32.2 | 75.1 | 8,944.5 | 20,861.120,861.1 | ||
Aluminum | 31.0 | 83.8 | 8,611.1 | 23,277.8 | ||
Ethanol | 30 | 24 | 8,333.3 | 6,666.7 | ||
Polyester plastic | 26.0[52] | 35.6 | 7,222.2 | 9,888.9 | ||
Magnesium | 24.7 | 43.0 | 6,861.1 | 11,944.5 | ||
Coal, bituminous[57] | 24–35 | 26–49 | 6,666.7–9,722.2 | 7,222.2–13,611.1 | ||
PET plastic | 23.5 (impure)[59] | 6,527.8 | ||||
Methanol | 19.7 | 15.6 | 5,472.2 | 4,333.3 | ||
Hydrazine (combusted to N2+H2O) | 19.5 | 19.3 | 5,416.7 | 5,361.1 | ||
| Liquid ammonia (combusted to N2+H2O) | 18.6 | 11.5 | 5,166.7 | 3,194.5 | ||
PVC plastic (improper combustion toxic)[clarification needed] | 18.0[52] | 25.2 | 5,000.0 | 7,000.0 | ||
Wood[60] | 18.0 | 5,000.0 | ||||
Peat briquette[61] | 17.7 | 4,916.7 | ||||
Sugars, carbohydrates, and protein metabolism[citation needed] | 17 | 26.2 (dextrose) | 4,722.2 | 7,277.8 | 22[62] | |
Calcium[citation needed] | 15.9 | 24.6 | 4,416.7 | 6,833.3 | ||
Glucose | 15.55 | 23.9 | 4,319.5 | 6,638.9 | ||
| Dry cow dung and camel dung | 15.5[63] | 4,305.6 | ||||
Coal, lignite[citation needed] | 10–20 | 2,777.8–5,555.6 | ||||
Sodium (burned to wet sodium hydroxide) | 13.3 | 12.8 | 3,694.5 | 3,555.6 | ||
| Sod peat | 12.8 | 3,555.6 | ||||
Nitromethane | 11.3 | 3,138.9 | ||||
Sulfur (burned to sulfur dioxide)[64] | 9.23 | 19.11 | 2,563.9 | 5,308.3 | ||
Sodium (burned to dry sodium oxide) | 9.1 | 8.8 | 2,527.8 | 2,444.5 | ||
Battery, lithium-air rechargeable | 9.0[65] | 2,500.0 | ||||
Household waste | 8.0[66] | 2,222.2 | ||||
Zinc | 5.3 | 38.0 | 1,472.2 | 10,555.6 | ||
Iron (burned to iron(III) oxide) | 5.2 | 40.68 | 1,444.5 | 11,300.0 | ||
Teflon plastic (combustion toxic, but flame retardant) | 5.1 | 11.2 | 1,416.7 | 3,111.1 | ||
Iron (burned to iron(II) oxide) | 4.9 | 38.2 | 1,361.1 | 10,611.1 | ||
ANFO | 3.7 | 1,027.8 | ||||
Battery, zinc-air[67] | 1.59 | 6.02 | 441.7 | 1,672.2 | ||
Liquid nitrogen[clarification needed] | 0.77[68] | 0.62 | 213.9 | 172.2 | ||
Compressed air at 300 bar (potential energy) | 0.5 | 0.2 | 138.9 | 55.6 | >50[citation needed] | |
Latent heat of fusion of ice[citation needed] (thermal) | 0.335 | 0.335 | 93.1 | 93.1 | ||
Water at 100 m dam height (potential energy) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.278 | 0.278 | 95 | 85–90[69][70] |
| Storage type | Energy density by mass (MJ/kg) | Energy density by volume (MJ/L) | Specific energy (Wh/kg) | Energy density (Wh/L) | Peak recovery efficiency % | Practical recovery efficiency % |
^ abcdefghijklmn Technically the actual value of the fuel alone is half the number indicated, because in order to burn the fuel must be mixed with 2 parts oxygen to 1 part fuel. In an oxygen-free environment the actual value is 0 as the fuel will not burn at all.
Divide joule/m3 by 109 to get MJ/L. Divide MJ/L by 3.6 to get kWh/L.
Energy density of electric and magnetic fields
Electric and magnetic fields store energy. In a vacuum, the (volumetric) energy density is given by
- u=ε02E2+12μ0B2{displaystyle u={frac {varepsilon _{0}}{2}}mathbf {E} ^{2}+{frac {1}{2mu _{0}}}mathbf {B} ^{2}}
where E is the electric field and B is the magnetic field. The solution will be (in SI units) in Joules per cubic metre. In the context of magnetohydrodynamics, the physics of conductive fluids, the magnetic energy density behaves like an additional pressure that adds to the gas pressure of a plasma.
In normal (linear and nondispersive) substances, the energy density (in SI units) is
- u=12(E⋅D+H⋅B){displaystyle u={frac {1}{2}}(mathbf {E} cdot mathbf {D} +mathbf {H} cdot mathbf {B} )}
where D is the electric displacement field and H is the magnetizing field.
In the case of absence of magnetic fields, by exploting Fröhlich's relationships it is also possible to extend these equations to anisotropy and nonlinearity dielectrics, as well as to calculate the correlated Helmholtz free energy and entropy densities.[71]
See also
- Bipolar battery
- Energy density Extended Reference Table
- High Energy Density Matter
Power density and specifically
- Power-to-weight ratio
- Orders of magnitude (specific energy)
- Figure of merit
- Energy content of biofuel
- Heat of combustion
- Heating value
- Rechargeable battery
- Specific impulse
- Food energy
Footnotes
^ "The Two Classes of SI Units and the SI Prefixes". NIST Guide to the SI. Retrieved 2012-01-25..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output .citation q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .citation .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-ws-icon a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4c/Wikisource-logo.svg/12px-Wikisource-logo.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-maint{display:none;color:#33aa33;margin-left:0.3em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ ab "Fossil and Alternative Fuels - Energy Content (2008)". Engineering ToolBox. Retrieved 2018-10-08.
^ J. D. Huba. "NRL Plasma Formulary (revised 2016)" (PDF). Naval Research Laboratory. p. 44. Retrieved 2017-05-16.
^ "Characteristics of Tritium" (PDF). springer.com. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
^ ab "Computing the energy density of nuclear fuel". whatisnuclear.com. Retrieved 2014-04-17.
^ "Characteristics of Tritium" (PDF). springer.com. Retrieved 2018-09-17.
^ http://www.exxonmobilaviation.com/AviationGlobal/Files/WorldJetFuelSpec2008.pdf
^ Wilfred Weihe "Electric Fireplace Costs Secrets"
^ Lu, Gui-e; Chang, Wen-ping; Jiang, Jin-yong; Du, Shi-guo (May 2011). "Study on the Energy Density of Gunpowder Heat Source". 2011 International Conference on Materials for Renewable Energy & Environment. IEEE. doi:10.1109/ICMREE.2011.5930549. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
^ "Overview of lithium ion batteries" (PDF). Panasonic. Jan 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 7, 2011.
^ "Panasonic NCR18650B" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-22.
^ [10][11]
^ "Test of Duracell Ultra Power AA". lygte-info.dk. Retrieved 2019-02-16.
^ "Energizer EN91 AA alkaline battery datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ ab "Test of GP ReCyko+ AA 2700mAh (Green)". lygte-info.dk. Retrieved 2019-02-16.
^ ab "Maxwell supercapacitor comparison" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ ab "Nesscap ESHSP series supercapacitor datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ ab "Cooper PowerStor XL60 series supercapacitor datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ ab "Kemet S301 series supercapacitor datasheet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ ab "Nichicon JJD series supercapatcitor datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ ab "skelcap High Energy Ultracapacitor" (PDF). Skeleton Technologies. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
^ [16][17][18][19][20][21]
^ [16][17][18][19][20][21]
^ ab "Vishay STE series tantalum capacitors datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ "nichicon TVX aluminum electrolytic capacitors datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ "nichicon LGU aluminum electrolytic capacitors datasheet" (PDF). Retrieved 2016-01-10.
^ [24][25][26]
^ ab "Battery Energy Tables".
^ "18650 Battery capacities".
^ "Calories in Lay's Classic Potato Chips". CalorieKing. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
^ "Calories in Ham And Cheese Sandwich". Retrieved 22 May 2014.
^ "Green Power Lacks the Energy Density to Run Our Civilization, LENR Might Provide It." LENR & Cold Fusion News. N.p., 24 July 2014. Web.
^ Jeong, Goojin, et al. "Nanotechnology enabled rechargeable Li–SO 2 batteries: another approach towards post-lithium-ion battery systems." Energy & Environmental Science 8.11 (2015): 3173-3180.
^ "Panasonic Develops New Higher-Capacity 18650 Li-Ion Cells." Green Car Congress. N.p., 25 Dec. 2009. Web.
^ Stura, Enrico, and Claudio Nicolini. "New nanomaterials for light weight lithium batteries." Analytica chimica acta 568.1 (2006): 57-64.
^ "Energy Density of Coal - Hypertextbook." The Energy Density of Coal. N.p., 2003. Web.
^ "Heat Values of Various Fuels - World Nuclear Association." World Nuclear Association. N.p., Sept. 2016. Web.
^ "Overview of Storage Development DOE Hydrogen Program." Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. N.p., May 2000. Web.
^ Wong, Kaufui Vincent and Dia, Sarah, “Nanotechnology in Batteries.” ASME J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2016.
^ "Supply of Uranium". world-nuclear.org. 2014-10-08. Retrieved 2015-06-13.
^ "Facts from Cohen". Formal.stanford.edu. 2007-01-26. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ "U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) - Annual Energy Review". Eia.doe.gov. 2009-06-26. Archived from the original on 2010-05-06. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ Ionescu-Zanetti, C.; et., al. (2005). "Nanogap capacitors: Sensitivity to sample permittivity changes". 99 (2). Bibcode:2006JAP....99b4305I. doi:10.1063/1.2161818.
^ Naoi, K.; et., al. (2013). "New generation "nanohybrid supercapacitor"". Accounts of Chemical Research. doi:10.1021/ar200308h.
^ Hubler, A.; Osuagwu, O. (2010). "Digital quantum batteries: Energy and information storage in nanovacuum tube arrays". Complexity. 15 (5). doi:10.1002/cplx.20306.
^ Lyon, D.; et., al. (2013). "Gap size dependence of the dielectric strength in nano vacuum gaps". : IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation. 2 (4). doi:10.1109/TDEI.2013.6571470.
^ abc College of the Desert, “Module 1, Hydrogen Properties”, Revision 0, December 2001 Hydrogen Properties. Retrieved 2014-06-08.
^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997), Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed) (page 164)
^ "Boron: A Better Energy Carrier than Hydrogen? (28 February 2009)". Eagle.ca. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ abcd Envestra Limited. Natural Gas Archived 2008-10-10 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 2008-10-05.
^ abcde IOR Energy. List of common conversion factors (Engineering conversion factors). Retrieved 2008-10-05.
^ abcde Paul A. Kittle, Ph.D. "ALTERNATE DAILY COVER MATERIALS AND SUBTITLE D - THE SELECTION TECHNIQUE" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-01-25.
^ "537.PDF" (PDF). June 1993. Retrieved 2012-01-25.
^ "Energy Density of Aviation Fuel". Hypertextbook.com. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ Román-Leshkov, Yuriy; Barrett, Christopher J.; Liu, Zhen Y.; Dumesic, James A. (21 June 2007). "Production of dimethylfuran for liquid fuels from biomass-derived carbohydrates". Nature. 447 (7147): 982–985. Bibcode:2007Natur.447..982R. doi:10.1038/nature05923. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
^ Justin Lemire-Elmore (2004-04-13). "The Energy Cost of Electric and Human-Powered Bicycles" (PDF). p. 5. Retrieved 2009-02-26.properly trained athlete will have efficiencies of 22 to 26%
^ ab Fisher, Juliya (2003). "Energy Density of Coal". The Physics Factbook. Retrieved 2006-08-25.
^ Silicon as an intermediary between renewable energy and hydrogen
^ "Elite_bloc.indd" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-15. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ "Biomass Energy Foundation: Fuel Densities". Woodgas.com. Archived from the original on 2010-01-10. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ "Bord na Mona, Peat for Energy" (PDF). Bnm.ie. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-11-19. Retrieved 2012-01-25.
^ Justin Lemire-Elmor (April 13, 2004). "The Energy Cost of Electric and Human-Powered Bicycle" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-01-25.
^ "energy buffers". Home.hccnet.nl. Retrieved 2010-05-07.
^ Anne Wignall and Terry Wales. Chemistry 12 Workbook, page 138 Archived 2011-09-13 at the Wayback Machine. Pearson Education NZ
ISBN 978-0-582-54974-6
^ Mitchell, Robert R.; Betar M. Gallant; Carl V. Thompson; Yang Shao-Horn (2011). "All-carbon-nanofiber electrodes for high-energy rechargeable Li–O2 batteries". Energy & Environmental Science. 4: 2952–2958. doi:10.1039/C1EE01496J.
^ David E. Dirkse. energy buffers. "household waste 8..11 MJ/kg"
^ "Technical bulletin on Zinc-air batteries". Duracell. Archived from the original on 2009-01-27. Retrieved 2009-04-21.
^ C. Knowlen, A.T. Mattick, A.P. Bruckner and A. Hertzberg, "High Efficiency Conversion Systems for Liquid Nitrogen Automobiles", Society of Automotive Engineers Inc, 1988.
^ "Hydroelectric Power Generation". www.mpoweruk.com. Woodbank Communications Ltd. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
^ "2.1 Power, discharge, head relationship | River Engineering & Restoration at OSU | Oregon State University". rivers.bee.oregonstate.edu. Retrieved 13 April 2018.Let ε = 0.85, signifying an 85% efficiency rating, typical of an older powerplant.
^ Parravicini, J. (2018). "Thermodynamic potentials in anisotropic and nonlinear dielectrics". Physica B. 541: 54–60. Bibcode:2018PhyB..541...54P. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2018.04.029.
Further reading
The Inflationary Universe: The Quest for a New Theory of Cosmic Origins by Alan H. Guth (1998)
ISBN 0-201-32840-2
Cosmological Inflation and Large-Scale Structure by Andrew R. Liddle, David H. Lyth (2000)
ISBN 0-521-57598-2
- Richard Becker, "Electromagnetic Fields and Interactions", Dover Publications Inc., 1964
External links
^ "Aircraft Fuels." Energy, Technology and the Environment Ed. Attilio Bisio. Vol. 1. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1995. 257–259- "Fuels of the Future for Cars and Trucks" – Dr. James J. Eberhardt – Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, U.S. Department of Energy – 2002 Diesel Engine Emissions Reduction (DEER) Workshop San Diego, California - August 25–29, 2002
"Heat values of various fuels – World Nuclear Association". www.world-nuclear.org. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
"Energy Density of Aviation Fuel – The Physics Factbook". hypertextbook.com. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
"Energy and Energy Types – Springer" (PDF). Retrieved 4 November 2018.

