Transposition of the great vessels
| Transposition of the great vessels | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Illustration of transposition of the great vessels | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries.
Contents
1 Variants
1.1 Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
1.2 Levo-Transposition of the great arteries
1.3 Simple and complex TGV
2 Risk factors
3 Diagnosis
4 Treatment
5 History
6 Additional images
7 See also
8 References
9 External links
Variants
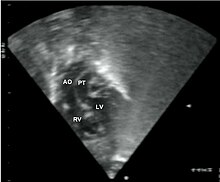
Subcostal echocardiographic view showing discordant ventriculoarterial connections together with the presence of parallel, rather than crossing, great arteries arising from the ventricles.
Transposed vessels can present a large variety of atriovenous, ventriculoarterial and/or arteriovenous discordance. The effects may range from a change in blood pressure to an interruption in circulation, depending on the nature and degree of the misplacement and which vessels are involved.
Although "transposed" literally means "swapped", many types of TGV involve vessels that are in abnormal positions, while not actually being swapped with each other. The terms TGV and TGA are most commonly used in reference to dextro-TGA – in which the arteries are in swapped positions; however, both terms are also commonly used, though to a slightly lesser extent, in reference to levo-TGA – in which both the arteries and the ventricles are swapped; while other defects in this category are almost never referred to by either of these terms.
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
In dextro-Transposition of the great arteries (dextro-TGA) deoxygenated blood from the right heart is pumped immediately through the aorta and circulated to the body and the heart itself, bypassing the lungs altogether, while the left heart pumps oxygenated blood continuously back into the lungs through the pulmonary artery. In effect, two separate "circular" (parallel) circulatory systems are created. It is called a cyanotic congenital heart defect (CHD) because the newborn infant turns blue from lack of oxygen.
Levo-Transposition of the great arteries
Levo-Transposition of the great arteries is an acyanotic heart defect in which the primary arteries are transposed, with the aorta anterior and to the left of the pulmonary artery, and the morphological left and right ventricles with their corresponding atrioventricular valves are also transposed. The systemic and the pulmonary circulation are connected. Complications arise from the fact that the right ventricle, which is adapted for pumping blood into the low pressure pulmonary circulation, is being tasked with pumping blood at a much higher pressure against the high resistance of the systemic circulation.
Simple and complex TGV
In many cases, TGV is accompanied by other heart defects, the most common type being intracardiac shunts such as atrial septal defect including patent foramen ovale, ventricular septal defect, and patent ductus arteriosus. Stenosis, or other defects, of valves and/or vessels may also be present.
When no other heart defects are present it is called 'simple' TGV; when other defects are present it is called 'complex' TGV.
Risk factors
Preexisting diabetes mellitus of a pregnant mother is a risk factor that has been described for the fetus having TGV.[1]

X-ray showing characteristic finding in case of Transposition of the great vessels which is called egg on side sign
Diagnosis
On chest X-ray, transposition of the great vessels typically shows a cardio-mediastinal silhouette appearing as an "egg on a string", wherein in which the enlarged heart represents an egg on its side and the narrowed, atrophic thymus of the superior mediastinum represents the string.[2]
Treatment
For newborns with transposition, prostaglandins can be given to keep the ductus arteriosus open which allows mixing of the otherwise isolated pulmonary and systemic circuits. Thus oxygenated blood that recirculates back to the lungs can mix with blood that circulates throughout the body. The arterial switch operation is the definitive treatment for dextro- transposition. [3]Rarely the arterial switch is not feasible due to particular coronary artery anatomy and an atrial switch operation is preferred.
History
TGV was first described in 1797 by Matthew Baillie.[4]
Additional images

Normal heart anatomy compared to d-TGA

Echocardiography of a complex transposition with a ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis.
Abbreviations: LV and RV=left and right ventricle, PT=pulmonary trunk, VSD=ventricular septal defect, PS=pulmonary stenosis.

Echocardiogram in transposition of the great arteries. This subcostal view shows the left ventricle giving rise to a vessel that bifurcates, which is thus identified as the pulmonary artery.
Abbreviations: RA=right atrium, RV=right ventricle, LV=left ventricle, PT=pulmonary trunk, LPA and RPA=left and right pulmonary artery.
See also
- levo-Transposition of the great arteries
- dextro-Transposition of the great arteries
- Mustard Procedure
References
^ Martins P, Castela E (2008). "Transposition of the great arteries". Orphanet J Rare Dis. 3: 27. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-3-27. PMC 2577629. PMID 18851735..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ Ferguson EC, Krishnamurthy R, Oldham SA (2007). "Classic imaging signs of congenital cardiovascular abnormalities". Radiographics. 27 (5): 1323–34. doi:10.1148/rg.275065148. ISSN 0271-5333. PMID 17848694.
^ Marathe SP, Talwar S. Surgery for transposition of great arteries: A historical perspective. Ann Pediatr Card [serial online] 2015 [cited 2018 Jun 22];8:122-8. Available from: http://www.annalspc.com/text.asp?2015/8/2/122/157025
^ The Morbid Anatomy of Some of the Most Important Parts of the Human Body (1793)
External links
| Classification | D
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
|