Mexican general election, 2018
This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in Spanish. (February 2018) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 63.43% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
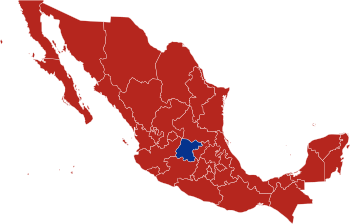 States won by López Obrador in red, Anaya in blue. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mexico |
|---|
 |
This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Mexico |
|
Executive
|
Legislative
|
Judiciary
|
Administrative divisions
|
Elections
|
Political parties
|
Foreign relations |
|
General elections were held in Mexico on 1 July 2018.[1] Voters elected a new President of Mexico to serve a term of five years and ten months (reduced by two months from the constitutional mandate due to a change in the inauguration date as of 2014),[2] 128 members of the Senate for a period of six years and 500 members of the Chamber of Deputies for a period of three years. It was one of the largest election days in Mexican history, with most of the nation's states holding state and local elections on the same day, including nine governorships, with over 3,400 positions subject to elections at all levels of government.[3] It was the most violent campaign Mexico has experienced in recent history, with 130 political figures killed since September 2017.[3]
The incumbent president Enrique Peña Nieto was not constitutionally eligible for a second term. Incumbent members of the legislature are term-limited, thus all members of Congress will be newly elected. As a consequence of the political reform of 2014, the members of the legislature elected in this election will be the first allowed to run for reelection in subsequent elections. The National Electoral Institute (INE) officially declared the new process underway on 8 September 2017.
The presidential election was won by Andrés Manuel López Obrador of the National Regeneration Movement (MORENA), running as the candidate of the Juntos Haremos Historia alliance.[4] This is the first time a candidate won an outright majority (according to official vote counts) since 1988,[5] and the first time that a candidate not from the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) or its predecessors has done so since the Mexican Revolution. This election also marked both the worst electoral defeat suffered by the PRI and the worst electoral defeat for a sitting Mexican government since universal suffrage was adopted in the country in 1917.[a]
Contents
1 Electoral system
2 Presidential candidates
2.1 Por México al Frente
2.2 Todos por México
2.3 Juntos Haremos Historia
2.4 Independents
3 Opinion polls
4 Campaigns
4.1 Timeline
4.1.1 January
4.1.2 February
4.1.3 March
4.1.4 April and May
4.2 Promises and proposals
5 Controversies
5.1 Ballot access requirements
5.2 PRI payments to Cambridge Analytica
5.3 Allegations of foreign intervention
5.4 Possibility of election tampering
5.4.1 Prior PRI election tampering controversies in 2017
6 Results
6.1 President
6.1.1 By state
6.2 Senate
6.2.1 By state
6.3 Chamber of Deputies
6.4 Governorships
6.4.1 Mexico City
6.4.2 Chiapas
6.4.3 Guanajuato
6.4.4 Jalisco
6.4.5 Morelos
6.4.6 Puebla
6.4.7 Tabasco
6.4.8 Veracruz
6.4.9 Yucatán
7 Notes
8 References
9 External links
Electoral system
The country's president is elected by plurality in a single round of voting.[6]
The 500 members of the Chamber of Deputies are elected to three-year terms by two methods; 300 are elected in single-member constituencies by first-past-the-post voting, with the remaining 200 elected from five regional constituencies by proportional representation, with seats allocated using the simple quotient and largest remainder method. No party is allowed to hold more than 300 seats.[7] Members may hold office for up to four consecutive terms.[8]
The 128 members of the Senate are elected to six-year terms, concurrent with the president, and also elected by two methods, with 96 elected in 32 three-member constituencies based on the states and 32 elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation. In the three-member constituencies, two winning candidates shall be allocated to the party receiving the highest number of votes and one seat to the party receiving the second-highest number of votes.[9] Members may hold office for up to two terms.[8]
Presidential candidates
Por México al Frente
(English: "For Mexico to the Front")
The center-right National Action Party and the center-left Party of the Democratic Revolution and Citizens' Movement – which both nominated Andrés Manuel López Obrador in the elections of 2006 and 2012 – formed an alliance for the election, in an effort to defeat both the ruling party, the PRI, and the front-runner Andrés Manuel López Obrador of the National Regeneration Movement.[10][11][12][13][14][13]
On 5 September, the electoral alliance was officially registered with the INE as Frente Ciudadano por México (Citizen Front for Mexico).[14] On 8 December the coalition changed its name to Por México al Frente (Mexico to the Front). The next day, Ricardo Anaya Cortés, president of the PAN, resigned from his position and expressed his intent to be the alliance's candidate.[15][16]
The former first lady Margarita Zavala submitted her resignation from the PAN on 6 October, after being a member for 33 years, and registered as an independent candidate six days later.[17] She sought the presidency through an independent bid, but withdrew on 16 May 2018.
Nominee
Ricardo Anaya Cortés, former president of the National Action Party.
Todos por México
(English: "Everyone for Mexico")
The coalition is composed of the Institutional Revolutionary Party, the Ecologist Green Party of Mexico, and the PANAL. On 9 August 2017, the PRI revised its requirements for presidential candidates, eliminating the requirement that candidates must have 10 years of party membership, and allowing non-party members to lead the party.[18]
This move benefited finance secretary José Antonio Meade Kuribreña, who is not a member of the PRI,[19] as well as education secretary Aurelio Nuño Mayer, whose length of membership was questioned.[18] Meade was considered the favorite, because while the PRI was dogged by scandal and controversy, Meade was personally unaffected.[20]
On 27 November, Meade resigned from cabinet and announced his intention to be the PRI's candidate in the upcoming election.[21] He quickly received the support of President Peña Nieto and PRI-linked institutions such as the CTM union.[22] With no challengers, Meade became the presumptive nominee.[23] On 18 February 2018, the PRI held its convention of delegates, where Meade was formally selected as the party's presidential candidate.[24] Meade is the PRI's first presidential candidate in its almost 90-year history not to be a member of the party.[25][26]
Due to the circumstances of Meade's candidacy, critics compared his selection to the PRI's historical practice of dedazo ("tap of the finger"), where presidents hand-picked their successor.[27][28]
The coalition was initially named Meade Ciudadano por México (English: Citizen Meade for Mexico), until the INE deemed it unconstitutional to include a candidate's name within the coalition's name, on the grounds that the presidential candidate would receive advertising from every piece of campaign advertising of the coalition used for local candidates. The coalition subsequently changed its name to Todos por México (Everyone for Mexico).[29]
Nominee
José Antonio Meade Kuribreña, former Secretary of Foreign Affairs, Secretary of Social Development, and Secretary of Finance and Public Credit during the Peña Nieto administration; Secretary of Finance and Public Credit and Secretary of Energy during the Felipe Calderón administration.
Juntos Haremos Historia
(English: "Together We Will Make History")
The coalition is composed of the National Regeneration Movement (MORENA), the Labor Party, and the Social Encounter Party.[30][31]
On 12 December Andrés Manuel López Obrador registered as the presumptive nominee for MORENA and submitted his resignation as party president. This is López Obrador's third presidential bid; the previous two attempts were with the PRD. After the 2012 presidential election, López Obrador left the PRD to found MORENA. This is MORENA's first presidential election. Joining MORENA in the Juntos Haremos Historia coalition is the left-wing Labor Party and the right-wing Social Encounter Party.[32]
Nominee
Andrés Manuel López Obrador, former Head of Government of Mexico City, 2006 and 2012 presidential candidate.
Independents

Logo for Rodríguez's campaign
For the first time in Mexico's modern democratic history, candidates were allowed to run for the presidency as independents.[33] Several people announced their intention to contest the election as an independent candidate.
Margarita Zavala, a lawyer, former deputy and wife of former president Felipe Calderón, had originally intended to run as the PAN nominee; however, on 6 October, she left the party and launched an independent bid. Explaining her decision, she said that the formation of Por México al Frente meant there would be no internal PAN selection, denying her a chance to be a candidate.[34]Jaime Rodríguez Calderón, the independent governor of Nuevo León, also announced his candidacy,[35] as did Senator Armando Ríos Piter.[36]
The National Indigenous Congress announced on 28 May 2017 the election of María de Jesús Patricio Martínez as their spokeswoman and indigenous representative for the 2018 general election, aiming to obtain an independent candidacy.[37]
Only Zavala gathered enough signatures to appear on the ballot;[38] however, on 10 April the Electoral Court accepted an appeal from Rodríguez and ordered the National Electoral Institute to register him as candidate.[39]
On 16 May Zavala announced she was withdrawing her candidacy.[40]
Opinion polls

Historical trend of voting intentions for the candidates for the Mexican presidency in 2018.
Campaigns
Timeline
January
As in the 2006 and 2012 federal elections, the 2018 campaign featured numerous accusations and attack advertisements directed at the leftist frontrunner candidate Andrés Manuel López Obrador, who contested the elections with the support of his party MORENA. A Red Scare-like campaign was used by the PRI and PAN candidates to convince voters that a López Obrador victory would turn Mexico into "another Venezuela".[41][42]
In a speech, PRI president Enrique Ochoa Reza said that "if the people from MORENA like Venezuela so much, they should just go and live there".[43] The PRI was believed to have hired Venezuelan right-wing political strategist JJ Rendón to work in their campaign, as he stated in January that he would do "everything within the law to prevent López Obrador from becoming President"; Rendón had previously worked for the PRI during Peña Nieto's 2012 presidential campaign.[44]
In January, former president Felipe Calderón shared a video on via social media, in which a Venezuelan citizen living in Mexico warned voters not to vote for López Obrador, as he would put Mexico in the "path to ruin" like Chavismo had done in her country. It later surfaced that the woman, whose name is Carmen Martilez, is an actress who previously had uploaded a video in which she asked for street vendors to be "exterminated".[45]
That same month, the PRI began to claim that López Obrador's campaign was supported by "Venezuelan and Russian interests". López Obrador dismissed the accusations and later joked about them, calling himself "Andrés Manuelovich".[46][47]
Later in January, citizens across the country received phone calls originating in the city of Puebla, in which a recorded message warned them not to vote for López Obrador because he supposedly agreed to sell Mexico's oil to "the Russians". The MORENA representative in Puebla asked for an investigation into the phone calls.[48][49] In March, telephone company Axtel traced the number that made the calls, revealing it was a number that the government of Puebla (whose governor is from the PAN) controlled. Puebla's government denied the accusations.[50] Also in January, López Obrador uploaded a video via social media asking president Peña Nieto and PRI president Ochoa Reza to "calm down", and advised them to take some "López Obradordipine".[51]
A jingle entitled Movimiento Naranja, which was recorded for the political party Movimiento Ciudadano (which is part of the Por México al Frente coalition, along with the PAN and the PRD) and performed by an indigenous child called Yuawi, became viral and Yuawi turned into a celebrity overnight.[52][53]
Drawing on its success, the pre-candidate for the Frente, Ricardo Anaya recorded a video in which he performed the song with Yuawi.[54]
PRI candidate José Antonio Meade was accused of plagiarism when it was noted that one of his ads, in which he criticized a "populist" speech on TV, was identical to an ad that was used by Justin Trudeau when he became leader of the Liberal Party of Canada in 2013.[55]
February
Later in February, the PRI's Enrique Ochoa Reza tweeted that PRI politicians who defected to MORENA as Prietos que no aprietan (Dark-skinned people who can't get a hold) while trying to make a pun on the word PRI-etos (because morena is a synonym for prieto). The expression was criticized, and Ochoa Reza quickly deleted the tweet as it was interpreted to be racist.[56]
Aristegui Noticias published that Ochoa Reza apologized, and also criticized the insensitive expression, additionally commenting that the part que ya no aprietan (who cannot hold) could also be interpreted as misogynistic due to being a double entendre referring to women in relation to the number of sexual relations they have had in their lifetime. Ochoa Reza's tweet apologized to dark-skinned people but not to women.[57] Later Sinembargo.mx revealed that José Antonio Meade justified Enrique Ochoa's usage of the expression, by saying: uno se excede y es natural (English: one gets-ahead-of-themselves and it is natural) and saying that his quick apology talked positively about him.[58]
March
In March, the Attorney General of the Republic (PGR) started an official investigation into money-laundering allegations against Ricardo Anaya. During the investigation, Santiago Nieto, the ex-chief of FEPADE (the prosecutor's office that focuses on electoral violations) was controversially removed from his job in October 2017, coincidentally right after starting an investigation regarding illicit campaign money from the 2012 presidential campaign that allegedly was received by Peña Nieto and by the future president of Pemex, Emilio Lozoya, from the Brazilian conglomerate Odebrecht.
The ex-chief of FEPADE said that the accusations against Anaya were minor in comparison to Odebretch and Peña Nieto scandal, adding also the same opinion about the money lost by Secretariat of Social Development, to corrupt governors from the PRI such as Javier Duarte, all while José Antonio Meade was the man in charge of the Secretariat of Social Development. The scandal is known as La Estafa Maestra (The Master Robbery), and about 435 million pesos were lost.[59] The same week the PRI legislators were criticized for voting for stopping the investigation of Odebretch against the wishes of Mexican people and organizations campaigning against corruption such as Mexicanos contra la corrupción (Mexicans against corruption).[60] The investigation about Odebretch against the Pemex leader at the time, Lozoya, was legally stopped after a judge controversially ordered it days after.[61]
Santiago Nieto said that the PGR was being used by Peña Nieto's government to tamper with elections and benefit Meade by removing Anaya from the race, complaining that it was a politically motivated use of law-enforcement agencies, which had made more efforts to investigate Anaya in a month than towards investigating Peña Nieto's Odebretch money and Meade's lost Secretariat of Social Development funds over the last six years. Santiago Nieto said the PGR and FEPADE were only attacking the rivals of the PRI, and the investigating organizations were not being neutral.[62]
In an interview with The Wall Street Journal, Santiago Nieto would later reveal that Peña Nieto's government tried to bribe him to keep him silent, which he refused saying, "Sorry, but I can't receive any money from Peña Nieto." He received menacing phone messages stating: "Death follows you" and "Words of advice: stay out of Trouble", and as a consequence, he feared for the safety of his, and his family's lives.[63]
Additionally as of 2018, it should be noted, that many of the politicians of the PRI political party who supported Peña Nieto during his presidential campaign would be later declared criminals by the Mexican government (some already elected, while others were campaigning concurrently with Peña Nieto, and would be elected),[64][65][66] near the end of Peña Nieto's time as president.
A total of 22 state ex-governors, all members from the PRI, were accused of misuse of public funds and misdirection of money (with some money speculated to have been directed to the PRI); only five were sent to jail, with PGR receiving criticism for not investigating further.[67] Among the most prominent criminals were: Tomás Yarrington from Tamaulipas (along his predecessor Eugenio Hernández Flores), Javier Duarte from Veracruz,[68]César Duarte Jáquez from Chihuahua[69] (no family relation between the two Duartes), and Roberto Borge from Quintana Roo, along their unknown multiple allies who enabled their corruption. Although Peña Nieto was not found to be their ally, by being part of the same political party, there were severely negative consequences to Peña Nieto's image as president, as well as of the PRI.[70]
Also, while not a member of the PRI at the time, Meade's image also received damage, because much of the money was lost while he was in charge of the Secretariat of Social Development, the government ministry that supervises the resources received by each state.[71]
Despite the overwhelming evidence against César Duarte, in March 2018 the PGR found him innocent of any crime. The successor governor Javier Corral from the PAN, who previously fought against the Televisa law, gave a similar opinion to Santiago Nieto, saying the PGR was being used to protect the allies of Peña Nieto and the PRI, and attack their rivals.[72]
López Obrador said that failure to take action against Duarte was one of the main reasons why Mexicans had lost their faith in the PRI, saying the few ex-governors that were declared criminals were only to a pretense of concern.[73]
April and May
After, Meade decided to change his strategy; and due to his poor reception, Ochoa Reza left his position as president of the PRI on 2 May.[74]
On 16 May, Margarita Zavala suspended her presidential campaign.[75]
Santiago Nieto decided to join AMLO's campaign, with both promising to continue the investigation into the alleged scandal involving Peña Nieto, the PRI and Odebretch.[76]
Meanwhile, César Duarte disappeared before being incarcerated, and was subsequently declared a fugitive from justice by the PGR.[77]
More than 130 political figures were killed from when the campaign began in September 2017 until July 2018.[3]
Promises and proposals
López Obrador promised to end many of the benefits received by ex-presidents, particularly the lifelong pension they receive.[78] He added that he would redirect the money saved to be used to help senior citizens.[79] Zavala said she would also attempt to end the practice, though she had not decided how to use the money saved, while Meade and Anaya said they would keep the practice going.[80]
Anaya promised to implement a basic income for Mexican citizens,[81] Anaya said Nobel prize-winning economist Milton Friedman supported the idea. While well received, El Economista criticized how Anaya announced it, and called the idea populist.[82]
Meade proposed to create an office that would track the unique needs of each individual citizen, in what he would call Registro Único de Necesidades de Cada Persona (Unique Register of the Necessities of Each Person). Citizens on social media mocked the idea as absurd and impossible to develop, comparing it to writing letters to Santa Claus or just plainly asking for miracles.[83][84]
Meade has supported Peña Nieto's energy reforms, saying that "everyone wins with the gasolinazo", and announcing that if he won he intended to continue it.[85]
López Obrador promised to end the gasolinazos by building two new fuel refineries, which would allow more petroleum to be processed into gasoline domestically, thus lowering the price by not outsourcing the refining to other countries.[86]
Anaya promised to investigate and do everything to make sure President Peña Nieto is sent to jail for his aforementioned multiple presidential scandals, with López Obrador agreeing and suggesting to up the ante by also investigating every living former president.[87]
On 26 January, López Obrador accused the International Monetary Fund of being an accomplice to corruption in Mexican politics and claimed that its policies are in part responsible for poverty, unemployment, and violence in the country. López Obrador promised that if he won the presidency, Mexico will follow "its own agenda".[88]
López Obrador called for a change in security strategy and offered the controversial proposal of giving amnesty for drug dealers as a way to combat the drug cartels.[89]
During a debate in April, Rodríguez Calderón said "We have to cut off the hands of those who rob (in public service). It's that simple." He later explained that it was intended to be applied to both criminals and government functionaries involved in acts of corruption citing the application of this measure in Saudi Arabia as an example to reduce corruption and violence. Rodríguez Calderón was trending ahead of the other candidates on Twitter during the debate.[90]
Rodríguez Calderón later proposed to bring back the death penalty (currently constitutionally abolished in Mexico and enforced for the last time in 1961) for drug traffickers, hijackers, infanticides and serial killers.[91]
Controversies
Ballot access requirements
The candidate put forward by the National Indigenous Congress and the Zapatista Army of National Liberation, María de Jesús Patricio Martínez (Marichuy), alleged that the process for collecting signatures to attain ballot access unfairly benefits the rich. Marichuy said, "the INE made a list of telephone makes and models so that you must have at a minimum an Android 5.0 operating system or higher and so many hours to begin with the download of the applications in the devices, we find that the list is not true; we find brands that are not included in the list and of those that are included they don’t all work. The download is tedious and can take hours." The INE declared each signature registration would take 4.3 minutes, but each actual signature registration has taken up to 16 hours, or more. 'With these "classist, racist and excluding measures," Marichuy said, you realize "that this electoral system is not made for those peoples below that govern ourselves and that the laws and institutions of the State are made for those above, for the capitalists and their corrupt political class, resulting in a big simulation." Ultimately she was not able to obtain ballot access. [92]
PRI payments to Cambridge Analytica
After the Facebook–Cambridge Analytica data scandal, in April 2018, Forbes published information from the British news program Channel 4 News that had mentioned the existence of proof revealing ties between the PRI and Cambridge Analytica, suggesting a modus operandi similar to the one in the United States. The info said they worked together at least until January.[93][94][95]
An investigation was requested.[96]The New York Times obtained the 57 page proposal of Cambridge Analytica's proposed collaboration strategy to benefit the PRI by hurting MORENA's candidate Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador; the political party rejected the offer but still paid Cambridge Analytica to not help the other candidates.[97]
Allegations of foreign intervention
In April 2017, the US Secretary of Homeland Security, John F. Kelly, stated that the election of a left-wing president in Mexico "would not be good for America or Mexico". The statement was widely believed to be a reference to López Obrador, the leftist, frontrunner candidate, and created controversy in Mexico, as it seemed to be an attempt to influence the election against him.[98][99][100]
In December 2017, US National Security Advisor H. R. McMaster claimed that Russia had launched a campaign to "influence Mexico’s 2018 presidential election and stir up division", without defining the methods of the supposed meddling, or indicating which would be the candidate favored by the Kremlin. The Russian government has denied the claims.[101]PRI president Enrique Ochoa Reza claimed that "Russian and Venezuelan interests" are supporting López Obrador's campaign.[102]
López Obrador responded that Ochoa's declarations are part of a smear campaign against him,[44] and later posted a video via social media, where he joked about the claims and called himself "Andres Manuelovich".[46][47]
Guatemalan right-wing commentator Gloria Álvarez embarked on a tour through Mexico, calling López Obrador a "dangerous populist" and urging citizens not to vote for him. She was invited to a PAN legislators assembly on 31 January, where she criticized the alliance with the PRD, which she called "a party just like MORENA".[103][104]
US Senators Bob Menendez and Marco Rubio asked US Secretary of State Rex Tillerson to "fight Russian meddling" in the Mexican elections.[105] On 2 February during a summit in Mexico, Tillerson stated that Mexico should "beware the Russian interference".[106] Dr. Tony Payan, director of the Mexico Center at Rice University noted that there was no evidence of actual Russian tampering in the Mexican electoral process, and considered the accusations "absurd" given that the Trump administration "will not admit Russia interfered in the US election".[107]
Possibility of election tampering
Bloomberg warned about the possibility of the PRI committing electoral fraud, with Tony Payan, director of the Mexico Center at Rice University’s Baker Institute in Houston, United States, suggesting that both vote buyout and computer hackings were possible and citing irregularities in the 1988 electoral process. Bloomberg's article also suggested Meade could be receiving unfair help from the over-budget amounts of money spent on publicity by incumbent president Enrique Peña Nieto.[108]
Additionally, Meade spent more money on pre-campaign efforts than López Obrador and Anaya together, while failing to report where his funds came from; in contrast, López Obrador has attended the most events while spending the least money and successfully reported better than his rivals where he obtained the resources to pay for those events.[109]
Prior PRI election tampering controversies in 2017
During 2017, the PRI had faced allegations of electoral fraud concerning the election of Peña Nieto's cousin Alfredo del Mazo Maza as Governor of the state of Mexico. Despite the official vote results given by the INE (Electoral National Institute) giving the win to del Mazo, the election was marred by irregularities including reports of vote-buying,[110] spending beyond legal campaign finance limits,[111] and electoral counts that gave del Mazo extra votes that awarded the election to him.[112] In November 2017, left-wing magazine Proceso published an article accusing the PRI of breaking at least 16 state laws during the elections, which were denounced 619 times. They said that all of them were broken in order to favor del Mazo during the election.[113]
Results
President
López Obrador won the election on 1 July 2018 with over 50% of the popular vote. In terms of states won, López Obrador won in a landslide, carrying 31 out of 32 of the country's states,[5] the most states won by a candidate since Ernesto Zedillo won every state in the 1994 election.
Around 30 minutes after polls closed in the country's north-west, José Antonio Meade, speaking at a news conference from PRI headquarters, conceded defeat and wished López Obrador "every success".[114][115]
Ricardo Anaya also conceded defeat within an hour of the polls closing,[116][117]
and independent candidate Jaime Rodríguez Calderón recognized López Obrador's victory shortly afterward.[118]
The results of the INE's official quick count were announced around midnight Mexico City time. It reported a turnout of around 63%, with the following approximate results for the candidates: López Obrador, 53%; Anaya, 22%; Meade, 16%; and Rodríguez Calderón, 5%. This is the first time since the (controversial) 1988 election that a presidential candidate was elected with an absolute majority (50%+1) of the votes cast.[119]
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrés Manuel López Obrador | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 30,113,483 | 53.19 | |
| Ricardo Anaya | National Action Party | Por México al Frente | 12,610,120 | 22.28 | |
| José Antonio Meade | Institutional Revolutionary Party | Todos por México | 9,289,853 | 16.41 | |
| Jaime Rodríguez Calderón | Independent | None | 2,961,732 | 5.23 | |
Margarita Zavala[b] | Independent | None | 32,743 | 0.06 | |
| Write-in votes | 31,982 | 0.06 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 1,571,114 | 2.78 | |||
| Total | 56,611,027 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 89,994,039 | 63.43 | |||
| Source: INE | |||||
By state
State | Anaya | Meade | López Obrador | Zavala[b] | Rodríguez | Write-ins | Invalid/blank votes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Aguascalientes | 178,988 | 103,639 | 222,528 | 547 | 40,299 | 391 | 14,714 |
| Baja California | 275,503 | 124,225 | 918,939 | 479 | 89,823 | 1,252 | 28,201 |
| Baja California Sur | 56,794 | 28,202 | 193,842 | 404 | 16,766 | 235 | 6,645 |
| Campeche | 54,417 | 96,584 | 275,262 | 209 | 11,194 | 146 | 11,735 |
Coahuila | 307,590 | 358,279 | 609,362 | 730 | 71,051 | 437 | 24,367 |
Colima | 56,428 | 62,004 | 197,316 | 346 | 15,753 | 200 | 9,062 |
Chiapas | 198,117 | 562,863 | 1,485,699 | 1,697 | 39,607 | 580 | 137,087 |
| Chihuahua | 425,919 | 240,725 | 643,652 | 1,604 | 132,242 | 1,717 | 48,846 |
Mexico City | 1,292,623 | 652,073 | 3,118,478 | 3,054 | 223,261 | 4,793 | 111,586 |
| Durango | 187,947 | 141,291 | 340,829 | 636 | 46,009 | 215 | 16,788 |
| Guanajuato | 940,133 | 381,692 | 707,222 | 1,655 | 223,214 | 1,859 | 69,232 |
| Guerrero | 217,838 | 285,799 | 1,018,163 | 277 | 24,531 | 362 | 66,168 |
| Hidalgo | 188,028 | 257,548 | 850,863 | 473 | 59,630 | 454 | 37,916 |
| Jalisco | 1,179,300 | 509,157 | 1,461,348 | 3,152 | 246,924 | 2,954 | 96,988 |
| México | 1,549,824 | 1,548,662 | 4,373,267 | 3,092 | 383,684 | 4,653 | 176,978 |
| Michoacán | 443,805 | 335,854 | 991,154 | 1,176 | 122,469 | 1,097 | 85,400 |
| Morelos | 142,553 | 99,506 | 638,689 | 680 | 60,083 | 510 | 26,169 |
| Nayarit | 79,818 | 66,447 | 315,816 | 280 | 10,382 | 183 | 11,750 |
| Nuevo León | 703,866 | 315,379 | 748,104 | 2,000 | 360,050 | 1,931 | 47,432 |
| Oaxaca | 221,686 | 342,108 | 1,260,562 | 931 | 39,020 | 548 | 64,602 |
| Puebla | 618,397 | 490,737 | 1,754,596 | 1,562 | 113,461 | 1,509 | 102,525 |
| Querétaro | 347,664 | 150,927 | 424,162 | 1,347 | 72,905 | 855 | 27,501 |
| Quintana Roo | 116,031 | 76,758 | 488,434 | 361 | 29,441 | 424 | 16,207 |
| San Luis Potosí | 334,763 | 260,211 | 527,546 | 717 | 82,956 | 677 | 51,722 |
| Sinaloa | 163,956 | 234,416 | 834,001 | 475 | 29,173 | 470 | 31,809 |
| Sonora | 167,273 | 181,059 | 651,806 | 858 | 63,800 | 505 | 26,366 |
| Tabasco | 91,342 | 107,538 | 961,710 | 378 | 9,749 | 279 | 29,849 |
| Tamaulipas | 475,201 | 228,386 | 786,210 | 1,143 | 110,246 | 531 | 33,933 |
| Tlaxcala | 66,729 | 74,744 | 433,127 | 213 | 25,941 | 276 | 12,392 |
| Veracruz | 1,050,599 | 471,313 | 2,059,209 | 1,224 | 132,737 | 1,307 | 98,061 |
| Yucatán | 320,144 | 324,055 | 455,216 | 384 | 39,111 | 333 | 25,509 |
| Zacatecas | 156,844 | 177,672 | 366,371 | 659 | 36,220 | 299 | 23,574 |
| Mexicans living abroad | 26,344 | 4,613 | 63,863 | 0 | 1,868 | 269 | 1,513 |
| Total | 12,610,120 | 9,289,853 | 30,113,483 | 32,743 | 2,961,732 | 31,982 | 1,571,114 |
Senate
| Party | Constituency | Proportional | Total seats | +/– | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | ||||
| National Regeneration Movement | 661,068 | 1.18 | 2 | 21,261,577 | 37.50 | 13 | 55 | New | |
| National Action Party | 600,423 | 1.07 | 1 | 9,971,804 | 17.59 | 6 | 23 | –15 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 3,855,984 | 6.86 | 0 | 9,013,658 | 15.90 | 6 | 13 | –44 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 96,393 | 0.17 | 0 | 2,984,861 | 5.27 | 2 | 8 | –15 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 570,774 | 1.01 | 2 | 2,654,452 | 4.68 | 2 | 7 | +6 | |
| Ecologist Green Party | 1,198,011 | 2.13 | 0 | 2,528,175 | 4.46 | 2 | 7 | +3 | |
| Labor Party | 51,260 | 0.09 | 0 | 2,164,442 | 3.82 | 1 | 6 | +2 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 28,878 | 0.05 | 0 | 1,320,559 | 2.33 | 0 | 8 | New | |
| New Alliance Party | 593,507 | 1.06 | 0 | 1,307,015 | 2.31 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
MORENA–PT–PES[a] | 23,754,422 | 42.24 | 53 | – | – | – | – | – | |
PAN–PRD–MC[b] | 14,222,046 | 25.29 | 25 | – | – | – | – | – | |
PRI–PVEM–PNA[c] | 7,145,869 | 12.71 | 13 | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Independents | 1,109,149 | 1.97 | – | 1,109,149 | 1.97 | – | 0 | 0 | |
| Write-ins | 30,568 | 0.05 | – | 31,820 | 0.06 | – | – | – | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 2,319,489 | 4.12 | – | 2,344,357 | 4.14 | – | – | – | |
| Total | 56,237,841 | 100 | 96 | 56,691,869 | 100 | 32 | 128 | 0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 89,994,039 | 62.49 | – | 89,994,039 | 63.52 | – | – | – | |
| Source: INE | |||||||||
a Of the 53 seats won by the MORENA-PT–PES alliance, 40 were taken by MORENA, 8 by the PES, and 5 by the PT
b Of the 25 seats won by the PAN–PRD–MC alliance, 16 were taken by the PAN, 6 by the PRD, and 3 by the MC
c Of the 13 seats won by the PRI–PVEM–PNA alliance, 7 were taken by the PRI, 5 by the PVEM, and 1 by the PNA


By state
State | Write-ins | Invalid/blank votes | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Aguascalientes | 198,362 | 159,219 | 144,216 | 18,395 | 14,205 | 396 | 20,504 | ||||||||
Baja California | 337,706 | 824,241 | 148,221 | 44,495 | 29,501 | 1,317 | 42,556 | ||||||||
Baja California Sur | 83,818 | 144,969 | 24,076 | 10,969 | 7,940 | 14,740 | 203 | 10,170 | |||||||
Campeche | 88,654 | 204,663 | 134,648 | 134 | 15,672 | ||||||||||
Chiapas | 237,732 | 1,158,463 | 707,648 | 98,459 | 1,394 | 194,827 | |||||||||
Chihuahua | 449,436 | 540,334 | 326,675 | 56,602 | 43,788 | 1,267 | 73,224 | ||||||||
Coahuila | 391,871 | 493,462 | 442,448 | 429 | 34,067 | ||||||||||
Colima | 77,594 | 147,042 | 97,982 | 192 | 12,247 | ||||||||||
Mexico City | 1,556,967 | 2,766,612 | 521,619 | 245,030 | 92,033 | 4,520 | 204,974 | ||||||||
Durango | 222,385 | 283,487 | 156,448 | 26,516 | 14,559 | 290 | 25,609 | ||||||||
Guanajuato | 1,015,901 | 592,822 | 322,681 | 190,372 | 71,543 | 1,709 | 111,975 | ||||||||
Guerrero | 357,786 | 764,328 | 367,618 | 20,801 | 709 | 85,359 | |||||||||
Hidalgo | 200,958 | 375,202 | 661,068 | 51,260 | 28,878 | 519 | 68,665 | ||||||||
Jalisco | 1,150,974 | 839,036 | 423,452 | 119,961 | 63,468 | 761,812 | 1,665 | 121,962 | |||||||
México | 1,981,671 | 3,842,212 | 1,944,697 | 4,186 | 246,048 | ||||||||||
Michoacán | 572,436 | 743,271 | 339,778 | 136,907 | 46,494 | 1,274 | 127,166 | ||||||||
Morelos | 489,871 | 193,595 | 89,195 | 79,681 | 44,415 | 802 | 58,202 | ||||||||
Nayarit | 105,395 | 267,757 | 68,231 | 11,050 | 10,252 | 188 | 17,340 | ||||||||
Nuevo León | 471,746 | 511,228 | 16,712 | 526,359 | 331,315 | 83,596 | 58,823 | 105,422 | 1,104 | 66,965 | |||||
Oaxaca | 302,631 | 1,088,347 | 438,077 | 548 | 87,440 | ||||||||||
Puebla | 776,758 | 1,440,489 | 467,783 | 133,596 | 82,077 | 1,356 | 157,416 | ||||||||
Querétaro | 389,334 | 354,517 | 147,062 | 41,067 | 21,249 | 767 | 48,819 | ||||||||
Quintana Roo | 147,478 | 427,700 | 112,859 | 742 | 27,269 | ||||||||||
San Luis Potosí | 428,815 | 379,627 | 354,927 | 981 | 82,140 | ||||||||||
Sinaloa | 243,630 | 604,603 | 306,995 | 93,894 | 455 | 37,118 | |||||||||
Sonora | 236,439 | 510,041 | 301,192 | 383 | 36,423 | ||||||||||
Tabasco | 149,677 | 809,074 | 140,184 | 41,569 | 12,095 | 380 | 41,790 | ||||||||
Tamaulipas | 605,418 | 610,306 | 294,243 | 37,886 | 25,480 | 585 | 48,518 | ||||||||
Tlaxcala | 107,944 | 357,345 | 106,257 | 14,021 | 461 | 24,715 | |||||||||
Veracruz | 1,261,288 | 1,820,499 | 576,857 | 1,084 | 126,420 | ||||||||||
Yucatán | 383,054 | 305,564 | 428,056 | 277 | 32,527 | ||||||||||
Zacatecas | 157,934 | 313,175 | 254,811 | 251 | 31,632 | ||||||||||
Total | 14,222,046 | 23,754,422 | 7,145,869 | 600,423 | 96,393 | 570,774 | 3,855,984 | 1,198,011 | 593,507 | 661,068 | 51,260 | 28,878 | 1,109,149 | 30,568 | 2,319,489 |
Chamber of Deputies
| Party | District | Proportional | Total seats | +/– | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Seats | Votes | % | Seats | ||||
| National Regeneration Movement | 709,840 | 1.27 | 8 | 20,972,573 | 37.25 | 84 | 189 | +154 | |
| National Action Party | 697,595 | 1.25 | 5 | 10,096,588 | 17.93 | 41 | 83 | –25 | |
| Institutional Revolutionary Party | 4,351,824 | 7.78 | 1 | 9,310,523 | 16.54 | 38 | 45 | –158 | |
| Party of the Democratic Revolution | 124,808 | 0.22 | 0 | 2,967,969 | 5.27 | 12 | 21 | –35 | |
| Ecologist Green Party | 1,429,802 | 2.55 | 0 | 2,695,405 | 4.79 | 11 | 16 | –31 | |
| Citizens' Movement | 268,876 | 0.48 | 0 | 2,485,198 | 4.41 | 10 | 27 | +1 | |
| Labor Party | 67,429 | 0.12 | 0 | 2,211,753 | 3.93 | 4 | 61 | +55 | |
| New Alliance Party | 705,432 | 1.26 | 0 | 1,391,376 | 2.47 | 0 | 2 | –8 | |
| Social Encounter Party | 54,906 | 0.10 | 0 | 1,353,941 | 2.40 | 0 | 56 | +48 | |
MORENA–PT–PES[a] | 23,513,132 | 42.01 | 210 | – | – | – | – | – | |
PAN–PRD–MC[b] | 14,381,872 | 25.70 | 63 | – | – | – | – | – | |
PRI–PVEM–PNA[c] | 6,862,372 | 12.26 | 13 | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Independents | 539,347 | 0.96 | 0 | 539,347 | 0.96 | 0 | 0 | –1 | |
| Write-ins | 32,625 | 0.06 | – | 32,959 | 0.06 | – | – | – | |
| Invalid/blank votes | 2,227,573 | 3.98 | – | 2,242,615 | 3.98 | – | – | – | |
| Total | 55,967,433 | 100 | 300 | 56,300,247 | 100 | 200 | 500 | 0 | |
| Registered voters/turnout | 89,994,039 | 62.20 | – | 89,994,039 | 63.21 | – | – | – | |
| Source: INE | |||||||||
a Of the 210 seats won by the MORENA-PT–PES alliance, 97 were taken by MORENA, 57 by the PT, and 56 by the PES
b Of the 63 seats won by the PAN–PRD–MC alliance, 37 were taken by the PAN, 17 by the MC, and 9 by the PRD
c Of the 13 seats won by the PRI–PVEM–PNA alliance, 6 were taken by the PRI, 5 by the PVEM, and 2 by the PNA


Governorships
Mexico City
- Election for Head of Government of Mexico City
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Claudia Sheinbaum Pardo | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 2,537,454 | 47.05 | |
Alejandra Barrales | Party of the Democratic Revolution | Por México al Frente | 1,673,015 | 31.02 | |
Mikel Arriola Peñalosa | Institutional Revolutionary Party | None | 691,772 | 15.30 | |
| Mariana Boy Tamborrell | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | None | 206,942 | 3.83 | |
| Lorena Osornio | Independent | None | 64,591 | 1.19 | |
| Marco Rascón | Humanist Party | None | 51,676 | 0.95 | |
Purificación Carpinteyro | New Alliance Party | None | 36,105 | 0.66 | |
| Write-ins | 5,727 | 0.11 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 125,605 | 2.33 | |||
Total | 5,392,887 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 7,628,256 | 70.70 | |||
| Source:IECM | |||||
Chiapas
- Election for Governor of Chiapas
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Rutilio Escandón Cadenas | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 922,310 | 39.26 | |
| Fernando Castellanos | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | La Fuerza de Chiapas | 529,508 | 22.54 | |
Roberto Albores Gleason | Institutional Revolutionary Party | Todos por Chiapas | 474,122 | 20.18 | |
José Antonio Aguilar Bodegas | National Action Party | Por Chiapas al Frente | 220,675 | 9.39 | |
| Jesús Alejo Orantes Ruiz | Independent | None | 62,611 | 2.66 | |
| Write-ins | 3,309 | 0.14 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 136,992 | 5.83 | |||
Total | 2,349,527 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 3,549,291 | 66.20 | |||
| Source:IEPC-Chiapas | |||||
Guanajuato
- Election for Governor of Guanajuato
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Diego Sinhué Rodríguez Vallejo | National Action Party | Por Guanajuato al Frente | 1,043,049 | 49.94 | |
| Ricardo Sheffield Padilla | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 553,639 | 24.19 | |
Gerardo Sánchez García | Institutional Revolutionary Party | None | 293,824 | 12.84 | |
| Felipe Camarena | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | None | 157,767 | 6.89 | |
| María Bertha Solórzano | New Alliance Party | None | 66,122 | 2.89 | |
| Write-ins | 1,673 | 0.08 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 72,183 | 3.30 | |||
Total | 2,188,257 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 4,359,531 | 50.19 | |||
| Source:IEEG | |||||
Jalisco
- Election for Governor of Jalisco
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Enrique Alfaro Ramírez | Citizens' Movement | None | 1,354,014 | 39.05 | |
| Carlos Lomelí Bolaños | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 857,011 | 24.71 | |
Miguel Castro Reynoso | Institutional Revolutionary Party | None | 575,744 | 16.60 | |
| Miguel Ángel Martínez Espinosa | National Action Party | None | 369,470 | 10.65 | |
| Salvador Cosío Gaona | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | None | 96,762 | 2.79 | |
| Martha Rosa Araiza Soltero | New Alliance Party | None | 68,597 | 1.98 | |
| Carlos Orozco Santillán | Party of the Democratic Revolution | None | 35,107 | 1.01 | |
| Write-ins | 2,691 | 0.08 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 108,368 | 3.13 | |||
Total | 3,467,764 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 5,904,211 | 58.73 | |||
| Source: IEPC-Jalisco | |||||
Morelos
- Election for Governor of Morelos
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cuauhtémoc Blanco | Social Encounter Party | Juntos Haremos Historia | 501,743 | 52.59 | |
| Víctor Caballero | National Action Party | Por Morelos al Frente | 134,054 | 14.05 | |
| Rodrigo Gayosso | Party of the Democratic Revolution | Juntos por Morelos | 111,198 | 11.66 | |
| Jorge Meade | Institutional Revolutionary Party | None | 57,943 | 6.07 | |
Fidel Demédicis Hidalgo | Independent | None | 45,280 | 4.75 | |
| Nadia Luz Lara | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | None | 35,047 | 3.67 | |
| Alejandro Vera Jiménez | New Alliance Party | None | 21,977 | 2.30 | |
| Mario Rojas Alba | Humanist Party | None | 13,871 | 1.45 | |
| Write-ins | 871 | 0.09 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 32,036 | 3.36 | |||
Total | 954,020 | 100% | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 1,442,857 | 66.12 | |||
| Source:IMPEPAC | |||||
Puebla
- Election for Governor of Puebla
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Martha Erika Alonso Hidalgo | National Action Party | Por Puebla al Frente | 1,153,043 | 38.14 | |
Miguel Barbosa Huerta | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 1,031,043 | 34.10 | |
| Enrique Doger | Institutional Revolutionary Party | None | 555,041 | 18.36 | |
| Michel Chaín | Ecologist Green Party of Mexico | None | 153,456 | 5.08 | |
| Write-ins | 1,947 | 0.06 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 129,023 | 4.27 | |||
Total | 3,023,553 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 4,500,580 | 67.18 | |||
| Source:IEE-Puebla | |||||
Tabasco
- Election for Governor of Tabasco
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Adán Augusto López Hernández | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 601,987 | 61.45 | |
Gerardo Gaudiano Rovirosa | Party of the Democratic Revolution | Por Tabasco al Frente | 189,564 | 19.35 | |
Georgina Trujillo Zentella | Institutional Revolutionary Party | None | 115,164 | 11.75 | |
| Nulls/blanks | 42,134 | 4.30 | |||
Jesús Alí de la Torre | Independent | None | 19,434 | 1.98 | |
| Manuel Paz Ojeda | New Alliance Party | None | 10,371 | 1.05 | |
| Write-ins | 843 | 0.08 | |||
Total | 979,497 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 1,687,618 | 70.06% | |||
| Source:IEPC-Tabasco | |||||
Veracruz
- Election for Governor of Veracruz
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cuitláhuac García Jiménez | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 1,667,239 | 44.03 | |
| Miguel Ángel Yunes Márquez | National Action Party | Por Veracruz al Frente | 1,453,938 | 38.39 | |
José Yunes Zorrilla | Institutional Revolutionary Party | Por un Veracruz Mejor | 528,663 | 13.96 | |
| Miriam González Sheridan | New Alliance Party | None | 36,404 | 0.96 | |
| Write-ins | 784 | 0.02 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 99,893 | 2.64 | |||
Total | 3,786,921 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 5,775,918 | 65.56 | |||
| Source: OPLE-Veracruz | |||||
Yucatán
- Election for Governor of Yucatán
| Candidate | Party | Alliance | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mauricio Vila Dosal | National Action Party | Por Yucatán al Frente | 447,753 | 39.60 | |
Mauricio Sahuí Rivero | Institutional Revolutionary Party | Todos por Yucatán | 407,802 | 36.09 | |
Joaquín Díaz Mena | National Regeneration Movement | Juntos Haremos Historia | 231,330 | 20.46 | |
| Jorge Zavala Castro | Party of the Democratic Revolution | None | 21,968 | 1.94 | |
| Write-ins | 251 | 0.02 | |||
| Nulls/blanks | 21,303 | 1.88 | |||
Total | 1,130,407 | 100% | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 1,544,062 | 73.21 | |||
| Source: IEPAC | |||||
Notes
^ Universal male suffrage was adopted in 1917, while women acquired the right to vote in Federal elections in 1953.
^ ab Dropped out of the race, but votes towards her were counted
References
^ Electoral Calendar Senate of the Republic (in Spanish)
^ Redacción (23 April 2018). "Más allá del debate: corrupción y violencia sin control marcan agenda en la elección mexicana". Sin Embargo. Retrieved 1 July 2018.Seis candidatos a la carrera para ocupar Los Pinos a partir del próximo primero de diciembre por un período de cinco años y 10 meses. (A partir de la Reforma Electora de 2014, el Presidente de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos tomará posesión el 1 de octubre de cada año empezando en 2024 por un período de seis años.)
.mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ abc Benjamin Sveen (2 July 2018). "Mexico's new president Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador is the result of political upheaval". ABC News (Australia).
^ "Mexico election: López Obrador vows profound change after win". BBC News. 2 July 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
^ ab Murray, Christine; Oré, Diego. "Mexican Lopez Obrador wins historic election landslide for left". Reuters. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
^ Election Guide - Mexico IFES
^ Electoral system IPU
^ ab David Agren (31 January 2014). "Mexico ends decades-long ban on re-election". USA Today. Retrieved 31 January 2014.
^ Electoral system Mexican Legislative Election Process IPU
^ "PAN, PRD y MC avalan Frente pero sin definir sus alcances". Retrieved 5 September 2017.
^ "Se confirma el Frente Opositor: PAN, MC y PRD irán en alianza para 2018". DiarioCambio.com.mx (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 September 2017.
^ "El PAN, el PRD y Movimiento Ciudadano constituirán un frente común para 2018". Expansión (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 September 2017.
^ ab "Registran Frente Amplio ante el INE". El Universal (in Spanish). 5 September 2017. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
^ ab "Formalizan PAN, PRD y MC Frente ante INE". www.reforma.com. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
^ "Anaya renunció al PAN, va por candidatura del Frente" (in Spanish). Político MX. 9 September 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
^ "'Todos por México' será el nombre de coalición de Meade". Excelsior (in Spanish). 15 January 2018. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
^ "Zavala renuncia al PAN, buscará candidatura independiente" (in Spanish). Político MX. 6 October 2017. Retrieved 11 December 2017.
^ ab Stargardter, Gabriel (10 August 2017). "Mexico ruling party's reform strengthens president ahead of 2018 vote". Retrieved 7 June 2018.
^
Webber, Jude (2 May 2018). "Mexico's embattled PRI replaces leader ahead of July election". Financial Times.
^ Villegas, Paulina (27 November 2017). "Mexico's Finance Minister Says He'll Run for President". New York Times.
^ Stevenson, Mark (27 November 2017). "Mexico Treasury Secretary announces presidential bid". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
^ Agren, David (27 November 2017). "Mexico is a democracy, but the ghosts of one-party rule live on".
^ Miranda, Kevin (3 December 2018). "José Antonio Meade, oficial precandidato del PRI para 2018". El Debate.
^ "Mexico Picks its Presidential Candidates, AMLO in the Lead". Telesur. 18 February 2018.
^ "Mexico's presidential campaign takes shape, with 3 candidates formally accepting party nominations". Los Angeles Times.
^ "¿Quién es José Antonio Meade? El candidato independiente del PRI". Milenio. Retrieved 29 June 2018.
^ "José Antonio Meade is the PRI's candidate for Mexico's presidency". The Economist. 30 November 2017. Retrieved 7 June 2018.
^ Ramos, Jorge (5 December 2017). "'El Dedazo' Makes a Comeback in Mexico". Splinter. Retrieved 7 June 2018.
^ "INE perfila quitar el nombre de Meade a la coalición del PRI". www.elfinanciero.com.mx. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
"Aprueba PT coalición con Morena en elecciones de 2018". SDPnoticias.com (in Spanish). 25 June 2017. Retrieved 5 September 2017.
^ "PES irá en alianza con Morena para presidencial de 2018". SDPnoticias.com (in Spanish). 26 November 2017. Retrieved 27 November 2017.
^
"López Obrador registra precandidatura y anuncia proyecto de nación" (in Spanish). Excelsior. 13 December 2017. Retrieved 16 January 2018.
^ "Independents stampede into Mexico's presidential election". The Economist. 26 October 2017. Retrieved 15 May 2018.
^ Graham, Dave (6 October 2017). "Mexico ex-first lady leaves opposition party for presidency bid". Reuters. Retrieved 15 May 2018.
^ Hootsen, Jan-Albert (16 October 2016). "'El Bronco,' Mexico's most successful independent, sets sight on 2018 presidency". Fox News. Retrieved 15 May 2018.
^ Badillo, Diego (21 May 2017). "Voy independiente pero no solo: Ríos Piter". El Economista. Archived from the original on 9 February 2018. Retrieved 8 February 2018.
^ Concheiro, Luciano (28 May 2017). "Los pueblos indígenas de México eligen a su vocera e irrumpen en el escenario político (The indigenous peoples of Mexico elect their spokesperson and break into the political scene)". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
^ ""El Bronco" y Ríos Piter, fuera de la boleta electoral". 16 March 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
"El Tribunal Electoral mete a El Bronco en la carrera presidencial con una polémica decisión". El País (in Spanish). 10 April 2018. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
^
"Margarita Zavala renuncia a su candidatura presidencial". Expansión (in Spanish). 16 May 2018. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
^
"La campaña del miedo contra López Obrador". Periodismo Negro (in Spanish). 19 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Las Campañas del miedo". Diario de Yucatán (in Spanish). 11 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Si a los de Morena les gusta Venezuela, que se vayan a vivir allá: Ochoa". Periodismo Negro (in Spanish). 15 November 2017. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ ab "PRI se desmarca del publicista JJ Rendón; López Obrador pide evitar violencia política". Aristegui Noticias (in Spanish). 14 January 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
^ ""Venezolana" que llora y pide no votar por López Obrador, también quiere exterminar vendedores en CdMx". Sin Embargo (in Spanish). 19 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ ab Editorial, Reuters. "'Andres Manuelovich': Mexican leftist laughs off Russia election jabs". Reuters. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ ab "PRI estrena spot sobre "miedo" al "Peje" (Video)". Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Arman campaña contra López Obrador en Puebla; "los rusos vienen a quitarnos nuestro petróleo", dicen en llamadas". Proceso (in Spanish). 31 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Pedirán que se investiguen llamadas telefónicas contra López Obrador". El Sol de Puebla (in Spanish). 31 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Gobierno de Puebla contrató línea telefónica desde donde se atacó a López Obrador; contrato ya venció, responde - Aristegui Noticias". aristeguinoticias.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
"Amlodipino is for whatever ails Peña Nieto". Mexico News Daily. 18 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^
"Movimiento Naranja, la propaganda política que suena hasta en las discotecas". Semana (in Spanish). 20 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^
"'Movimiento Naranja' la pegadiza canción de una campaña política que suena en todas partes". Europa FM (in Spanish). 22 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Yuawi y Anaya se avientan un "palomazo"". Milenio (in Spanish). 23 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Destacan parecido estilo en spot de Meade a uno de Trudeau". SDP Noticias (in Spanish). 18 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Otra de Ochoa Reza: llama 'prietos' a seguidores de López Obrador; lo acusan de racista". 10 February 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Ochoa Reza arremete contra "prietos" que dejan el PRI; lo tachan de racista y se disculpa - Aristegui Noticias". aristeguinoticias.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Meade justifica a Ochoa Reza: el comentario fue "un exceso", dice, pero "uno se excede y es natural"".
^ "Con Robles y Meade hubo desvíos al estilo Estafa Maestra por 540 mdp en Sedesol, revela Auditoría". Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
Pérez, D. M. (8 March 2018). "El PRI bloquea en el Congreso una investigación del 'caso Odebrecht'". Retrieved 9 April 2018 – via elpais.com.
^ "Caso Odebrecht deja detenidos en todo el mundo, menos en México". 2 March 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Por menos que lo que ha hecho la PGR contra Anaya, me removieron a mí: Santiago Nieto - Aristegui Noticias". aristeguinoticias.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
Montes, Juan (14 March 2018). "Ex-Mexican Prosecutor Says He Was Fired to Stymie Corruption Probe". Wsj.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Corrupción envuelve a 11 exgobernadores". 17 April 2017.
^ Malkin, Elisabeth (19 April 2017). "En México se acumulan los gobernadores corruptos, e impunes". Nytimes.com.
^
"Conoce a los 11 exgobernadores más corruptos de México". 17 April 2017.
^ Olvera, Dulce. "Son 22 gobernadores del PRI los acusados de desvíos con EPN; el monto en duda: 258 mil millones".
^ McDonnell, Patrick J. (17 July 2017). "Former governor of Mexico's Veracruz state extradited from Guatemala to face corruption charges" – via LA Times.
^ "Mexico: Ex-governor flees to Texas to evade corruption allegations". Dallas News. 30 March 2017.
^ "PGR e Interpol capturan a Roberto Borge en Panamá". 5 June 2017.
^ "Los desvíos que Meade no vio en Sedesol - Proceso". Proceso.com. 24 February 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Perdonan a Duarte; es cinismo.- Corral". Reforma.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Por acciones como no proceder contra César Duarte, la gente ya no le cree al PRI: López Obrador - Proceso". Proceso.com. 14 March 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Con Meade en la lona, Ochoa Reza deja la presidencia del PRI; entra al relevo Juárez Cisneros - Proceso". 2 May 2018.
^ "Margarita Zavala renuncia a su candidatura". Expansión (in Spanish). 16 May 2018. Retrieved 16 May 2018.
^ "Santiago Nieto se suma a campaña de AMLO". 22 May 2018.
^ "Aseguran 4 ranchos a César Duarte en Belleza, Chihuahua". 28 May 2018.
^ "López Obrador se pronuncia por gobierno austero y sin privilegios". Excelsior.com.mx. 9 March 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "AMLO dice que en caso de ganar las elecciones eliminará pensiones millonarias a ex presidentes".
^ "Margarita Zavala ofrece quitarle la pensión a los ex Presidentes, entre ellos su marido".
^ "Ingreso básico universal, principal propuesta social del Frente: PAN". Eluniversal.com.mx. 26 November 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ Velasco, Armando Regil. "Desmintiendo a Ricardo Anaya". Eleconomista.com.mx. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
"Meade propone un 'Registro Nacional de Necesidades de Cada Persona'; lo tunden en redes". Regeneracion.mx. 18 February 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Meade prometió crear un "Registro Nacional de Necesidades de Cada Persona" y le están lloviendo peticiones". Buzzfeed.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^
Rodríguez, Silvia. "Con 'gasolinazo' ganan nuestros hijos: Meade". Milenio.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Si triunfa Morena bajarán los costos de la gasolina: López Obrador". Milenio.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Pide López Obrador a Ricardo Anaya extender denuncia a expresidentes". Excelsior.com.mx. 10 March 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "El FMI es cómplice de la corrupción en el país: López Obrador" (in Spanish). Excélsior. 26 January 2018.
^ David Agren (3 May 2018). "Amnesty for drug dealers? This Mexico presidential candidate is pushing for forgiveness". USA Today. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
^ "'Cut off hands': Mexican presidential candidate's plan to deter thieves".
^ "Ciudadanos quieren pena de muerte para narcos y asesinos, asegura 'El Bronco'". Reporte Indigo. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
^ "Marichuy denounces INE's system for collecting signatures via cell phone". chiapas-support.org. 22 March 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
^ Staff, Forbes (30 March 2018). "Cambridge Analytica trabajó con el PRI: Channel 4 News • Forbes México". Forbes.com.mx. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ Murillo, Javier. "Cambridge Analytica, sigan la ruta del dinero". Elfinanciero.com.mx. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ Peinado, Fernando; Palomo, Elvira; Galán, Javier (22 March 2018). "The distorted online networks of Mexico's election campaign". Elpais.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Exigen al INAI investigar a Cambridge Analytica, Facebook y desarrolladoras de Apps en México - Proceso". Proceso.com.mx. 2 April 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Mexico's Hardball Politics Get Even Harder as PRI Fights to Hold On to Power". New York Times. 24 June 2018. Retrieved 4 July 2018.
^ Dinan, Stephen (5 April 2017). "Trump administration wades into Mexican election, warns against left-wing candidate". The Washington Times. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
^ "Mexico urges respect from U.S. for 2018 presidential election". Reuters. 6 April 2017. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
^ "Mexico wants John Kelly and John McCain to butt out of its election". Business Insider. 17 April 2017. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
^ "Russia meddling in Mexican election: White House aide McMaster". Reuters. 7 January 2018. Retrieved 9 January 2018.
^ "Intereses de Rusia y Venezuela apoyan a "López": PRI". Proceso (in Spanish). 12 January 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2018.
^ "Preparación académica, la mejor arma contra el populismo: politóloga". Milenio (in Spanish). 31 January 2018. Retrieved 30 September 2017.
^ "Critican en plenaria a panistas por aliarse al PRD". El Universal (in Spanish). 31 January 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
^ "Senators ask Tillerson to fight Russian interference in Mexico election: report". TheHill. 31 January 2018. Retrieved 2 February 2018.
^ "Tillerson warns Mexico to watch Russian election meddling". Business Insider. 2 February 2018. Retrieved 2 February 2018.
^ "Rex Tillerson urged to raise Russian meddling in Mexico election on upcoming trip to region". The Independent. 2 February 2018. Retrieved 2 February 2018.
^ "Mexico's Presidential Election Could Get Really Dirty". Bloomberg.com. 18 December 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Meade reporta más del doble de gastos que Anaya y López Obrador en precampañas - Aristegui Noticias". aristeguinoticias.com. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ Hernández, Leopoldo (4 June 2017). "Denuncian compra de votos a favor de Alfredo del Mazo". El Economista. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
^ Olvera, Dulce (8 June 2017). "Del Mazo gastó 412 millones 225 mil en Edomex, cuando sólo podía disponer de 285 millones: Morena". SinEmbargo. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
^ "El PREP sumó al PRI 238 mil 145 votos de más en el Edomex, con los que da ventaja a Del Mazo". SinEmbargo. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
^ ""Ni libre, ni auténtica", la elección en Edomex: Ni un Fraude Más - Proceso". Proceso.com.mx. 16 November 2017. Retrieved 9 April 2018.
^ "Jose Antonio Meade of Mexico's ruling party concedes defeat to Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador in presidential vote". ABC News (USA). 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
^ "Le deseo el mayor de los éxitos a AMLO: Meade". Excélsior. 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
^ "Anaya reconoce victoria de AMLO". El Universal (Mexico City). 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
^ "Mexico election: Exit polls put López Obrador in front". BBC News. 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
^ García, Aracely (1 July 2018). "'El Bronco' reconoce triunfo de López Obrador". Excélsior. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
^ "Conteo rápido del INE da victoria a Andrés Manuel López Obrador". El Universal (Mexico City). 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mexican general election, 2018. |
National Electoral Institute (in Spanish)



