Tuned mass damper

Tuned mass damper atop Taipei 101.
A tuned mass damper (TMD), also known as a harmonic absorber or seismic damper, is a device mounted in structures to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations. Their application can prevent discomfort, damage, or outright structural failure. They are frequently used in power transmission, automobiles, and buildings.
Contents
1 Principle
2 Mass dampers in automobiles
2.1 Motorsport
2.2 Production cars
3 Mass dampers in spacecraft
4 Dampers in power transmission lines
5 Dampers in wind turbines
6 Dampers in buildings and related structures
6.1 Sources of vibration and resonance
6.1.1 Earthquakes
6.1.2 Mechanical human sources
6.1.3 Wind
6.1.4 Examples of buildings and structures with tuned mass dampers
6.1.4.1 Canada
6.1.4.2 China
6.1.4.3 Germany
6.1.4.4 India
6.1.4.5 Iran
6.1.4.6 Ireland
6.1.4.7 Japan
6.1.4.8 Russia
6.1.4.9 Taiwan
6.1.4.10 United Arab Emirates
6.1.4.11 United States of America
6.1.4.12 United Kingdom
7 See also
8 References
9 External links
Principle

A schematic of a simple spring–mass–damper system used to demonstrate the tuned mass damper system.
Tuned mass dampers stabilize against violent motion caused by harmonic vibration. A tuned damper reduces the vibration of a system with a comparatively lightweight component so that the worst-case vibrations are less intense. Roughly speaking, practical systems are tuned to either move the main mode away from a troubling excitation frequency, or to add damping to a resonance that is difficult or expensive to damp directly. An example of the latter is a crankshaft torsional damper. Mass dampers are frequently implemented with a frictional or hydraulic component that turns mechanical kinetic energy into heat, like an automotive shock absorber.
Given a motor with mass m1{displaystyle m_{1}}









Response of the system excited by one unit of force, with (red) and without (blue) the 10% tuned mass. The peak response is reduced from 9 units down to 5.5 units. While the maximum response force is reduced, there are some operating frequencies for which the response force is increased.
The graph shows the effect of a tuned mass damper on a simple spring–mass–damper system, excited by vibrations with an amplitude of one unit of force applied to the main mass, m1{displaystyle m_{1}}

The heights of the two peaks can be adjusted by changing the stiffness of the spring in the tuned mass damper. Changing the damping also changes the height of the peaks, in a complex fashion. The split between the two peaks can be changed by altering the mass of the damper (m2{displaystyle m_{2}}

A Bode plot of displacements in the system with (red) and without (blue) the 10% tuned mass.
The Bode plot is more complex, showing the phase and magnitude of the motion of each mass, for the two cases, relative to F1.
In the plots at right, the black line shows the baseline response (m2=0{displaystyle m_{2}=0}






Mass dampers in automobiles
Motorsport
The tuned mass damper was introduced as part of the suspension system by Renault, on its 2005 F1 car (the Renault R25), at the 2005 Brazilian Grand Prix. It was deemed to be legal at first, and it was in use up to the 2006 German Grand Prix.
At Hockenheim, the mass damper was deemed illegal by the FIA, because the mass was not rigidly attached to the chassis and, due to the influence it had on the pitch attitude of the car, which in turn significantly affected the gap under the car and hence the ground effects of the car, to be a movable aerodynamic device and hence as a consequence, to be illegally influencing the performance of the aerodynamics.
The Stewards of the meeting deemed it legal, but the FIA appealed against that decision. Two weeks later, the FIA International Court of Appeal deemed the mass damper illegal.[1][2]
Production cars
Tuned mass dampers are widely used in production cars, typically on the crankshaft pulley to control torsional vibration and, more rarely, the bending modes of the crankshaft. They are also used on the driveline for gearwhine, and elsewhere for other noises or vibrations on the exhaust, body, suspension or anywhere else. Almost all modern cars will have one mass damper, some may have 10 or more.
The usual design of damper on the crankshaft consists of a thin band of rubber between the hub of the pulley and the outer rim. This device, often called a harmonic damper, is located on the other end of the crankshaft opposite of where the flywheel and the transmission is. An alternative design is the centrifugal pendulum absorber which is used to reduce the internal combustion engine's torsional vibrations on a few modern cars.
All four wheels of the Citroen 2cv incorporated a tuned mass damper (referred to as a "Batteur" in the original French) of very similar design to that used in the Renault F1 car, from the start of production in 1949 on all four wheels, before being removed from the rear and eventually the front wheels in the mid 1970s.
Mass dampers in spacecraft
One proposal to reduce vibration on NASA's Ares solid fuel booster was to use 16 tuned mass dampers as part of a design strategy to reduce peak loads from 6g to 0.25 g, the TMDs being responsible for the reduction from 1 g to 0.25 g, the rest being done by conventional vibration isolators between the upper stages and the booster.[3][4]
Dampers in power transmission lines

Stockbridge dampers on a 400 kV power line near Castle Combe, England
High-tension lines often have small barbell-shaped Stockbridge dampers hanging from the wires to reduce the high-frequency, low-amplitude oscillation termed flutter.[5][6]
Dampers in wind turbines
A standard tuned mass damper for wind turbines consists of an auxiliary mass which is attached to the main structure by means of springs and dashpot elements. The natural frequency of the tuned mass damper is basically defined by its spring constant and the damping ratio determined by the dashpot. The tuned parameter of the tuned mass damper enables the auxiliary mass to oscillate with a phase shift with respect to the motion of the structure. In a typical configuration an auxiliary mass hung below the nacelle of a wind turbine supported by dampers or friction plates.
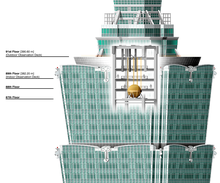
Location of Taipei 101's largest tuned mass damper
Typically, the dampers are huge concrete blocks or steel bodies mounted in skyscrapers or other structures, and moved in opposition to the resonance frequency oscillations of the structure by means of springs, fluid or pendulums.
Sources of vibration and resonance
Unwanted vibration may be caused by environmental forces acting on a structure, such as wind or earthquake, or by a seemingly innocuous vibration source causing resonance that may be destructive, unpleasant or simply inconvenient.
Earthquakes
The seismic waves caused by an earthquake will make buildings sway and oscillate in various ways depending on the frequency and direction of ground motion, and the height and construction of the building. Seismic activity can cause excessive oscillations of the building which may lead to structural failure. To enhance the building's seismic performance, a proper building design is performed engaging various seismic vibration control technologies.
As mentioned above, damping devices had been used in the aeronautics and automobile industries long before they were standard in mitigating seismic damage to buildings. In fact, the first specialized damping devices for earthquakes were not developed until late in 1950.[7]
Mechanical human sources

Dampers on the Millennium Bridge in London. The white disk is not part of the damper.
Masses of people walking up and down stairs at once, or great numbers of people stomping in unison, can cause serious problems in large structures like stadiums if those structures lack damping measures.
Wind
The force of wind against tall buildings can cause the top of skyscrapers to move more than a meter. This motion can be in the form of swaying or twisting, and can cause the upper floors of such buildings to move. Certain angles of wind and aerodynamic properties of a building can accentuate the movement and cause motion sickness in people. A TMD is usually tuned to a certain building's frequency to work efficiently. However, during their lifetimes, high-rise and slender buildings may experience natural frequency changes under wind speed, ambient temperatures and relative humidity variations, among other factors, which requires a robust TMD design.[8]
Examples of buildings and structures with tuned mass dampers
Canada
One Wall Centre in Vancouver — employs tuned liquid column dampers, a unique form of tuned mass damper at the time of their installation.
China
Shanghai World Financial Center in Shanghai, China
Shanghai Tower in Shanghai, China is the eighth largest building in the world.
Germany
Berlin Television Tower (Fernsehturm) — tuned mass damper located in the spire.
VLF transmitter DHO38 - cylindrical containers filled with granulate in the mast structure
India
- ATC Tower Delhi Airport in New Delhi, India — a 50-ton tuned mass damper installed just beneath the ATC floor at 90m.
Statue of Unity in Gujarat, India - a 400-ton tuned mass damper located at the chest level of Sardar Patel statue.
Iran
World Trade Center Tabriz[9]
- Tehran International Tower
Ireland
Dublin Spire in Dublin, Ireland — designed with a tuned mass damper to ensure aerodynamic stability during a wind storm .
Japan
Akashi Kaikyō Bridge, between Honshu and Shikoku in Japan, currently the world's longest suspension bridge, uses pendulums within its suspension towers as tuned mass dampers.
Ribbon Chapel [10] in Hiroshima, Japan uses a TMD to damp vibrations in two intertwined helical stairways.[11]
- Tokyo Skytree
- Yokohama Landmark Tower
Russia
Sakhalin-I — An offshore drilling platform
Taiwan
Taipei 101 skyscraper — Contains the world's largest and heaviest tuned mass dampers, at 660 metric tons (730 short tons).[12]
United Arab Emirates
Burj al-Arab in Dubai — 11 tuned mass dampers.
United States of America
432 Park Avenue in New York City, NY[13]
Bally's to Bellagio, Bally's to Caesars Palace, and Treasure Island to The Venetian Pedestrian Bridges in Las Vegas, NV
Bloomberg Tower/731 Lexington in New York City, NY
Citigroup Center in New York City, NY — Designed by William LeMessurier and completed in 1977, it was one of the first skyscrapers to use a tuned mass damper to reduce sway.[14] Uses a concrete version.
Comcast Center in Philadelphia, PA — Contains the largest Tuned Liquid Column Damper (TLCD) in the world at 1,300 tons.[15]
Comcast Technology Center in Philadelphia, PA — A set of five tuned dampers containing 125,000 gallons of water—about 500 tons—are located on the 57th floor between the hotel's rooms and lobby.[16]
Grand Canyon Skywalk, AZ
The Hancock Tower in Boston, MA — A tuned mass damper was added to it after it was built making it the 1st building to use a tuned mass damper.
One Rincon Hill South Tower, San Francisco, CA— First building in California to have a liquid tuned mass damper
Park Tower in Chicago, IL — The first building in the United States to be designed with a tuned mass damper from the outset.
Random House Tower — Uses two liquid filled dampers in New York City, NY
Theme Building at Los Angeles International Airport Los Angeles, CA
Trump World Tower in New York City, NY
United Kingdom
London Millennium Bridge — nicknamed 'The Wobbly Bridge' due to swaying under heavy foot traffic. Dampers were fitted in response.
One Canada Square — Prior to the topping out of the Shard in 2012, this was the tallest building in the UK.
See also
- Antiresonance
References
^ Bishop, Matt (2006). "The Long Interview: Flavio Briatore". F1 Racing (October): 66–76..mw-parser-output cite.citation{font-style:inherit}.mw-parser-output q{quotes:"""""""'""'"}.mw-parser-output code.cs1-code{color:inherit;background:inherit;border:inherit;padding:inherit}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-free a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/65/Lock-green.svg/9px-Lock-green.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-limited a,.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-registration a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Lock-gray-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-gray-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-lock-subscription a{background:url("//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/aa/Lock-red-alt-2.svg/9px-Lock-red-alt-2.svg.png")no-repeat;background-position:right .1em center}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration{color:#555}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription span,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration span{border-bottom:1px dotted;cursor:help}.mw-parser-output .cs1-hidden-error{display:none;font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-visible-error{font-size:100%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-subscription,.mw-parser-output .cs1-registration,.mw-parser-output .cs1-format{font-size:95%}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-left,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-left{padding-left:0.2em}.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-right,.mw-parser-output .cs1-kern-wl-right{padding-right:0.2em}
^ "FIA bans controversial damper system". Pitpass.com. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
^ "Ares I Thrust Oscillation meetings conclude with encouraging data, changes". NASASpaceFlight.com. 2008-12-09. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
^ "Shock Absorber Plan Set for NASA's New Rocket". SPACE.com. 2008-08-19. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
^ "On the hysteresis of wire cables in Stockbridge dampers". Cat.inist.fr. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
^ "Cable clingers - 27 October 2007". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 5 May 2008. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
^ Reitherman, Robert (2012). Earthquakes and Engineers: An International History. Reston, VA: ASCE Press. ISBN 9780784410714. Archived from the original on 2012-07-26.
^ ALY, Aly Mousaad (2012). "Proposed robust tuned mass damper for response mitigation in buildings exposed to multidirectional wind". The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings. doi:10.1002/tal.1068.
^ Tabriz WCT
^ RIBBON CHAPEL on Vimeo
^ Nakamura, Hiroshi (4 February 2015). "Ribbon Chapel / Hiroshi Nakamura & NAP Architects". ArchDaily. Retrieved 2017-02-15.
^ taipei-101.com.tw
^ Stewart, Aaron. "In Detail> 432 Park Avenue". The Architect's Newspaper. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
^ Petroski, Henry (1996). Invention by Design: How Engineers Get from Thought to Thing. Harvard University Press. pp. 205–208.
^ "Comcast Center" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on February 17, 2012. Retrieved 2010-02-07.
^ Bob Fernandez (December 10, 2014). "Engineers on the rise: Four young professionals tackle a career-making project". philly.com. Philadelphia Media Network (Digital), LLC. Archived from the original on November 22, 2017. Retrieved December 3, 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tuned mass dampers. |
- Structures Incorporating Tuned Mass Dampers